Microsoft DP-200 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (372 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
A company runs Microsoft SQL Server in an on-premises virtual machine (VM).
You must migrate the database to Azure SQL Database. You synchronize users from Active Directory to Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
You need to configure Azure SQL Database to use an Azure AD user as administrator.
What should you configure?
You must migrate the database to Azure SQL Database. You synchronize users from Active Directory to Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
You need to configure Azure SQL Database to use an Azure AD user as administrator.
What should you configure?
- AFor each Azure SQL Database, set the Access Control to administrator.
- BFor each Azure SQL Database server, set the Active Directory to administrator.
- CFor each Azure SQL Database, set the Active Directory administrator role.
- DFor each Azure SQL Database server, set the Access Control to administrator.
Correct Answer:
C
There are two administrative accounts (Server admin and Active Directory admin) that act as administrators.
One Azure Active Directory account, either an individual or security group account, can also be configured as an administrator. It is optional to configure an Azure
AD administrator, but an Azure AD administrator must be configured if you want to use Azure AD accounts to connect to SQL Database.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-manage-logins
C
There are two administrative accounts (Server admin and Active Directory admin) that act as administrators.
One Azure Active Directory account, either an individual or security group account, can also be configured as an administrator. It is optional to configure an Azure
AD administrator, but an Azure AD administrator must be configured if you want to use Azure AD accounts to connect to SQL Database.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-manage-logins
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a credit card function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a credit card function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
The last four suffix characters must be exposed.

✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use an email function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
The last four suffix characters must be exposed.

✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use an email function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a random number function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a random number function mask.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
B
Must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
DRAG DROP -
You are responsible for providing access to an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account.
Your user account has contributor access to the storage account, and you have the application ID and access key.
You plan to use PolyBase to load data into an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
You need to configure PolyBase to connect the data warehouse to the storage account.
Which three components should you create in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate components from the list of components to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You are responsible for providing access to an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account.
Your user account has contributor access to the storage account, and you have the application ID and access key.
You plan to use PolyBase to load data into an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
You need to configure PolyBase to connect the data warehouse to the storage account.
Which three components should you create in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate components from the list of components to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:

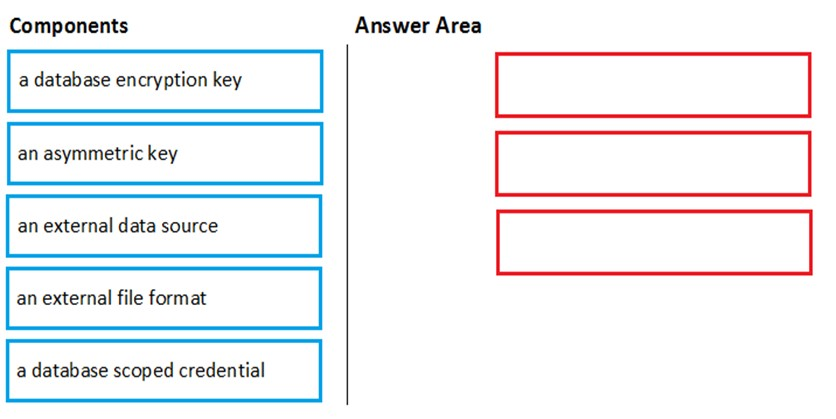
Step 1: a database scoped credential
To access your Data Lake Storage account, you will need to create a Database Master Key to encrypt your credential secret used in the next step. You then create a database scoped credential.
Step 2: an external data source -
Create the external data source. Use the CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE command to store the location of the data. Provide the credential created in the previous step.
Step 3: an external file format -
Configure data format: To import the data from Data Lake Storage, you need to specify the External File Format. This object defines how the files are written in
Data Lake Storage.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store

Step 1: a database scoped credential
To access your Data Lake Storage account, you will need to create a Database Master Key to encrypt your credential secret used in the next step. You then create a database scoped credential.
Step 2: an external data source -
Create the external data source. Use the CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE command to store the location of the data. Provide the credential created in the previous step.
Step 3: an external file format -
Configure data format: To import the data from Data Lake Storage, you need to specify the External File Format. This object defines how the files are written in
Data Lake Storage.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
You plan to create a dimension table in Azure Synapse Analytics that will be less than 1 GB.
You need to create the table to meet the following requirements:
✑ Provide the fastest query time.
✑ Minimize data movement during queries.
Which type of table should you use?
You need to create the table to meet the following requirements:
✑ Provide the fastest query time.
✑ Minimize data movement during queries.
Which type of table should you use?
- Ahash distributed
- Bheap
- CreplicatedMost Voted
- Dround-robin
Correct Answer:
D
Usually common dimension tables or tables that doesn't distribute evenly are good candidates for round-robin distributed table.
Note: Dimension tables or other lookup tables in a schema can usually be stored as round-robin tables. Usually these tables connect to more than one fact tables and optimizing for one join may not be the best idea. Also usually dimension tables are smaller which can leave some distributions empty when hash distributed.
Round-robin by definition guarantees a uniform data distribution.
Reference:
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/sqlcat/2015/08/11/choosing-hash-distributed-table-vs-round-robin-distributed-table-in-azure-sql-dw-service/
D
Usually common dimension tables or tables that doesn't distribute evenly are good candidates for round-robin distributed table.
Note: Dimension tables or other lookup tables in a schema can usually be stored as round-robin tables. Usually these tables connect to more than one fact tables and optimizing for one join may not be the best idea. Also usually dimension tables are smaller which can leave some distributions empty when hash distributed.
Round-robin by definition guarantees a uniform data distribution.
Reference:
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/sqlcat/2015/08/11/choosing-hash-distributed-table-vs-round-robin-distributed-table-in-azure-sql-dw-service/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
You have an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Using PolyBase, you create an external table named [Ext].[Items] to query Parquet files stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 without importing the data to the data warehouse.
The external table has three columns.
You discover that the Parquet files have a fourth column named ItemID.
Which command should you run to add the ItemID column to the external table?

Using PolyBase, you create an external table named [Ext].[Items] to query Parquet files stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 without importing the data to the data warehouse.
The external table has three columns.
You discover that the Parquet files have a fourth column named ItemID.
Which command should you run to add the ItemID column to the external table?

- AOption A
- BOption B
- COption C
- DOption D
Correct Answer:
A
Incorrect Answers:
B, D: Only these Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are allowed on external tables:
✑ CREATE TABLE and DROP TABLE
✑ CREATE STATISTICS and DROP STATISTICS
✑ CREATE VIEW and DROP VIEW
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-table-transact-sql
A
Incorrect Answers:
B, D: Only these Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are allowed on external tables:
✑ CREATE TABLE and DROP TABLE
✑ CREATE STATISTICS and DROP STATISTICS
✑ CREATE VIEW and DROP VIEW
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-table-transact-sql
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
DRAG DROP -
You have a table named SalesFact in an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics. SalesFact contains sales data from the past 36 months and has the following characteristics:
✑ Is partitioned by month
✑ Contains one billion rows
✑ Has clustered columnstore indexes
At the beginning of each month, you need to remove data from SalesFact that is older than 36 months as quickly as possible.
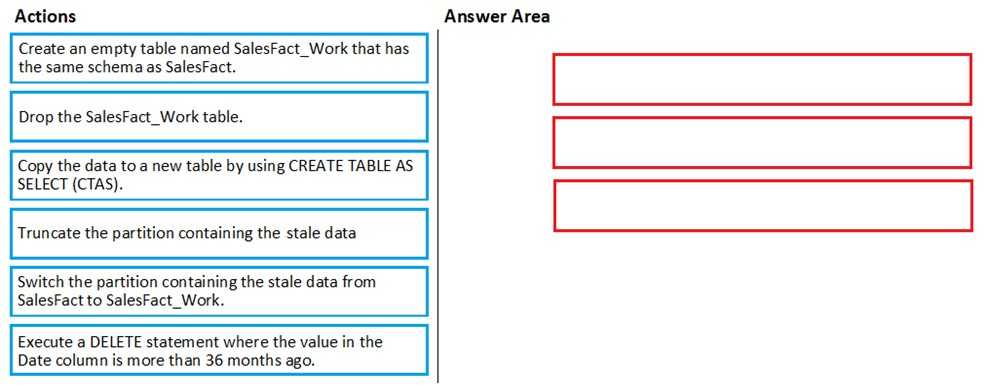
Which three actions should you perform in sequence in a stored procedure? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You have a table named SalesFact in an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics. SalesFact contains sales data from the past 36 months and has the following characteristics:
✑ Is partitioned by month
✑ Contains one billion rows
✑ Has clustered columnstore indexes
At the beginning of each month, you need to remove data from SalesFact that is older than 36 months as quickly as possible.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence in a stored procedure? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
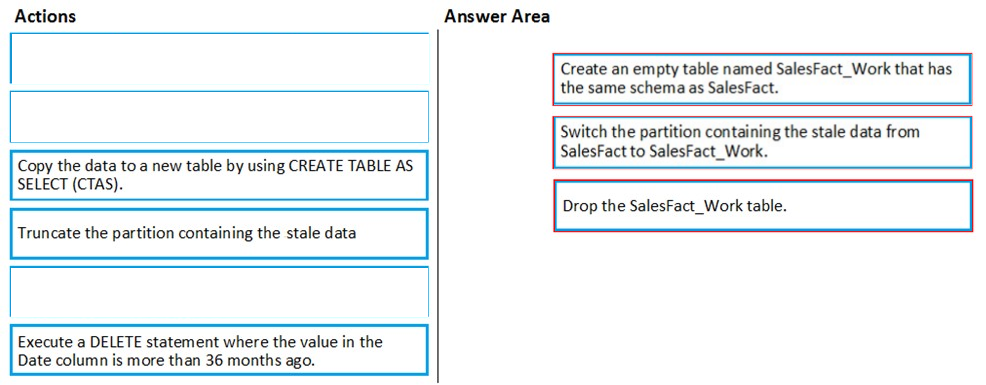
Step 1: Create an empty table named SalesFact_work that has the same schema as SalesFact.
Step 2: Switch the partition containing the stale data from SalesFact to SalesFact_Work.
SQL Data Warehouse supports partition splitting, merging, and switching. To switch partitions between two tables, you must ensure that the partitions align on their respective boundaries and that the table definitions match.
Loading data into partitions with partition switching is a convenient way stage new data in a table that is not visible to users the switch in the new data.
Step 3: Drop the SalesFact_Work table.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-partition

Step 1: Create an empty table named SalesFact_work that has the same schema as SalesFact.
Step 2: Switch the partition containing the stale data from SalesFact to SalesFact_Work.
SQL Data Warehouse supports partition splitting, merging, and switching. To switch partitions between two tables, you must ensure that the partitions align on their respective boundaries and that the table definitions match.
Loading data into partitions with partition switching is a convenient way stage new data in a table that is not visible to users the switch in the new data.
Step 3: Drop the SalesFact_Work table.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-partition
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
You plan to implement an Azure Cosmos DB database that will write 100,000,000 JSON records every 24 hours. The database will be replicated to three regions.
Only one region will be writable.
You need to select a consistency level for the database to meet the following requirements:
✑ Guarantee monotonic reads and writes within a session.
✑ Provide the fastest throughput.
✑ Provide the lowest latency.
Which consistency level should you select?
Only one region will be writable.
You need to select a consistency level for the database to meet the following requirements:
✑ Guarantee monotonic reads and writes within a session.
✑ Provide the fastest throughput.
✑ Provide the lowest latency.
Which consistency level should you select?
- AStrong
- BBounded Staleness
- CEventual
- DSession
- EConsistent Prefix
Correct Answer:
D
Session: Within a single client session reads are guaranteed to honor the consistent-prefix (assuming a single ג€writerג€ session), monotonic reads, monotonic writes, read-your-writes, and write-follows-reads guarantees. Clients outside of the session performing writes will see eventual consistency.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/consistency-levels
D
Session: Within a single client session reads are guaranteed to honor the consistent-prefix (assuming a single ג€writerג€ session), monotonic reads, monotonic writes, read-your-writes, and write-follows-reads guarantees. Clients outside of the session performing writes will see eventual consistency.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/consistency-levels
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a custom text mask.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table1. Table1 has a field named Customer_ID that is varchar(22).
You need to implement masking for the Customer_ID field to meet the following requirements:
✑ The first two prefix characters must be exposed.
✑ The last four suffix characters must be exposed.
✑ All other characters must be masked.
Solution: You implement data masking and use a custom text mask.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
A
We must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
A
We must use Custom Text data masking, which exposes the first and last characters and adds a custom padding string in the middle.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-dynamic-data-masking-get-started
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
