Test Prep CPA Auditing and Attestation Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (1025 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
Which of the following is not an example of the application of professional skepticism?
- ADesigning additional auditing procedures to obtain more reliable evidence in support of a particular financial statement assertion.
- BObtaining corroboration of management's Explanations through consultation with a specialist.
- CInquiring of prior year engagement personnel regarding their assessment of management's honesty and integrity.
- DUsing third party confirmations to provide support for management's representations.
Correct Answer:
C
Choice "c" is correct. The auditor should consider that fraud might occur regardless of any past experience with the entity. An assessment of management's honesty and integrity performed during the previous year would not necessarily be relevant to the current year's audit.
Choice "a" is incorrect. An auditor might apply professional skepticism by performing additional audit procedures designed to improve the reliability of evidence.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Corroborating management's Explanations is an example of the application of professional skepticism, since the auditor is obtaining additional support rather than simply accepting the Explanation as given.
Choice "d" is incorrect. Using third party confirmations to provide support for management's representations is an example of the application of professional skepticism, since the auditor is obtaining additional support rather than simply accepting the Explanation as given.
C
Choice "c" is correct. The auditor should consider that fraud might occur regardless of any past experience with the entity. An assessment of management's honesty and integrity performed during the previous year would not necessarily be relevant to the current year's audit.
Choice "a" is incorrect. An auditor might apply professional skepticism by performing additional audit procedures designed to improve the reliability of evidence.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Corroborating management's Explanations is an example of the application of professional skepticism, since the auditor is obtaining additional support rather than simply accepting the Explanation as given.
Choice "d" is incorrect. Using third party confirmations to provide support for management's representations is an example of the application of professional skepticism, since the auditor is obtaining additional support rather than simply accepting the Explanation as given.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Which of the following categories is included in generally accepted auditing standards?
- AStandards of review.
- BStandards of planning.
- CStandards of fieldwork.
- DStandards of evidence.
Correct Answer:
C
Choice "c" is correct. Generally accepted auditing standards include three categories: general standards, standards of fieldwork, and standards of reporting.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect, based on the above Explanation.
C
Choice "c" is correct. Generally accepted auditing standards include three categories: general standards, standards of fieldwork, and standards of reporting.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect, based on the above Explanation.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
When qualifying an opinion because of an insufficiency of audit evidence, an auditor should refer to the situation in the:
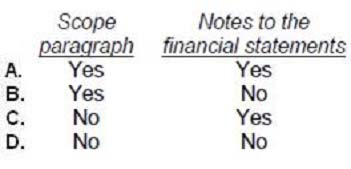

- AOption A
- BOption B
- COption C
- DOption D
Correct Answer:
B
Choice "b" is correct. When a qualified opinion is issued due to a lack of sufficient audit evidence, the lack of evidence should be disclosed in an explanatory paragraph before the opinion paragraph. Since insufficient evidence is a scope limitation, the scope paragraph should also be modified to refer to the limitation and to the explanatory paragraph that discusses it.
Choices "a" and "c" are incorrect. Management (and not the auditor) prepares the notes to the financial statements. The auditor therefore would not refer to this (or any other) situation in the notes to the financial statements.
Choice "d" is incorrect. The auditor does refer to the situation in the scope paragraph.
B
Choice "b" is correct. When a qualified opinion is issued due to a lack of sufficient audit evidence, the lack of evidence should be disclosed in an explanatory paragraph before the opinion paragraph. Since insufficient evidence is a scope limitation, the scope paragraph should also be modified to refer to the limitation and to the explanatory paragraph that discusses it.
Choices "a" and "c" are incorrect. Management (and not the auditor) prepares the notes to the financial statements. The auditor therefore would not refer to this (or any other) situation in the notes to the financial statements.
Choice "d" is incorrect. The auditor does refer to the situation in the scope paragraph.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
When an auditor believes there is substantial doubt about the ability of an entity to continue as a going concern, all of the following should be included in the audit documentation, except:
- AThe conditions that gave rise to the substantial doubt.
- BThe auditor's conclusion about whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated.
- CManagement's conclusion regarding whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated.
- DThe effect of the auditor's conclusion on the auditor's report.
Correct Answer:
C
Choice "c" is correct. Whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated is a judgment call made by the auditor, and there is no requirement to document management's opinion on the matter.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect. When an auditor believes there is substantial doubt about the ability of an entity to continue as a going concern, the conditions that gave rise to the substantial doubt, the auditor's conclusion about whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated, and the effect of the auditor's conclusion on the auditor's report should all be documented.
C
Choice "c" is correct. Whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated is a judgment call made by the auditor, and there is no requirement to document management's opinion on the matter.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect. When an auditor believes there is substantial doubt about the ability of an entity to continue as a going concern, the conditions that gave rise to the substantial doubt, the auditor's conclusion about whether substantial doubt remains or is alleviated, and the effect of the auditor's conclusion on the auditor's report should all be documented.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
After considering an entity's negative trends and financial difficulties, an auditor has substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern. The auditor's considerations relating to management's plans for dealing with the adverse effects of these conditions most likely would include management's plans to:
- AIncrease current dividend distributions.
- BReduce existing lines of credit.
- CIncrease ownership equity.
- DPurchase assets formerly leased. C
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Choice "c" is correct. The auditor considers any of management's plans that might serve to mitigate the adverse effects of particular conditions and events.
Typically, plans to increase ownership equity, to borrow money, to restructure debt, to sell assets, and/or to reduce or delay expenditures might all be considered mitigating factors.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect. Increasing dividend distributions, reducing lines of credit, and purchasing assets would not improve a weak cash flow situation.
Explanation
Choice "c" is correct. The auditor considers any of management's plans that might serve to mitigate the adverse effects of particular conditions and events.
Typically, plans to increase ownership equity, to borrow money, to restructure debt, to sell assets, and/or to reduce or delay expenditures might all be considered mitigating factors.
Choices "a", "b", and "d" are incorrect. Increasing dividend distributions, reducing lines of credit, and purchasing assets would not improve a weak cash flow situation.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #16
In which of the following situations would an auditor ordinarily choose between expressing a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion?
- AThe auditor did not observe the entity's physical inventory and is unable to become satisfied about its balance by other auditing procedures.
- BConditions that cause the auditor to have substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern are inadequately disclosed.
- CThere has been a change in accounting principles that has a material effect on the comparability of the entity's financial statements.
- DThe auditor is unable to apply necessary procedures concerning an investor's share of an investee's earnings recognized on the equity method.
Correct Answer:
B
Choice "b" is correct. Inadequate disclosure of the substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern is a departure from GAAP, resulting in either a qualified or adverse opinion.
Choices "a" and "d" are incorrect. Scope limitations result in either a qualified opinion or in a disclaimer of opinion, but not in an adverse opinion.
Choice "c" is incorrect. A change in accounting principle results in a modified unqualified report, as long as the change was accounted for properly.
B
Choice "b" is correct. Inadequate disclosure of the substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern is a departure from GAAP, resulting in either a qualified or adverse opinion.
Choices "a" and "d" are incorrect. Scope limitations result in either a qualified opinion or in a disclaimer of opinion, but not in an adverse opinion.
Choice "c" is incorrect. A change in accounting principle results in a modified unqualified report, as long as the change was accounted for properly.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
Which of the following conditions or events most likely would cause an auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern?
- ASignificant related party transactions are pervasive.
- BUsual trade credit from suppliers is denied.
- CArrearages in preferred stock dividends are paid.
- DRestrictions on the disposal of principal assets are present.
Correct Answer:
B
Choice "b" is correct. Indications of possible financial difficulties, such as denial of usual trade credit from suppliers, may cause an auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "a" is incorrect. The existence of related parties and the occurrence of related party transactions do not indicate doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "c" is incorrect. Payment of preferred stock dividends in arrears might very well indicate an improvement in the entity's financial situation. It is the lack of payment of preferred, cumulative dividends (a possible indication of financial difficulty) that might cause an auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "d" is incorrect. Restrictions on the disposal of assets might limit the options available to management as far as mitigating adverse conditions, but it would not in and of itself cause the auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
B
Choice "b" is correct. Indications of possible financial difficulties, such as denial of usual trade credit from suppliers, may cause an auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "a" is incorrect. The existence of related parties and the occurrence of related party transactions do not indicate doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "c" is incorrect. Payment of preferred stock dividends in arrears might very well indicate an improvement in the entity's financial situation. It is the lack of payment of preferred, cumulative dividends (a possible indication of financial difficulty) that might cause an auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Choice "d" is incorrect. Restrictions on the disposal of assets might limit the options available to management as far as mitigating adverse conditions, but it would not in and of itself cause the auditor to have substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
In the first audit of a client, an auditor was not able to gather sufficient evidence about the consistent application of accounting principles between the current and prior year, as well as the amounts of assets or liabilities at the beginning of the current year. This was due to the client's record retention policies. If the amounts in question could materially affect current operating results, the auditor would:
- ABe unable to express an opinion on the current year's results of operations and cash flows.
- BExpress a qualified opinion on the financial statements because of a client-imposed scope limitation.
- CWithdraw from the engagement and refuse to be associated with the financial statements.
- DSpecifically state that the financial statements are not comparable to the prior year due to an uncertainty.
Correct Answer:
A
Choice "a" is correct. Since the auditor was unable to gather sufficient evidence on the beginning balances of the balance sheet accounts, the auditor would be unable to express an opinion on the current year's results of operations and cash flows. The auditor could express an opinion on the statement of financial position.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Since the scope limitation could have a pervasive effect on the financial statements (affecting all assets and liabilities), a disclaimer of opinion (and not merely a qualified opinion) is required on the income statement and statement of cash flows. An opinion may be expressed on the year-end statement of financial position.
Choice "c" is incorrect. The auditor does not need to withdraw from the engagement and refuse to be associated with the financial statements.
Choice "d" is incorrect. An uncertainty does not exist. The auditor can express an opinion on one of the financial statements.
A
Choice "a" is correct. Since the auditor was unable to gather sufficient evidence on the beginning balances of the balance sheet accounts, the auditor would be unable to express an opinion on the current year's results of operations and cash flows. The auditor could express an opinion on the statement of financial position.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Since the scope limitation could have a pervasive effect on the financial statements (affecting all assets and liabilities), a disclaimer of opinion (and not merely a qualified opinion) is required on the income statement and statement of cash flows. An opinion may be expressed on the year-end statement of financial position.
Choice "c" is incorrect. The auditor does not need to withdraw from the engagement and refuse to be associated with the financial statements.
Choice "d" is incorrect. An uncertainty does not exist. The auditor can express an opinion on one of the financial statements.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
Pell, CPA, decides to serve as principal auditor in the audit of the financial statements of Tech
Consolidated, Inc. Smith, CPA, audits one of Tech's subsidiaries. In which situation(s) should Pell make reference to Smith's audit?
I. Pell reviews Smith's audit documentation and assumes responsibility for Smith's work, but expresses a qualified opinion on Tech's financial statements.
II. Pell is unable to review Smith's audit documentation; however, Pell's inquiries indicate that Smith has an excellent reputation for professional competence and integrity.
Consolidated, Inc. Smith, CPA, audits one of Tech's subsidiaries. In which situation(s) should Pell make reference to Smith's audit?
I. Pell reviews Smith's audit documentation and assumes responsibility for Smith's work, but expresses a qualified opinion on Tech's financial statements.
II. Pell is unable to review Smith's audit documentation; however, Pell's inquiries indicate that Smith has an excellent reputation for professional competence and integrity.
- AI only.
- BII only.
- CBoth I and II.
- DNeither I nor II.
Correct Answer:
B
Choice "b" is correct. The principal auditor makes reference in the audit report to the work of the other auditor when the principal auditor is unable to review the other auditor's audit documentation. This is because the principal auditor will be unable to be satisfied concerning the work performed by the other auditor. Even though the other auditor has an excellent reputation, the principal auditor must see the work to be able to assume responsibility for it.
Choice "a" is incorrect. When the principal auditor decides to assume responsibility for the work of the other independent auditor, no reference is made to the work of the other auditor, regardless of the type of audit report expressed.
Choice "c" is incorrect. When the principal auditor decides to assume responsibility for the work of the other independent auditor, no reference is made to the work of the other auditor, regardless of the type of audit report expressed.
Choice "d" is incorrect. The principal auditor will make reference in the audit report to the work of the other auditor when the principal auditor is unable to review the other auditor's audit documentation. This is because the principal auditor will be unable to be satisfied concerning the work performed by the other auditor.
Even though the other auditor has an excellent reputation, the principal auditor must see the work to be able to assume responsibility for it.
B
Choice "b" is correct. The principal auditor makes reference in the audit report to the work of the other auditor when the principal auditor is unable to review the other auditor's audit documentation. This is because the principal auditor will be unable to be satisfied concerning the work performed by the other auditor. Even though the other auditor has an excellent reputation, the principal auditor must see the work to be able to assume responsibility for it.
Choice "a" is incorrect. When the principal auditor decides to assume responsibility for the work of the other independent auditor, no reference is made to the work of the other auditor, regardless of the type of audit report expressed.
Choice "c" is incorrect. When the principal auditor decides to assume responsibility for the work of the other independent auditor, no reference is made to the work of the other auditor, regardless of the type of audit report expressed.
Choice "d" is incorrect. The principal auditor will make reference in the audit report to the work of the other auditor when the principal auditor is unable to review the other auditor's audit documentation. This is because the principal auditor will be unable to be satisfied concerning the work performed by the other auditor.
Even though the other auditor has an excellent reputation, the principal auditor must see the work to be able to assume responsibility for it.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
Cooper, CPA, believes there is substantial doubt about the ability of Zero Corp. to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. In evaluating
Zero's plans for dealing with the adverse effects of future conditions and events, Cooper most likely would consider, as a mitigating factor, Zero's plans to:
Zero's plans for dealing with the adverse effects of future conditions and events, Cooper most likely would consider, as a mitigating factor, Zero's plans to:
- ADiscuss with lenders the terms of all debt and loan agreements.
- BStrengthen internal controls over cash disbursements.
- CPurchase production facilities currently being leased from a related party.
- DPostpone expenditures for research and development projects.
Correct Answer:
B
Choice "d" is correct. When assessing management's plans for dealing with the adverse effects of future conditions and events, mitigating factors would include:
1. The postponement of expenditures (including R&D),
2. Plans to dispose of assets,
3. Plans to borrow money or restructure debt,
4. Plans to increase ownership equity (sell stock).
Choice "a" is incorrect. Discussions with lenders regarding terms would not be a mitigating factor. Actual agreements regarding restructuring of debt or amendments to covenants would be required.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Strengthening internal controls over cash would not qualify as a management tactic to address going concern issues.
Choice "c" is incorrect. Purchasing facilities which are currently being leased would only further decrease cash flow.
B
Choice "d" is correct. When assessing management's plans for dealing with the adverse effects of future conditions and events, mitigating factors would include:
1. The postponement of expenditures (including R&D),
2. Plans to dispose of assets,
3. Plans to borrow money or restructure debt,
4. Plans to increase ownership equity (sell stock).
Choice "a" is incorrect. Discussions with lenders regarding terms would not be a mitigating factor. Actual agreements regarding restructuring of debt or amendments to covenants would be required.
Choice "b" is incorrect. Strengthening internal controls over cash would not qualify as a management tactic to address going concern issues.
Choice "c" is incorrect. Purchasing facilities which are currently being leased would only further decrease cash flow.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
