Microsoft DP-300 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (373 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #31
HOTSPOT -
You have an Azure subscription.
You need to deploy an Azure SQL resource that will support cross database queries by using an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
How should you complete the ARM template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

You have an Azure subscription.
You need to deploy an Azure SQL resource that will support cross database queries by using an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
How should you complete the ARM template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Box 1: Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances
The Managed Instance depends on the Virtual Network.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/managed-instance/create-template-quickstart?tabs=azure-powershell

Box 1: Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances
The Managed Instance depends on the Virtual Network.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/managed-instance/create-template-quickstart?tabs=azure-powershell
send
light_mode
delete
Question #32
HOTSPOT -
You have the following Azure Resource Manager template.

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
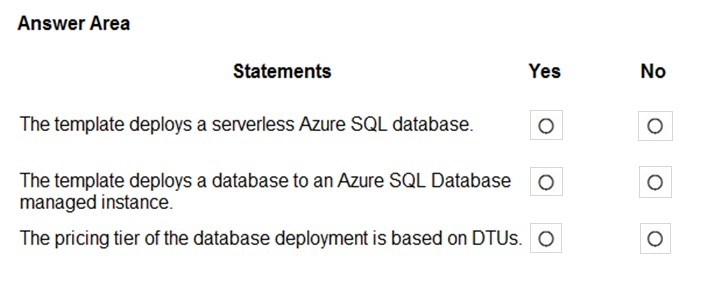
You have the following Azure Resource Manager template.

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
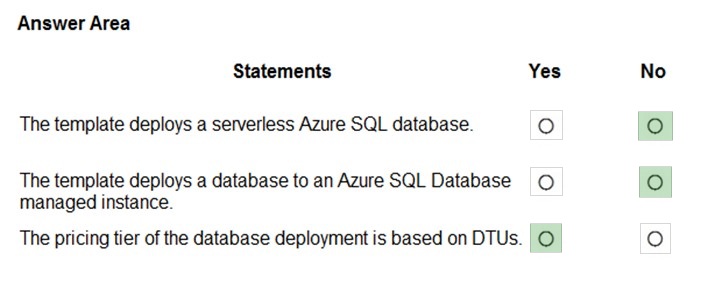
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/purchasing-models https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/single-database-create-arm-template-quickstart

Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/purchasing-models https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/single-database-create-arm-template-quickstart
send
light_mode
delete
Question #33
HOTSPOT -
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2019 instance that hosts a database named DB1.
You plan to perform an online migration of DB1 to an Azure SQL managed instance by using the Azure Database Migration Service.
You need to create a backup of DB1 that is accessible to the Azure Database Migration Service.
What should you run for the backup and where should you store the backup? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
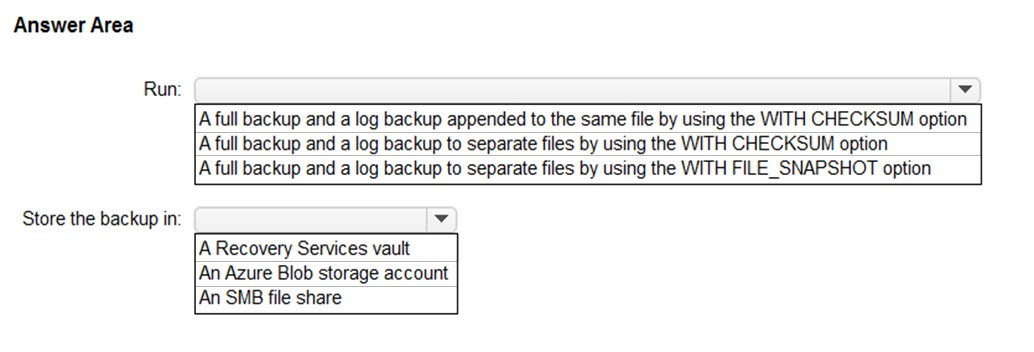
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2019 instance that hosts a database named DB1.
You plan to perform an online migration of DB1 to an Azure SQL managed instance by using the Azure Database Migration Service.
You need to create a backup of DB1 that is accessible to the Azure Database Migration Service.
What should you run for the backup and where should you store the backup? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
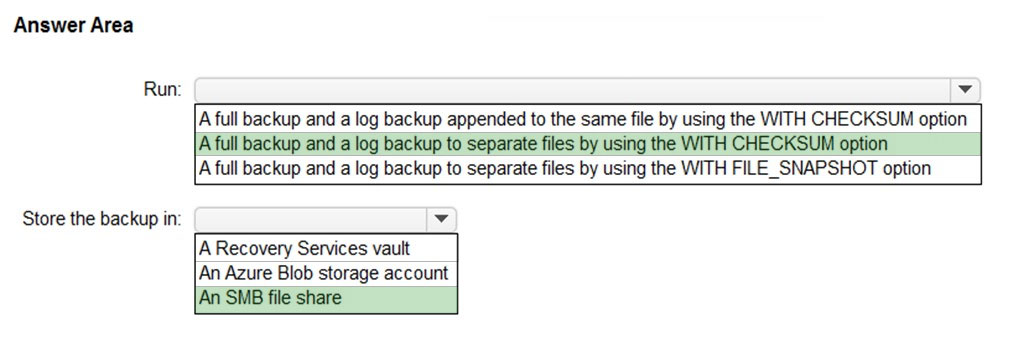
Box 1: ..with CHECKSUM option -
Azure Database Migration Service does not initiate any backups, and instead uses existing backups, which you may already have as part of your disaster recovery plan, for the migration. Be sure that you take backups using the WITH CHECKSUM option.
Box 2: An SMB share -
For online migrations from SQL Server to SQL Managed Instance using Azure Database Migration Service, you must provide the full database backup and subsequent log backups in the SMB network share that the service can use to migrate your databases.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/tutorial-sql-server-managed-instance-online

Box 1: ..with CHECKSUM option -
Azure Database Migration Service does not initiate any backups, and instead uses existing backups, which you may already have as part of your disaster recovery plan, for the migration. Be sure that you take backups using the WITH CHECKSUM option.
Box 2: An SMB share -
For online migrations from SQL Server to SQL Managed Instance using Azure Database Migration Service, you must provide the full database backup and subsequent log backups in the SMB network share that the service can use to migrate your databases.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/tutorial-sql-server-managed-instance-online
send
light_mode
delete
Question #34
HOTSPOT -
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy an Azure SQL database by using an Azure Resource Manager template.
How should you complete the template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
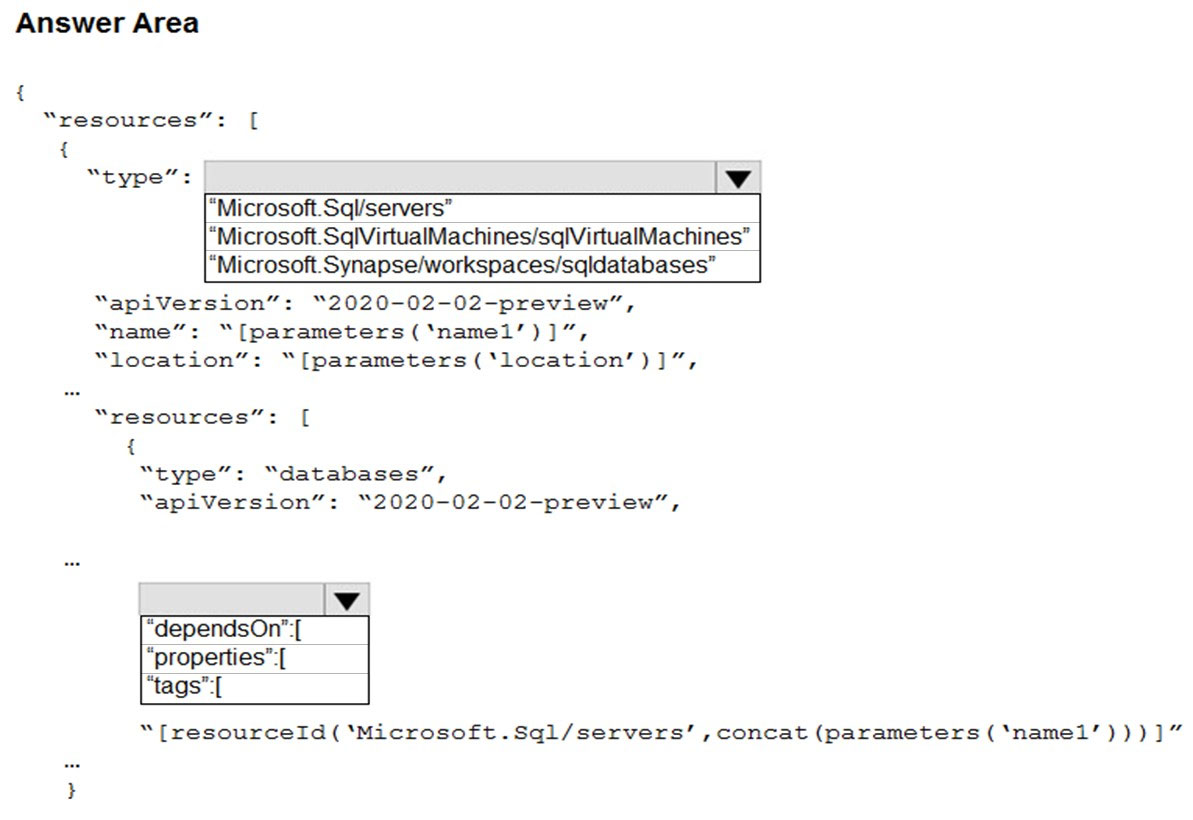
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy an Azure SQL database by using an Azure Resource Manager template.
How should you complete the template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
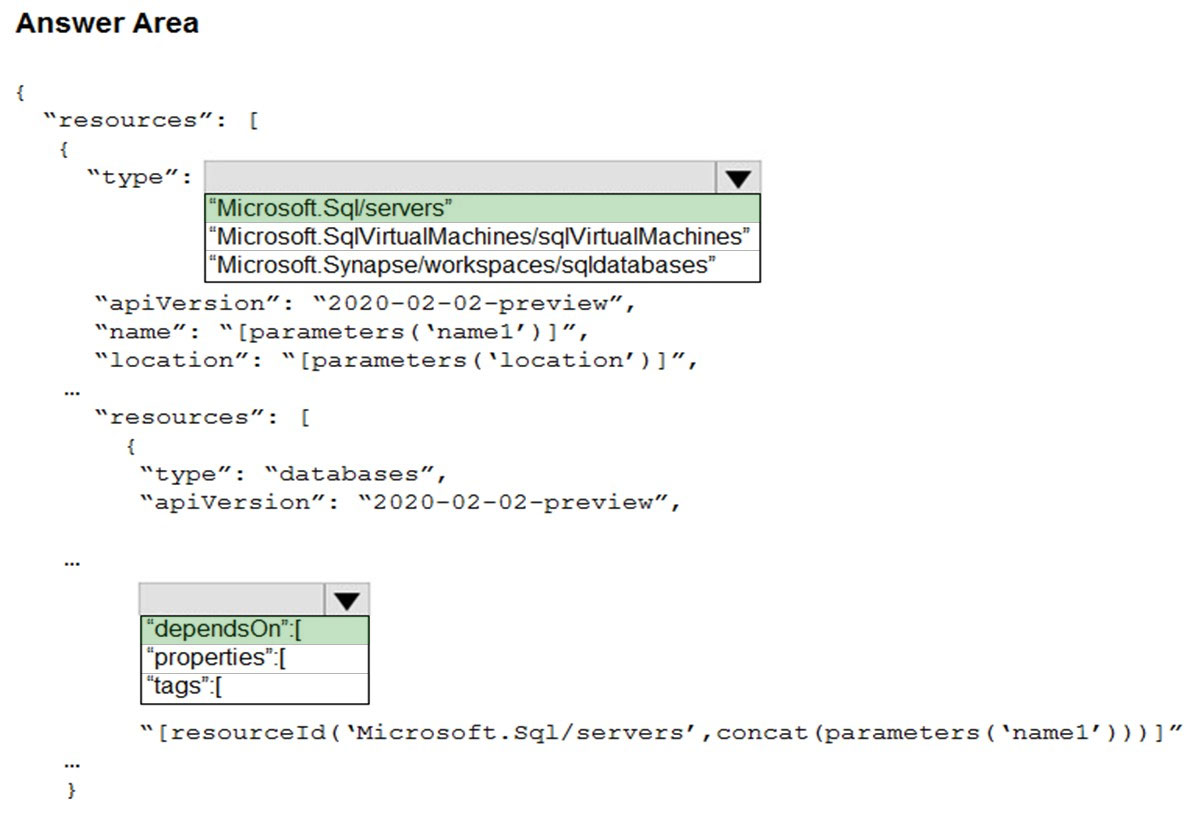
Box 1: "Microsoft.Sql/servers"
Example:
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Sql/servers",
"apiVersion": "2021-08-01-preview",
"name": "[parameters('serverName')]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"properties": {
"administratorLogin": "[parameters('administratorLogin')]",
"administratorLoginPassword": "[parameters('administratorLoginPassword')]"
}
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases",
"apiVersion": "2021-08-01-preview",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('serverName'), parameters('sqlDBName'))]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"sku": {
"name": "Standard",
"tier": "Standard"
},
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Sql/servers', parameters('serverName'))]"
]
}
Box 2: "dependsOn": [
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/single-database-create-arm-template-quickstart

Box 1: "Microsoft.Sql/servers"
Example:
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Sql/servers",
"apiVersion": "2021-08-01-preview",
"name": "[parameters('serverName')]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"properties": {
"administratorLogin": "[parameters('administratorLogin')]",
"administratorLoginPassword": "[parameters('administratorLoginPassword')]"
}
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases",
"apiVersion": "2021-08-01-preview",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('serverName'), parameters('sqlDBName'))]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"sku": {
"name": "Standard",
"tier": "Standard"
},
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Sql/servers', parameters('serverName'))]"
]
}
Box 2: "dependsOn": [
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/single-database-create-arm-template-quickstart
send
light_mode
delete
Question #35
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2019 server that hosts a database named DB1.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure SQL managed instance named SQLMI1 and a virtual network named VNET1. SQLMI1 resides on VNET1.
The on-premises network connects to VNET1 by using an ExpressRoute connection.
You plan to migrate DB1 to SQLMI1 by using Azure Database Migration Service.
You need to configure VNET1 to support the migration.
What should you do?
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure SQL managed instance named SQLMI1 and a virtual network named VNET1. SQLMI1 resides on VNET1.
The on-premises network connects to VNET1 by using an ExpressRoute connection.
You plan to migrate DB1 to SQLMI1 by using Azure Database Migration Service.
You need to configure VNET1 to support the migration.
What should you do?
- AConfigure service endpoints.Most Voted
- BConfigure virtual network peering.
- CDeploy an Azure firewall.
- DConfigure network security groups (NSGs).
Correct Answer:
A
During virtual network setup, if you use ExpressRoute with network peering to Microsoft, add the following service endpoints to the subnet in which the service will be provisioned:
* Target database endpoint (for example, SQL endpoint, Cosmos DB endpoint, and so on)
* Storage endpoint
* Service bus endpoint
This configuration is necessary because Azure Database Migration Service lacks internet connectivity.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/tutorial-sql-server-to-managed-instance
A
During virtual network setup, if you use ExpressRoute with network peering to Microsoft, add the following service endpoints to the subnet in which the service will be provisioned:
* Target database endpoint (for example, SQL endpoint, Cosmos DB endpoint, and so on)
* Storage endpoint
* Service bus endpoint
This configuration is necessary because Azure Database Migration Service lacks internet connectivity.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/tutorial-sql-server-to-managed-instance
send
light_mode
delete
Question #36
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL server that uses the FileTables and Filestream features.
You plan to migrate to Azure SQL.
Which service should you use?
You plan to migrate to Azure SQL.
Which service should you use?
- AAzure SQL Database
- BSQL Server on an Azure Virtual MachineMost Voted
- CAzure SQL Managed Instance
- DAzure Database for MySQL
Correct Answer:
B
SQL Server VM alternative.
Your business might have requirements that make SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines a more suitable target than Azure SQL Database.
If one of the following conditions applies to your business, consider moving to a SQL Server virtual machine (VM) instead:
* You have strict dependency on features that are still not supported, such as FileStream/FileTable, PolyBase, and cross-instance transactions.
* Etc.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/migration-guides/database/sql-server-to-sql-database-overview
B
SQL Server VM alternative.
Your business might have requirements that make SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines a more suitable target than Azure SQL Database.
If one of the following conditions applies to your business, consider moving to a SQL Server virtual machine (VM) instead:
* You have strict dependency on features that are still not supported, such as FileStream/FileTable, PolyBase, and cross-instance transactions.
* Etc.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/migration-guides/database/sql-server-to-sql-database-overview
send
light_mode
delete
Question #37
You need to migrate an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server database to Azure SQL Database. The solution must minimize downtime.
What should you do?
What should you do?
- AConfigure Transaction Log Shipping.
- BImplement Always On availability groups.
- CConfigure transactional replication.Most Voted
- DImport a BACPAC.
Correct Answer:
C
Use Transactional Replication.
When you can't afford to remove your SQL Server database from production while the migration is occurring, you can use SQL Server transactional replication as your migration solution.
Note: There are two primary methods for migrating a SQL Server 2005 or later database to Azure SQL Database. The first method (database copy or BACPAC importation) is simpler but requires some, possibly substantial, downtime during the migration. The second method (transactional replication) is more complex, but substantially eliminates downtime during the migration.
Incorrect:
Not D: The import BACPAC method includes downtime during migration.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/migrate-to-database-from-sql-server#method-1-migration-with-downtime-during-the-migration
C
Use Transactional Replication.
When you can't afford to remove your SQL Server database from production while the migration is occurring, you can use SQL Server transactional replication as your migration solution.
Note: There are two primary methods for migrating a SQL Server 2005 or later database to Azure SQL Database. The first method (database copy or BACPAC importation) is simpler but requires some, possibly substantial, downtime during the migration. The second method (transactional replication) is more complex, but substantially eliminates downtime during the migration.
Incorrect:
Not D: The import BACPAC method includes downtime during migration.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/migrate-to-database-from-sql-server#method-1-migration-with-downtime-during-the-migration
send
light_mode
delete
Question #38
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1.
You have a table name Table1 that has 20 columns of type CHAR(400). Row compression for Table1 is enabled.
During a database audit, you discover that none of the fields contain more than 150 characters.
You need to ensure that you can apply page compression to Table1.
What should you do?
You have a table name Table1 that has 20 columns of type CHAR(400). Row compression for Table1 is enabled.
During a database audit, you discover that none of the fields contain more than 150 characters.
You need to ensure that you can apply page compression to Table1.
What should you do?
- AConfigure the columns as sparse.
- BChange the column type to NVARCHAR(MAX).
- CChange the column type to VARCHAR(MAX).
- DChange the column type to VARCHAR(200).Most Voted
Correct Answer:
D
We reduce the max length of the column from 400 to 200.
Incorrect:
Not A: Sparse column is useful when there are many null columns.
The SQL Server Database Engine uses the SPARSE keyword in a column definition to optimize the storage of values in that column. Therefore, when the column value is NULL for any row in the table, the values require no storage.
Not B, Not C: SQL Server 2005 got around the limitation of 8KB storage size and provided a workaround with varchar(max). It is a non-Unicode large variable- length character data type and can store a maximum of 2^31-1 bytes (2 GB) of non-Unicode characters.
Reference:
https://www.sqlshack.com/sql-varchar-data-type-deep-dive/
https://36chambers.wordpress.com/2020/06/18/nvarchar-everywhere-a-thought-experiment/
D
We reduce the max length of the column from 400 to 200.
Incorrect:
Not A: Sparse column is useful when there are many null columns.
The SQL Server Database Engine uses the SPARSE keyword in a column definition to optimize the storage of values in that column. Therefore, when the column value is NULL for any row in the table, the values require no storage.
Not B, Not C: SQL Server 2005 got around the limitation of 8KB storage size and provided a workaround with varchar(max). It is a non-Unicode large variable- length character data type and can store a maximum of 2^31-1 bytes (2 GB) of non-Unicode characters.
Reference:
https://www.sqlshack.com/sql-varchar-data-type-deep-dive/
https://36chambers.wordpress.com/2020/06/18/nvarchar-everywhere-a-thought-experiment/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #39
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server named SQL1 that hosts five databases.
You need to migrate the databases to an Azure SQL managed instance. The solution must minimize downtime and prevent data loss.
What should you use?
You need to migrate the databases to an Azure SQL managed instance. The solution must minimize downtime and prevent data loss.
What should you use?
- AAlways On availability groups
- BBackup and RestoreMost Voted
- Clog shipping
- DDatabase Migration Assistant
Correct Answer:
D
The Data Migration Assistant (DMA) helps you upgrade to a modern data platform by detecting compatibility issues that can impact database functionality in your new version of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. DMA recommends performance and reliability improvements for your target environment and allows you to move your schema, data, and uncontained objects from your source server to your target server.
Capabilities include:
Assess on-premises SQL Server instance(s) migrating to Azure SQL database(s).
Note: For large migrations (in terms of number and size of databases), we recommend that you use the Azure Database Migration Service, which can migrate databases at scale.
Migrate an on-premises SQL Server instance to a modern SQL Server instance hosted on-premises or on an Azure virtual machine (VM) that is accessible from your on-premises network.
Incorrect:
Not B: Native RESTORE DATABASE FROM URL - uses native backups from SQL Server and requires some downtime.
Not C: What is the purpose of log shipping?
Similar to replication, the primary purpose of log shipping is to increase database availability by maintaining a backup server that can replace a production server quickly.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/dma/dma-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/migration-guides/managed-instance/sql-server-to-managed-instance-guide
D
The Data Migration Assistant (DMA) helps you upgrade to a modern data platform by detecting compatibility issues that can impact database functionality in your new version of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. DMA recommends performance and reliability improvements for your target environment and allows you to move your schema, data, and uncontained objects from your source server to your target server.
Capabilities include:
Assess on-premises SQL Server instance(s) migrating to Azure SQL database(s).
Note: For large migrations (in terms of number and size of databases), we recommend that you use the Azure Database Migration Service, which can migrate databases at scale.
Migrate an on-premises SQL Server instance to a modern SQL Server instance hosted on-premises or on an Azure virtual machine (VM) that is accessible from your on-premises network.
Incorrect:
Not B: Native RESTORE DATABASE FROM URL - uses native backups from SQL Server and requires some downtime.
Not C: What is the purpose of log shipping?
Similar to replication, the primary purpose of log shipping is to increase database availability by maintaining a backup server that can replace a production server quickly.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/dma/dma-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/migration-guides/managed-instance/sql-server-to-managed-instance-guide
send
light_mode
delete
Question #40
You have a new Azure SQL database. The database contains a column that stores confidential information.
You need to track each time values from the column are returned in a query. The tracking information must be stored for 365 days from the date the query was executed.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You need to track each time values from the column are returned in a query. The tracking information must be stored for 365 days from the date the query was executed.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- ATurn on auditing and write audit logs to an Azure Storage account.Most Voted
- BAdd extended properties to the column.
- CTurn on auditing and write audit logs to an Event HubMost Voted
- DApply sensitivity labels named Highly Confidential to the column.Most Voted
- ETurn on Azure Defender for SQL
Correct Answer:
ADE
D: You can apply sensitivity-classification labels persistently to columns by using new metadata attributes that have been added to the SQL Server database engine. This metadata can then be used for advanced, sensitivity-based auditing and protection scenarios.
A: An important aspect of the information-protection paradigm is the ability to monitor access to sensitive data. Azure SQL Auditing has been enhanced to include a new field in the audit log called data_sensitivity_information. This field logs the sensitivity classifications (labels) of the data that was returned by a query. Here's an example:
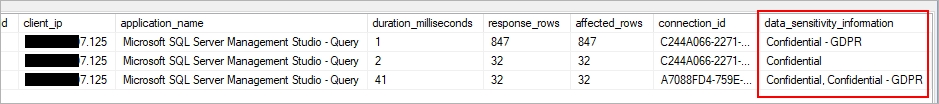
E: Enable Microsoft Defender for Azure SQL Database at the subscription level from Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Note: Microsoft Defender for SQL is a unified package for advanced SQL security capabilities. Microsoft Defender for Cloud is available for Azure SQL Database,
Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/data-discovery-and-classification-overview https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/azure-defender-for-sql
ADE
D: You can apply sensitivity-classification labels persistently to columns by using new metadata attributes that have been added to the SQL Server database engine. This metadata can then be used for advanced, sensitivity-based auditing and protection scenarios.
A: An important aspect of the information-protection paradigm is the ability to monitor access to sensitive data. Azure SQL Auditing has been enhanced to include a new field in the audit log called data_sensitivity_information. This field logs the sensitivity classifications (labels) of the data that was returned by a query. Here's an example:

E: Enable Microsoft Defender for Azure SQL Database at the subscription level from Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Note: Microsoft Defender for SQL is a unified package for advanced SQL security capabilities. Microsoft Defender for Cloud is available for Azure SQL Database,
Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/data-discovery-and-classification-overview https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/azure-defender-for-sql
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
