Microsoft 70-342 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (191 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #16
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named adatum.com.
You have a database availability group (DAG) that contains four Exchange servers named Server1, Server2, Server3, and Server4. The file share witness is on a server named Share1.
The organization has two Send connectors. The Send connectors are configured as shown in the following table.

Users report that email sent to external recipients is not being received.
You discover that outbound email messages are queued on Server3 and Server4.
You need to ensure that all of the email messages queued on Server3 and Server4 are delivered to the Internet as quickly as possible.
What should you do?
You have a database availability group (DAG) that contains four Exchange servers named Server1, Server2, Server3, and Server4. The file share witness is on a server named Share1.
The organization has two Send connectors. The Send connectors are configured as shown in the following table.

Users report that email sent to external recipients is not being received.
You discover that outbound email messages are queued on Server3 and Server4.
You need to ensure that all of the email messages queued on Server3 and Server4 are delivered to the Internet as quickly as possible.
What should you do?
- AModify the cost of External2.
- BDisable External1.
- CModify the list of source bridgehead servers of External2.
- DModify the cost of External1.
Correct Answer:
B
Note:
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, a Send connector controls the flow of outbound messages to the receiving server.
When a message is to be delivered to a remote delivery group, a routing path must be determined for the message. Exchange 2013 uses the same logic as
Exchange 2010 to select the routing path for a message:
Calculate the least-cost routing path by adding the cost of the IP site links that must be traversed to reach the destination. If the destination is a connector, the cost assigned to the address space is added to the cost to reach the selected connector. If multiple routing paths are possible, the routing path with the lowest aggregate cost is used;
If more than one routing path has the same cost, the routing path with the least number of hops is used;
If more than one routing path is still available, the name assigned to the AD sites before the destination is considered. The routing path where the AD site nearest the destination is lowest in alphanumeric order is used. If the site nearest the destination is the same for all routing paths being evaluated, an earlier site name is considered.
B
Note:
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, a Send connector controls the flow of outbound messages to the receiving server.
When a message is to be delivered to a remote delivery group, a routing path must be determined for the message. Exchange 2013 uses the same logic as
Exchange 2010 to select the routing path for a message:
Calculate the least-cost routing path by adding the cost of the IP site links that must be traversed to reach the destination. If the destination is a connector, the cost assigned to the address space is added to the cost to reach the selected connector. If multiple routing paths are possible, the routing path with the lowest aggregate cost is used;
If more than one routing path has the same cost, the routing path with the least number of hops is used;
If more than one routing path is still available, the name assigned to the AD sites before the destination is considered. The routing path where the AD site nearest the destination is lowest in alphanumeric order is used. If the site nearest the destination is the same for all routing paths being evaluated, an earlier site name is considered.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
You are a network administrator for a company named Humongous Insurance. Humongous Insurance has an Active Directory forest that contains two domains.
You install the Active Directory Rights Management Services server role on a server named ADRMS1. The Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD
RMS) server uses an internal certification authority (CA) for all certificates.
You plan to provide users with the ability to use AD RMS to protect all of the email messages sent to a partner company named Contoso, Ltd.
Contoso does not have AD RMS deployed.
You need to identify which components from the Humongous Insurance network must be accessible to Contoso to ensure that the users at Contoso can open protected messages.
Which two components should you identify? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
You install the Active Directory Rights Management Services server role on a server named ADRMS1. The Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD
RMS) server uses an internal certification authority (CA) for all certificates.
You plan to provide users with the ability to use AD RMS to protect all of the email messages sent to a partner company named Contoso, Ltd.
Contoso does not have AD RMS deployed.
You need to identify which components from the Humongous Insurance network must be accessible to Contoso to ensure that the users at Contoso can open protected messages.
Which two components should you identify? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- Athe AD RMS cluster
- Bthe certificate revocation list (CRL)
- Cthe Active Directory domain controllers
- Dthe Client Access servers
- Ethe Mailbox servers
- Fthe Global Catalog servers
Correct Answer:
BC
B: The CRL is exactly what its name implies: a list of subscribers paired with digital certificate status. The list enumerates revoked certificates along with the reason(s) for revocation. The dates of certificate issue, and the entities that issued them, are also included. In addition, each list contains a proposed date for the next release. When a potential user attempts to access a server, the server allows or denies access based on the CRL entry for that particular user.
C: If federation cannot be implemented and the external organization cannot implement their own AD RMS infrastructure, hosting the user accounts can be the best option. However, the cost of managing such accounts (for both the IT department and each user) must be considered.
In this case, the users will need to be authenticated by a domain controller.
BC
B: The CRL is exactly what its name implies: a list of subscribers paired with digital certificate status. The list enumerates revoked certificates along with the reason(s) for revocation. The dates of certificate issue, and the entities that issued them, are also included. In addition, each list contains a proposed date for the next release. When a potential user attempts to access a server, the server allows or denies access based on the CRL entry for that particular user.
C: If federation cannot be implemented and the external organization cannot implement their own AD RMS infrastructure, hosting the user accounts can be the best option. However, the cost of managing such accounts (for both the IT department and each user) must be considered.
In this case, the users will need to be authenticated by a domain controller.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
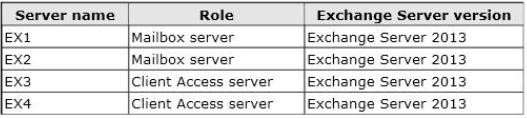
You have an Exchange Server organization that contains four servers. The servers are configured as shown in the following table.
You are deploying Unified Messaging (UM).
You create a dial plan named UMPlan1 and a UM mailbox policy named UMPlan Mailbox Policy.
You need to ensure that all voice mail sent to the existing extension of a user is delivered to the user's mailbox.
Which three actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)

You are deploying Unified Messaging (UM).
You create a dial plan named UMPlan1 and a UM mailbox policy named UMPlan Mailbox Policy.
You need to ensure that all voice mail sent to the existing extension of a user is delivered to the user's mailbox.
Which three actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)
- ACreate a UM hunt group
- BCreate a UM IP gateway.
- CConfigure the IP-PBX to route calls to EX3 and EX4
- DConfigure the IP-PBX to route calls to EX I and EX2.
- EAssign EX I and EX2 to UMPlan1.
- FAssign EX3 and EX4 to UMPlan1.
Correct Answer:
ABC
When you're setting up Unified Messaging (UM), you must configure the IP PBXs on your network to communicate with the Client Access servers running the
Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging Call Router service and the Mailbox servers running the Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service in your Exchange organization. You must also configure the Client Access and Mailbox servers to communicate with the IP PBXs.
C: A Unified Messaging (UM) IP gateway represents a physical Voice over IP (VoIP) gateway, IP Private Branch eXchange (PBX), or session border controller
(SBC) hardware device.
Here are the basic steps for connecting VoIP gateways, IP PBXs, SIP-enabled PBXs, or SBCs to Client Access and Mailbox servers:
Step 1: Install the Client Access and Mailbox servers in your organization.
Step 2: Create and configure a Telephone Extension, SIP URI, or E.164 UM dial plan.
Step 3: Create and configure a UM IP gateway. You must create and configure a UM IP gateway for each VoIP gateway, IP PBX, SIP-enabled PBX, or SBC that will be accepting incoming calls and sending outgoing calls.
Step 4: Create a new UM hunt group if needed. If you create a UM IP gateway and don't specify a UM dial plan, a UM hunt group will be automatically created.
Incorrect:
B, D:
The question states, "You need to ensure that all voice mail sent to the existing extension of a user is delivered to the user's mailbox". The dial plan is therefore a
Telephone Extension dial plan. Client Access and Mailbox servers cannot be associated with Telephone Extension or E.164 dial plans.
ABC
When you're setting up Unified Messaging (UM), you must configure the IP PBXs on your network to communicate with the Client Access servers running the
Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging Call Router service and the Mailbox servers running the Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service in your Exchange organization. You must also configure the Client Access and Mailbox servers to communicate with the IP PBXs.
C: A Unified Messaging (UM) IP gateway represents a physical Voice over IP (VoIP) gateway, IP Private Branch eXchange (PBX), or session border controller
(SBC) hardware device.
Here are the basic steps for connecting VoIP gateways, IP PBXs, SIP-enabled PBXs, or SBCs to Client Access and Mailbox servers:
Step 1: Install the Client Access and Mailbox servers in your organization.
Step 2: Create and configure a Telephone Extension, SIP URI, or E.164 UM dial plan.
Step 3: Create and configure a UM IP gateway. You must create and configure a UM IP gateway for each VoIP gateway, IP PBX, SIP-enabled PBX, or SBC that will be accepting incoming calls and sending outgoing calls.
Step 4: Create a new UM hunt group if needed. If you create a UM IP gateway and don't specify a UM dial plan, a UM hunt group will be automatically created.
Incorrect:
B, D:
The question states, "You need to ensure that all voice mail sent to the existing extension of a user is delivered to the user's mailbox". The dial plan is therefore a
Telephone Extension dial plan. Client Access and Mailbox servers cannot be associated with Telephone Extension or E.164 dial plans.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
DRAG DROP -
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two Mailbox servers and two Client Access servers.
You have an Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) cluster. Information Rights Management (IRM) is enabled for the Exchange Server organization.
All company executives are in a security group named Execs. All of the executives use smartphones that are managed by using a mobile device mailbox policy.
The executives frequently read IRM-protected email messages by using Microsoft Outlook.
You need to ensure that the executives can read the IRM-protected messages on their smartphone.
Which task should you perform in each environment? (To answer, drag the appropriate tasks to the correct environments. Each task may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Select and Place:
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two Mailbox servers and two Client Access servers.
You have an Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) cluster. Information Rights Management (IRM) is enabled for the Exchange Server organization.
All company executives are in a security group named Execs. All of the executives use smartphones that are managed by using a mobile device mailbox policy.
The executives frequently read IRM-protected email messages by using Microsoft Outlook.
You need to ensure that the executives can read the IRM-protected messages on their smartphone.
Which task should you perform in each environment? (To answer, drag the appropriate tasks to the correct environments. Each task may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
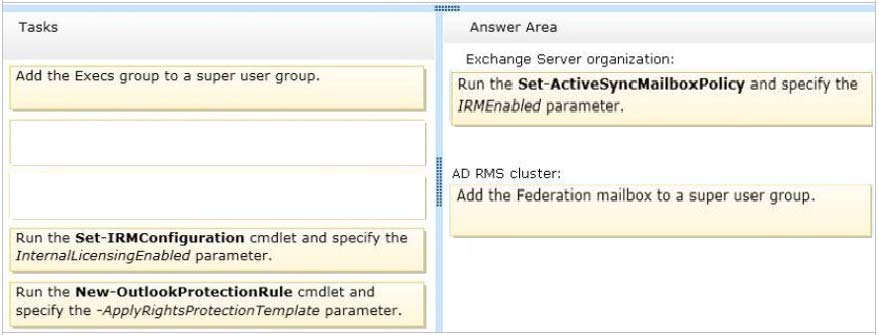
Note:
Set-ActiveSyncMailboxPolicy -
Use the Set-ActiveSyncMailboxPolicy cmdlet to apply a variety of Mobile Device mailbox policy settings to a server. You can set any of the parameters by using one command.
Parameters include:
IrmEnabled -
The IrmEnabled parameter specifies whether Information Rights Management (IRM) is enabled for the mailbox policy.
AD RMS super users -
To enable transport decryption, journal report decryption, IRM in Outlook Web App, and IRM for Exchange Search, you must add the Federation mailbox, a system mailbox created by Exchange 2013 Setup, to the super users group on the AD RMS cluster.
Reference: Information Rights Management

Note:
Set-ActiveSyncMailboxPolicy -
Use the Set-ActiveSyncMailboxPolicy cmdlet to apply a variety of Mobile Device mailbox policy settings to a server. You can set any of the parameters by using one command.
Parameters include:
IrmEnabled -
The IrmEnabled parameter specifies whether Information Rights Management (IRM) is enabled for the mailbox policy.
AD RMS super users -
To enable transport decryption, journal report decryption, IRM in Outlook Web App, and IRM for Exchange Search, you must add the Federation mailbox, a system mailbox created by Exchange 2013 Setup, to the super users group on the AD RMS cluster.
Reference: Information Rights Management
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
DRAG DROP -
Your company has two offices. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site. The sites are named Site1 and Site2.
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that is configured as shown in the following exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
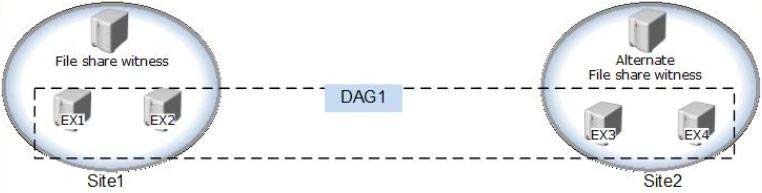
Datacenter Activation Coordination (DAC) mode is enabled on the database availability group (DAG) named DAG1.
You are testing a site failover by shutting down all of the servers in Site1.
You need to mount the databases in Site2.
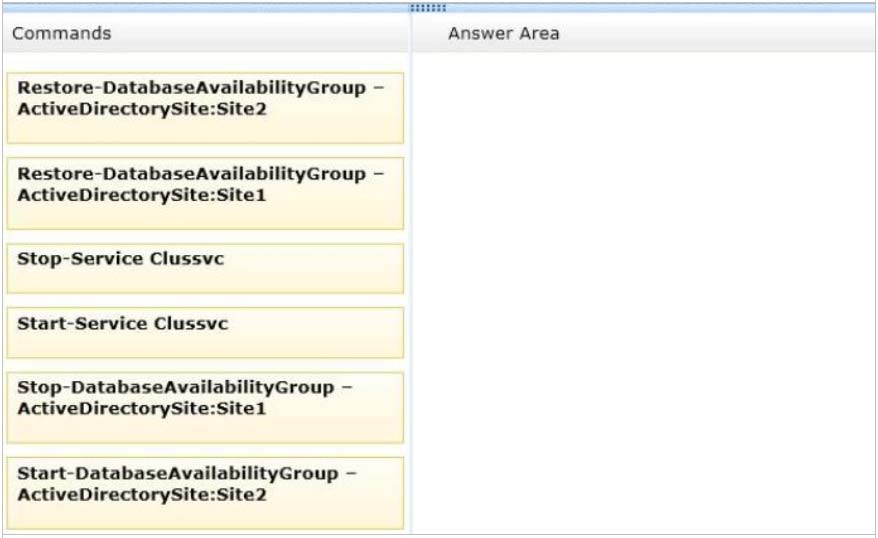
Which three commands should you run in sequence? (To answer, move the appropriate three commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
Select and Place:
Your company has two offices. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site. The sites are named Site1 and Site2.
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that is configured as shown in the following exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

Datacenter Activation Coordination (DAC) mode is enabled on the database availability group (DAG) named DAG1.
You are testing a site failover by shutting down all of the servers in Site1.
You need to mount the databases in Site2.
Which three commands should you run in sequence? (To answer, move the appropriate three commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
Select and Place:

send
light_mode
delete
All Pages