Cisco® 400-101 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (2105 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #41
DRAG DROP -
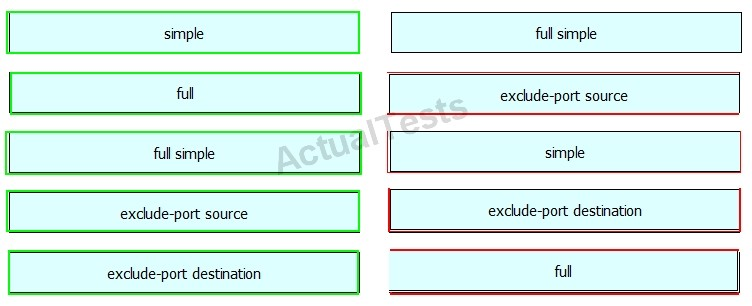
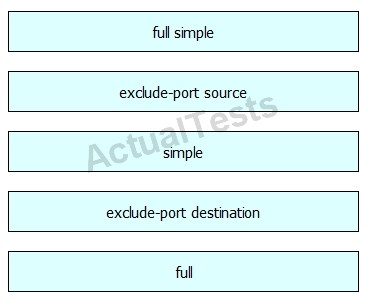
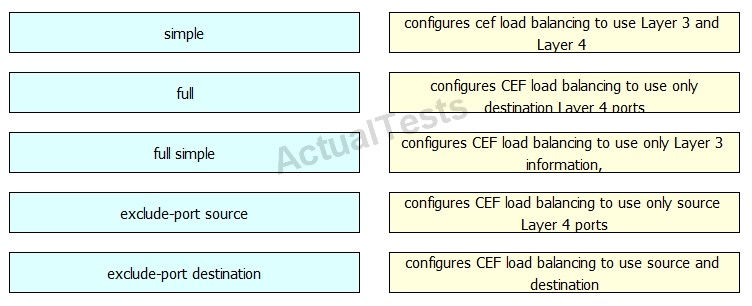
Drag and drop the argument of the mpls ip cef load-sharing command on the left to the function it performs on the right.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 45
A.
B.
C.
D.
Drag and drop the argument of the mpls ip cef load-sharing command on the left to the function it performs on the right.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 45

A.
B.
C.
D.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #42
DRAG DROP -
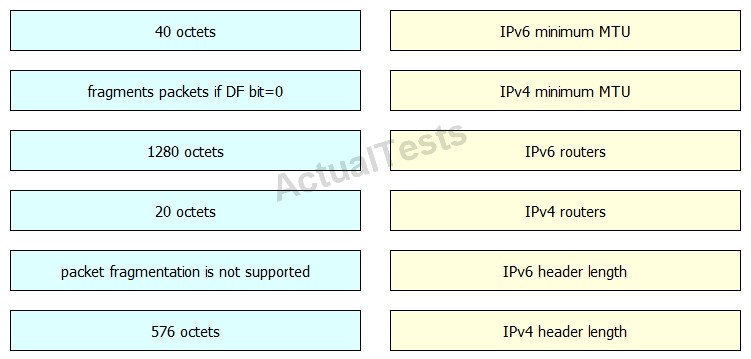
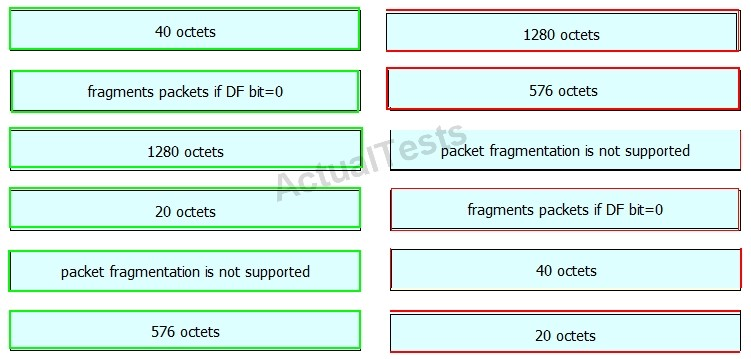
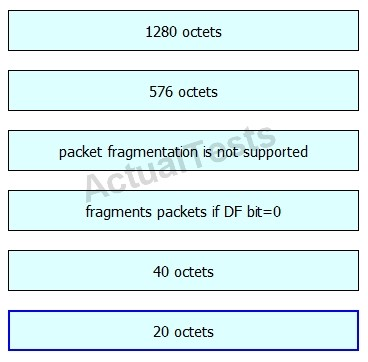
Drag and drop the fragmentation characteristics on the left to the corresponding protocol on the right.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Drag and drop the fragmentation characteristics on the left to the corresponding protocol on the right.

A.
B.
C.
D.
Correct Answer:
Explanation
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 47
Topic 2, Layer 2 Technologies
Explanation

"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 47

Topic 2, Layer 2 Technologies
send
light_mode
delete
Question #43
Refer to the exhibit.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 48
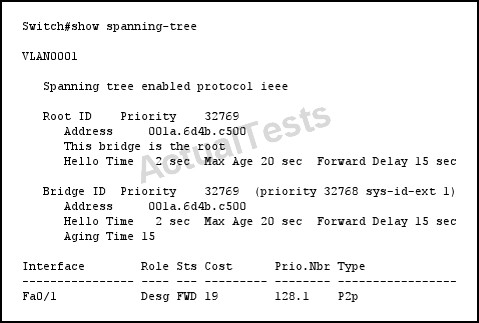
If you change the Spanning Tree Protocol from pvst to rapid-pvst, what is the effect on the interface Fa0/1 port state?
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 48

If you change the Spanning Tree Protocol from pvst to rapid-pvst, what is the effect on the interface Fa0/1 port state?
- AIt transitions to the listening state, and then the forwarding state.
- BIt transitions to the learning state and then the forwarding state.
- CIt transitions to the blocking state, then the learning state, and then the forwarding state.
- DIt transitions to the blocking state and then the forwarding state.
Correct Answer:
C
First, the port will transition to the blocking state, immediately upon the change, then it will transition to the new RSTP states of learning and forwarding.
Port States -
There are only three port states left in RSTP that correspond to the three possible operational states. The 802.1D disabled, blocking, and listening states are merged into a unique 802.1w discarding state.
STP (802.1D) Port State -
RSTP (802.1w) Port State -
Is Port Included in Active Topology?
Is Port Learning MAC Addresses?
Disabled -
Discarding -
No -
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 49
No -
Blocking -
Discarding -
No -
No -
Listening -
Discarding -
Yes -
No -
Learning -
Learning -
Yes -
Yes -
Forwarding -
Forwarding -
Yes -
Yes
C
First, the port will transition to the blocking state, immediately upon the change, then it will transition to the new RSTP states of learning and forwarding.
Port States -
There are only three port states left in RSTP that correspond to the three possible operational states. The 802.1D disabled, blocking, and listening states are merged into a unique 802.1w discarding state.
STP (802.1D) Port State -
RSTP (802.1w) Port State -
Is Port Included in Active Topology?
Is Port Learning MAC Addresses?
Disabled -
Discarding -
No -
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 49
No -
Blocking -
Discarding -
No -
No -
Listening -
Discarding -
Yes -
No -
Learning -
Learning -
Yes -
Yes -
Forwarding -
Forwarding -
Yes -
Yes
send
light_mode
delete
Question #44
Which type of port would have root guard enabled on it?
- AA root port
- BAn alternate port
- CA blocked port
- DA designated port
Correct Answer:
D
The root guard feature provides a way to enforce the root bridge placement in the network. The root guard ensures that the port on which root guard is enabled is the designated port. Normally, root bridge ports are all designated ports, unless two or more ports of the root bridge are connected together. If the bridge receives superior STP Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) on a root guard-enabled port, root guard moves this port to a root-inconsistent STP state. This root- inconsistent state is effectively equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 50
protocol/10588-74.html
D
The root guard feature provides a way to enforce the root bridge placement in the network. The root guard ensures that the port on which root guard is enabled is the designated port. Normally, root bridge ports are all designated ports, unless two or more ports of the root bridge are connected together. If the bridge receives superior STP Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) on a root guard-enabled port, root guard moves this port to a root-inconsistent STP state. This root- inconsistent state is effectively equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 50
protocol/10588-74.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #45
Refer to the exhibit.

While troubleshooting high CPU utilization on one of your Cisco Catalyst switches, you find that the issue is due to excessive flooding that is caused by STP. What can you do to prevent this issue from happening again?

While troubleshooting high CPU utilization on one of your Cisco Catalyst switches, you find that the issue is due to excessive flooding that is caused by STP. What can you do to prevent this issue from happening again?
- ADisable STP completely on the switch.
- BChange the STP version to RSTP.
- CConfigure PortFast on port-channel 1.
- DConfigure UplinkFast on the switch.
- EConfigure PortFast on interface Gi0/15.
Correct Answer:
E
Topology Changes (TC) should be a rare event in a well-configured network. When a link on a switch port goes up or down, there is eventually a TC, once the
STP state of the port is changing to or from forwarding. When the port is flapping, this would cause repetitive TCs and flooding. Ports with the STP portfast feature enabled will not cause TCs when going to or from the forwarding state. The configuration of portfast on all end-device ports (such as printers, PCs, and servers) should limit TCs to a low amount and is highly recommended.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree- protocol/28943-170.html
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 51
E
Topology Changes (TC) should be a rare event in a well-configured network. When a link on a switch port goes up or down, there is eventually a TC, once the
STP state of the port is changing to or from forwarding. When the port is flapping, this would cause repetitive TCs and flooding. Ports with the STP portfast feature enabled will not cause TCs when going to or from the forwarding state. The configuration of portfast on all end-device ports (such as printers, PCs, and servers) should limit TCs to a low amount and is highly recommended.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree- protocol/28943-170.html
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 51
send
light_mode
delete
Question #46
Refer to the exhibit.
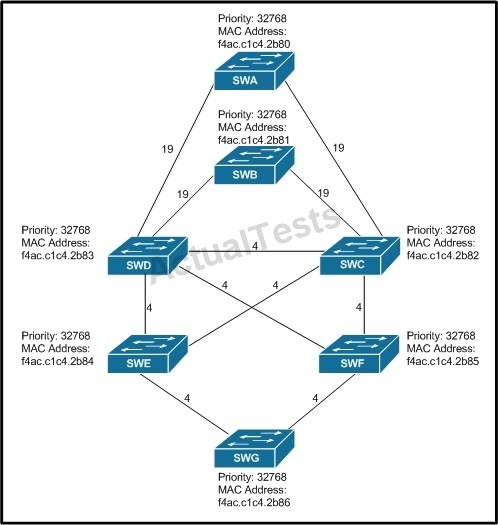
All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are forwarding traffic after STP converges? (Choose two.)

All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are forwarding traffic after STP converges? (Choose two.)
- AThe port connecting switch SWD with switch SWE
- BThe port connecting switch SWG with switch SWF
- CThe port connecting switch SWC with switch SWE
- DThe port connecting switch SWB with switch SWC
Correct Answer:
CD
Here, we know SWB to SWC are forwarding because we already identified the blocking port. So
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 52
for the last correct answer let's consider what must be done to prevent a switch loop between SWC/SWD/SWE. SWE to SWD will be blocked because SWC has a lower MAC address so it wins the forwarding port. And to look at it further, you could try to further understand what would happen with ports on SWG. Would the ports on SWG try to go through SWE or SWF? SWE has the lower MAC address so the port from SWG to SWE would win the forwarding election.
Therefore, answer B could never be correct.
CD
Here, we know SWB to SWC are forwarding because we already identified the blocking port. So
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 52
for the last correct answer let's consider what must be done to prevent a switch loop between SWC/SWD/SWE. SWE to SWD will be blocked because SWC has a lower MAC address so it wins the forwarding port. And to look at it further, you could try to further understand what would happen with ports on SWG. Would the ports on SWG try to go through SWE or SWF? SWE has the lower MAC address so the port from SWG to SWE would win the forwarding election.
Therefore, answer B could never be correct.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #47
Refer to the exhibit.

Which three statements about the output are true? (Choose three.)

Which three statements about the output are true? (Choose three.)
- AAn mrouter port can be learned by receiving a PIM hello packet from a multicast router.
- BThis switch is configured as a multicast router.
- CGi2/0/1 is a trunk link that connects to a multicast router.
- DAn mrouter port is learned when a multicast data stream is received on that port from a multicast router.
- EThis switch is not configured as a multicast router. It is configured only for IGMP snooping.
- FIGMP reports are received only on Gi2/0/1 and are never transmitted out Gi2/0/1 for VLANs 10 and 20.
Correct Answer:
ABC
In this example, the switch has been configured as a multicast router since IGMP snooping has been enabled. All mrouters can learn about other mrouters by receiving a PIM hello packet from another multicast router. Also, since two different VLANs are being used by the same port of gi 2/0/1, it must be a trunk link that connects to another multicast router.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 53
ABC
In this example, the switch has been configured as a multicast router since IGMP snooping has been enabled. All mrouters can learn about other mrouters by receiving a PIM hello packet from another multicast router. Also, since two different VLANs are being used by the same port of gi 2/0/1, it must be a trunk link that connects to another multicast router.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 53
send
light_mode
delete
Question #48
Refer to the exhibit.

If a port is configured as shown and receives an untagged frame, of which VLAN will the untagged frame be a member?

If a port is configured as shown and receives an untagged frame, of which VLAN will the untagged frame be a member?
- AVLAN 1
- BVLAN 2
- CVLAN 3
- DVLAN 4
Correct Answer:
B
When typing:
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode?
access Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 54
dynamic Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk mode trunk Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally and
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic?
auto Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to AUTO
desirable Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to DESIRABLE
So if we configure Fa0/1 as dynamic auto mode, it will not initiate any negotitation but waiting for the other end negotiate to be a trunk with DTP. If the other end does not ask it to become a trunk then it will become an access port. Therefore when using the "show interface fastEthernet0/1 switchport" command we will see two output lines "Administrative Mode. dynamic auto" and " Operational Mode. static access"
Note. To set this port to VLAN 2 as the output above just use one additional command. "switchport access vlan 2".
Now back to our question, from the output we see that Fa0/1 is operating as an access port on VLAN 2 so if it receive untagged frame it will suppose that frame is coming from VLAN 2.
B
When typing:
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode?
access Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 54
dynamic Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk mode trunk Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally and
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic?
auto Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to AUTO
desirable Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to DESIRABLE
So if we configure Fa0/1 as dynamic auto mode, it will not initiate any negotitation but waiting for the other end negotiate to be a trunk with DTP. If the other end does not ask it to become a trunk then it will become an access port. Therefore when using the "show interface fastEthernet0/1 switchport" command we will see two output lines "Administrative Mode. dynamic auto" and " Operational Mode. static access"
Note. To set this port to VLAN 2 as the output above just use one additional command. "switchport access vlan 2".
Now back to our question, from the output we see that Fa0/1 is operating as an access port on VLAN 2 so if it receive untagged frame it will suppose that frame is coming from VLAN 2.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #49
Refer to the exhibit.
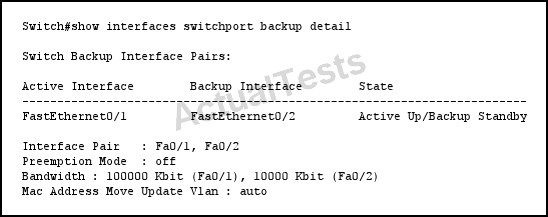
Which statement describes the effect on the network if FastEthernet0/1 goes down temporarily?

Which statement describes the effect on the network if FastEthernet0/1 goes down temporarily?
- AFastEthernet0/2 forwards traffic only until FastEthernet0/1 comes back up.
- BFastEthernet0/2 stops forwarding traffic until FastEthernet0/1 comes back up.
- CFastEthernet0/2 forwards traffic indefinitely.
- DFastEthernet0/1 goes into standby.
Correct Answer:
C
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 55
Use the switchport backup interface interface configuration command on a Layer 2 interface to configure Flex Links, a pair of interfaces that provide backup to each other. Use the no form of this command to remove the Flex Links configuration.
With Flex Links configured, one link acts as the primary interface and forwards traffic, while the other interface is in standby mode, ready to begin forwarding traffic if the primary link shuts down. The interface being configured is referred to as the active link; the specified interface is identified as the backup link. The feature provides an alternative to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), allowing users to turn off STP and still retain basic link redundancy.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2960/software/release/12- 2_53_se/command/reference/2960ComRef/cli3.html#wp3269214
C
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 55
Use the switchport backup interface interface configuration command on a Layer 2 interface to configure Flex Links, a pair of interfaces that provide backup to each other. Use the no form of this command to remove the Flex Links configuration.
With Flex Links configured, one link acts as the primary interface and forwards traffic, while the other interface is in standby mode, ready to begin forwarding traffic if the primary link shuts down. The interface being configured is referred to as the active link; the specified interface is identified as the backup link. The feature provides an alternative to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), allowing users to turn off STP and still retain basic link redundancy.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2960/software/release/12- 2_53_se/command/reference/2960ComRef/cli3.html#wp3269214
send
light_mode
delete
Question #50
Refer to the exhibit.
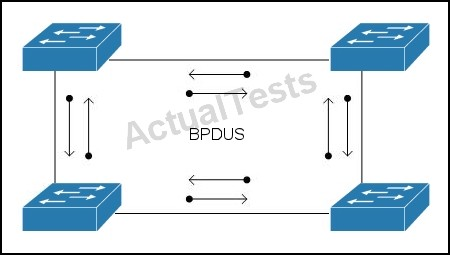
Which technology does the use of bi-directional BPDUs on all ports in the topology support?

Which technology does the use of bi-directional BPDUs on all ports in the topology support?
- ARSTP
- BMST
- CBridge Assurance
- DLoop Guard
- ERoot Guard "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 56
- FUDLD
Correct Answer:
C
Spanning Tree Bridge Assurance -
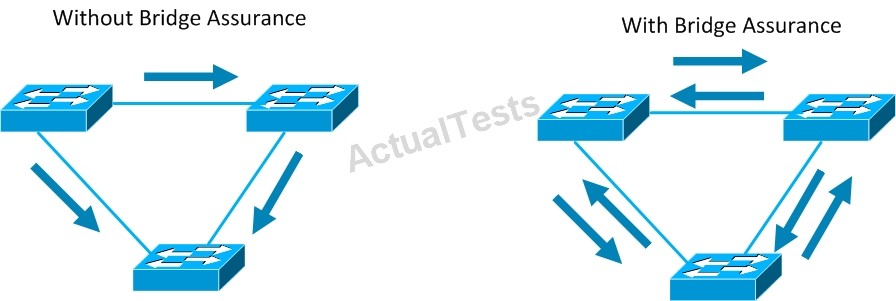
Bridge Assurance (BA) can help protect against bridging loops where a port becomes designated because it has stopped receiving BPDUs. This is similar to the function of loop guard.
Reference: http://lostintransit.se/tag/convergence/
C
Spanning Tree Bridge Assurance -

Bridge Assurance (BA) can help protect against bridging loops where a port becomes designated because it has stopped receiving BPDUs. This is similar to the function of loop guard.
Reference: http://lostintransit.se/tag/convergence/
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages