Cisco® 400-101 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (2105 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
- AUnicast flooding occurs when multicast traffic arrives on a Layer 2 switch that has directly connected multicast receivers.
- BWhen PIM snooping is not enabled, unicast flooding occurs on the switch that interconnects the PIM-enabled routers. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 17
- CA man-in-the-middle attack can cause the ARP cache of an end host to have the wrong MAC address. Instead of having the MAC address of the default gateway, it has a MAC address of the man-in-the-middle. This causes all traffic to be unicast flooded through the man-in-the-middle, which can then sniff all packets.
- DForwarding table overflow prevents new MAC addresses from being learned, and packets destined to those MAC addresses are flooded until space becomes
D
Causes of Flooding -
The very cause of flooding is that destination MAC address of the packet is not in the L2 forwarding table of the switch. In this case the packet will be flooded out of all forwarding ports in its VLAN (except the port it was received on). Below case studies display most common reasons for destination MAC address not being known to the switch.
Cause 1: Asymmetric Routing -
Large amounts of flooded traffic might saturate low-bandwidth links causing network performance issues or complete connectivity outage to devices connected across such low-bandwidth links Cause 2: Spanning-Tree Protocol Topology Changes
Another common issue caused by flooding is Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Topology Change Notification (TCN). TCN is designed to correct forwarding tables after the forwarding topology has changed. This is necessary to avoid a connectivity outage, as after a topology change some destinations previously accessible via particular ports might become accessible via different ports. TCN operates by shortening the forwarding table aging time, such that if the address is not relearned, it will age out and flooding will occur
Cause 3: Forwarding Table Overflow
Another possible cause of flooding can be overflow of the switch forwarding table. In this case, new addresses cannot be learned and packets destined to such addresses are flooded until some space becomes available in the forwarding table. New addresses will then be learned. This is possible but rare, since most modern switches have large enough forwarding tables to accommodate MAC addresses for most designs.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-6000-series-switches/23563- 143.html

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #12
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 18
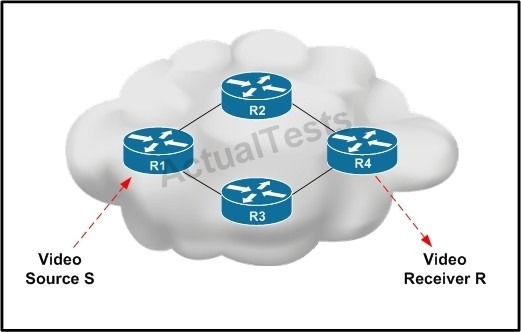
Video Source S is sending interactive video traffic to Video Receiver R. Router R1 has multiple routing table entries for destination R. Which load-balancing mechanism on R1 can cause out-of- order video traffic to be received by destination R?
- Aper-flow load balancing on R1 for destination R
- Bper-source-destination pair load balancing on R1 for destination R
- CCEF load balancing on R1 for destination R
- Dper-packet load balancing on R1 for destination R
D
Per-packet load balancing guarantees equal load across all links, however potentially the packets may arrive out-of-order at the destination as differential delay may exist within the network.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps2033/prod_technical_reference09186a00800 afeb7.html

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #13
- ATo increase the latency "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 19
- BTo calculate the best path in distance vector routing protocols
- CTo calculate the best path in link state routing protocols
- DTo resolve issues caused by poorly implemented TCP flow control.
D
Silly window syndrome is a problem in computer networking caused by poorly implemented TCP flow control. A serious problem can arise in the sliding window operation when the sending application program creates data slowly, the receiving application program consumes data slowly, or both. If a server with this problem is unable to process all incoming data, it requests that its clients reduce the amount of data they send at a time (the window setting on a TCP packet). If the server continues to be unable to process all incoming data, the window becomes smaller and smaller, sometimes to the point that the data transmitted is smaller than the packet header, making data transmission extremely inefficient. The name of this problem is due to the window size shrinking to a "silly" value. When there is no synchronization between the sender and receiver regarding capacity of the flow of data or the size of the packet, the window syndrome problem is created. When the silly window syndrome is created by the sender, Nagle's algorithm is used. Nagle's solution requires that the sender sends the first segment even if it is a small one, then that it waits until an ACK is received or a maximum sized segment (MSS) is accumulated.
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silly_window_syndrome

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #14
- AIt is used for congestion control.
- BIt cannot be all zeros.
- CIt is used by some Internet worms to hide their propagation.
- DIt is computed based on the IP pseudo-header.
D
The method used to compute the checksum is defined in RFC 768:
"Checksum is the 16-bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of a pseudo header of information from the IP header, the UDP header, and the data, padded with zero octets at the end (if necessary) to make a multiple of two octets."
In other words, all 16-bit words are summed using one's complement arithmetic. Add the 16-bit
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 20
values up. Each time a carry-out (17th bit) is produced, swing that bit around and add it back into the least significant bit. The sum is then one's complemented to yield the value of the UDP checksum field.
If the checksum calculation results in the value zero (all 16 bits 0) it should be sent as the one's complement (all 1s).
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_Datagram_Protocol

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #15
- AIt identifies the signaling protocol.
- BIt identifies the codec.
- CIt identifies the port numbers for RTP.
- DIt identifies the port numbers for RTCP.
B
PT, Payload Type. 7 bits: Identifies the format of the RTP payload and determines its interpretation by the application. A profile specifies a default static mapping of payload type codes to payload formats. Additional payload type codes may be defined dynamically through non-RTP means. An RTP sender emits a single
RTP payload type at any given time; this field is not intended for multiplexing separate media streams. A full list of codecs and their payload type values can be found at the link below:
Reference: http://www.networksorcery.com/enp/protocol/rtp.htm

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #16
- AForwarding manager
- BInterface manager
- CCisco IOS
- DHost manager "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 21
C
Some of the processes are listed in the table below:
Process -
Purpose -
Affected FRUs -
SubPackage Mapping -
Host Manager -
Provides an interface between the IOS process and many of the information-gathering functions of the underlying platform kernel and operating system.
RP (one instance per RP)
SIP (one instance per SIP)
ESP (one instance per ESP)
RPControl -
SIPBase -
ESPBase -
Interface Manager -
Provides an interface between the IOS process and the per-SPA interface processes on the SIP.
RP (one instance per RP)
SIP (one instance per SIP)
RPControl -
SIPBase -
IOS -
The IOS process implements all forwarding and routing features for the router. RP (one per software redundancy instance per RP). Maximum of two instances per
RP.
RPIOS -
Forwarding Manager -
Manages the downloading of configuration to each of the ESPs and the communication of forwarding plane information, such as statistics, to the IOS process.
RP (one per software redundancy instance per RP). Maximum of two instances per RP.
ESP (one per ESP)
RPControl -
ESPBase -
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr1000/configuration/guide/chassis/asrswcfg/Softwa
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 22
re_Packaging_Architecture.html

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #17
- Aslow convergence
- Ba blocked spanning-tree port
- Cprocess switching
- Dinsufficient buffers
D
Micro-bursting is a phenomenon where rapid bursts of data packets are sent in quick succession, leading to periods of full line-rate transmission that can overflow packet buffers of the network stack, both in network endpoints and routers and switches inside the network. Symptoms of micro bursts will manifest in the form of ignores and/ or overruns (also shown as accumulated in "input error" counter within show interface output). This is indicative of receive ring and corresponding packet buffer being overwhelmed due to data bursts coming in over extremely short period of time (microseconds).
Reference: http://ccieordie.com/?tag=micro-burst

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #18
- AIt is supported on networks without ARP.
- BIt allows machines to spoof packets.
- CIt must be used on a network with the host on a different subnet.
- DIt requires larger ARP tables.
- EIt reduces the amount of ARP traffic.
BD
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 23
Disadvantages of Proxy ARP -
Hosts have no idea of the physical details of their network and assume it to be a flat network in which they can reach any destination simply by sending an ARP request. But using ARP for everything has disadvantages. These are some of the disadvantages:
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/dynamic-address-allocation- resolution/13718-5.html

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #19
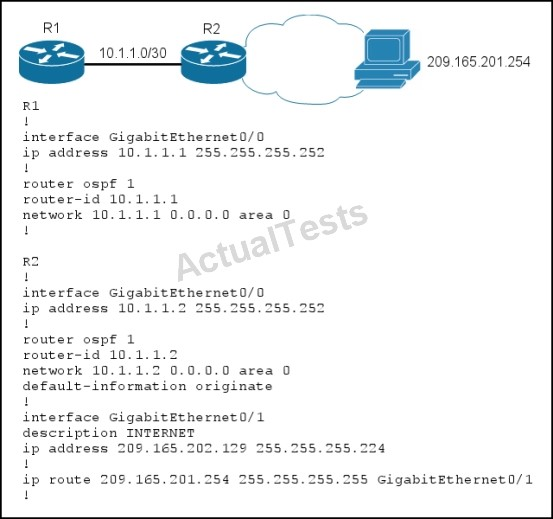
Routers R1 and R2 are configured as shown, and traffic from R1 fails to reach host 209.165.201.254.
Which action can you take to correct the problem?
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 24
- AEnsure that R2 has a default route in its routing table.
- BChange the OSPF area type on R1 and R2.
- CEdit the router configurations so that address 209.165.201.254 is a routable address.
- DRemove the default-information originate command from the OSPF configuration of R2.
A
Not sure that any of these answers are correct, it appears that this configuration is valid for reaching that one specific host IP. Answer A does have a route to that host so it would not need a default route to get to it. Choice B is incorrect as the area types have nothing to do with this. C is incorrect as that IP address is routable, and D is needed so that R1 will have a default route advertised to it from R2 so that it can reach this destination.

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
Question #20
- Athe finger service
- Bthe Telnet service
- Cthe Maintenance Operation Protocol service
- Dthe chargen service
D
The TCP small servers are:
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ios-nx-os-software/ios-software-releases- 110/12815-23.html

Hi! Do you need help with this question ?
- Why isn't the A the right answer?
- Traducir la pregunta al español
Contributor get free access to an augmented ChatGPT 4 trained with the latest IT Questions.
All Pages
