Cisco® 400-101 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (2105 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #31
Which two packet types does an RTP session consist of? (Choose two.)
- ATCP
- BRTCP
- CRTP
- DICMP
- EBOOTP
- FARP
Correct Answer:
BC
An RTP session is established for each multimedia stream. A session consists of an IP address with a pair of ports for RTP and RTCP. For example, audio and video streams use separate RTP sessions, enabling a receiver to deselect a particular stream. The ports which form a session are negotiated using other protocols such as RTSP (using SDP in the setup method) and SIP. According to the specification, an RTP port should be even and the RTCP port is the next higher odd port number.
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real-time_Transport_Protocol
BC
An RTP session is established for each multimedia stream. A session consists of an IP address with a pair of ports for RTP and RTCP. For example, audio and video streams use separate RTP sessions, enabling a receiver to deselect a particular stream. The ports which form a session are negotiated using other protocols such as RTSP (using SDP in the setup method) and SIP. According to the specification, an RTP port should be even and the RTCP port is the next higher odd port number.
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real-time_Transport_Protocol
send
light_mode
delete
Question #32
Which technology can create a filter for an embedded packet capture?
- AControl plane policing
- BAccess lists
- CNBAR "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 37
- DTraffic shaping
Correct Answer:
B
A filter can be applied to limit the capture to desired traffic. Define an Access Control List (ACL) within config mode and apply the filter to the buffer: ip access-list extended BUF-FILTER permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 172.16.1.1 permit ip host 172.16.1.1 host 192.168.1.1 monitor capture buffer BUF filter access-list BUF-FILTER
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ios-nx-os-software/ios-embedded-packet- capture/116045-productconfig-epc-00.html
B
A filter can be applied to limit the capture to desired traffic. Define an Access Control List (ACL) within config mode and apply the filter to the buffer: ip access-list extended BUF-FILTER permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 172.16.1.1 permit ip host 172.16.1.1 host 192.168.1.1 monitor capture buffer BUF filter access-list BUF-FILTER
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ios-nx-os-software/ios-embedded-packet- capture/116045-productconfig-epc-00.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #33
Which option describes a limitation of Embedded Packet Capture?
- AIt can capture data only on physical interfaces and subinterfaces.
- BIt can store only packet data.
- CIt can capture multicast packets only on ingress.
- DIt can capture multicast packets only on egress.
Correct Answer:
C
Restrictions for Embedded Packet Capture
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/epc/configuration/15-mt/epc-15-mt- book/nm-packet-capture.html
C
Restrictions for Embedded Packet Capture
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/epc/configuration/15-mt/epc-15-mt- book/nm-packet-capture.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #34
Refer to the exhibit.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 38
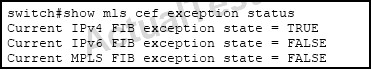
A Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch experiences high CPU utilization. What can be the cause of this issue, and how can it be prevented?
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 38

A Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch experiences high CPU utilization. What can be the cause of this issue, and how can it be prevented?
- AThe hardware routing table is full. Redistribute from BGP into IGP.
- BThe software routing table is full. Redistribute from BGP into IGP.
- CThe hardware routing table is full. Reduce the number of routes in the routing table.
- DThe software routing table is full. Reduce the number of routes in the routing table.
Correct Answer:
C
FIB TCAM Exception - If you try to install more routes than are possible into the FIB TCAM you will see the following error message in the logs:
CFIB-SP-STBY-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception, Some entries will be software switched
%CFIB-SP-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception, Some entries will be software switched. %CFIB-SP-STBY-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception,
Some entries will be software switched.
This error message is received when the amount of available space in the TCAM is exceeded. This results in high CPU. This is a FIB TCAM limitation. Once
TCAM is full, a flag will be set and FIB TCAM exception is received. This stops from adding new routes to the TCAM. Therefore, everything will be software switched. The removal of routes does not help resume hardware switching. Once the TCAM enters the exception state, the system must be reloaded to get out of that state. You can view if you have hit a FIB TCAM exception with the following command:
6500-2#sh mls cef exception status
Current IPv4 FIB exception state = TRUE
Current IPv6 FIB exception state = FALSE
Current MPLS FIB exception state = FALSE
When the exception state is TRUE, the FIB TCAM has hit an exception.
The maximum routes that can be installed in TCAM is increased by the mls cef maximum-routes command.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 39
: https://supportforums.cisco.com/document/59926/troubleshooting-high-cpu-6500-sup720
C
FIB TCAM Exception - If you try to install more routes than are possible into the FIB TCAM you will see the following error message in the logs:
CFIB-SP-STBY-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception, Some entries will be software switched
%CFIB-SP-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception, Some entries will be software switched. %CFIB-SP-STBY-7-CFIB_EXCEPTION : FIB TCAM exception,
Some entries will be software switched.
This error message is received when the amount of available space in the TCAM is exceeded. This results in high CPU. This is a FIB TCAM limitation. Once
TCAM is full, a flag will be set and FIB TCAM exception is received. This stops from adding new routes to the TCAM. Therefore, everything will be software switched. The removal of routes does not help resume hardware switching. Once the TCAM enters the exception state, the system must be reloaded to get out of that state. You can view if you have hit a FIB TCAM exception with the following command:
6500-2#sh mls cef exception status
Current IPv4 FIB exception state = TRUE
Current IPv6 FIB exception state = FALSE
Current MPLS FIB exception state = FALSE
When the exception state is TRUE, the FIB TCAM has hit an exception.
The maximum routes that can be installed in TCAM is increased by the mls cef maximum-routes command.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 39
: https://supportforums.cisco.com/document/59926/troubleshooting-high-cpu-6500-sup720
send
light_mode
delete
Question #35
Refer to the exhibit.
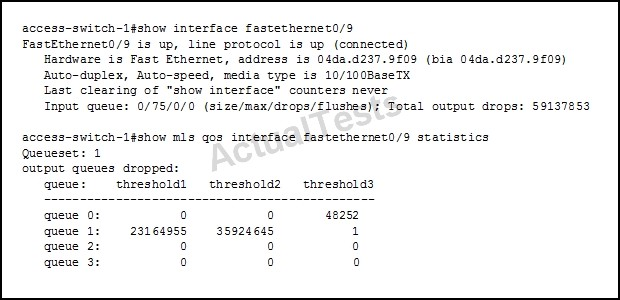
Your network is suffering excessive output drops. Which two actions can you take to resolve the problem? (Choose two.)

Your network is suffering excessive output drops. Which two actions can you take to resolve the problem? (Choose two.)
- AInstall a switch with larger buffers.
- BConfigure a different queue set.
- CReconfigure the switch buffers.
- DConfigure the server application to use TCP.
- EUpdate the server operating system.
Correct Answer:
AB
Installing a switch with larger buffers and correctly configuring the buffers can solve output queue problems.
For each queue we need to configure the assigned buffers. The buffer is like the `storage' space for the interface and we have to divide it among the different queues. This is how to do it: mls qos queue-set output <queue set> buffers Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
In this example, there is nothing hitting queue 2 or queue 3 so they are not being utilized.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 40
AB
Installing a switch with larger buffers and correctly configuring the buffers can solve output queue problems.
For each queue we need to configure the assigned buffers. The buffer is like the `storage' space for the interface and we have to divide it among the different queues. This is how to do it: mls qos queue-set output <queue set> buffers Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
In this example, there is nothing hitting queue 2 or queue 3 so they are not being utilized.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 40
send
light_mode
delete
Question #36
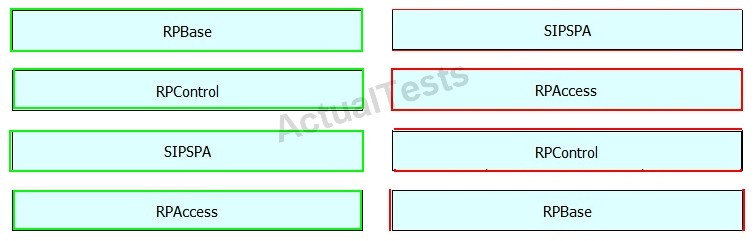
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the Cisco IOS XE subpackage on the left to the function it performs on the right.
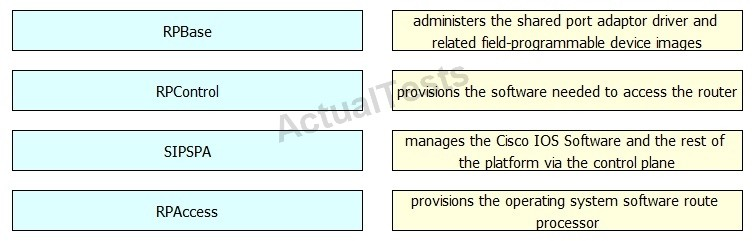
A.
B.
C.
D.
Drag and drop the Cisco IOS XE subpackage on the left to the function it performs on the right.

A.
B.
C.
D.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #37
Which two Cisco IOS XE commands can install a subpackage onto a router? (Choose two.)
- Arequest platform software package install rp rpSlotNumber file fileURL
- Bboot system flash bootflash:filename
- Ccopy sourceUrl destinationUrl
- Dlicense install file storedLocationUrl
- Eissu loadversion rp identifier file diskType imageFilename
- Fconfig-register value
Correct Answer:
AC
In the following example, the request platform software package install command is used to upgrade a consolidated package running on RP 0. The force option, which forces the upgrade past any prompt (such as already having the same consolidated package installed), is used in this example.
Router# request platform software package install rp 0 file bootflash:asr1000rp1- adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122-33.XNA.bin force
To upgrade a consolidated package on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers using the copy command, copy the consolidated package into the bootflash: directory on the router using the copy command as you would on most other Cisco routers. After making this copy, configure the router to boot using the consolidated package file.
In the following example, the consolidated package file is copied onto the bootflash: file system from TFTP. The config-register is then set to boot using boot system commands, and the boot system commands instruct the router to boot using the consolidated package stored in the bootflash: file system. The new configuration is then saved using the copy running-config startup-config command, and the system is then reloaded to complete the process.
Router# dir bootflash:
Directory of bootflash:/
11 drwx 16384 Dec 4 2007 04:32:46 -08:00 lost+found
86401 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 06:06:24 -08:00.ssh
14401 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 06:06:36 -08:00.rollback_timer
28801 drwx 4096 Mar 18 2008 17:31:17 -07:00.prst_sync
43201 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 04:34:45 -08:00.installer
13 -rw- 45977 Apr 9 2008 16:48:46 -07:00 target_support_output.tgz.tgz
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 42
928862208 bytes total (712273920 bytes free)
Router# copy tftp bootflash:
Address or name of remote host []? 172.17.16.81
Source filename []? /auto/tftp-users/user/asr1000rp1-adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122- 33.XNA.bin
Destination filename [asr1000rp1-adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122-33.XNA.bin]?
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr1000/configuration/guide/chassis/asrswcfg/Packa ge_Management.html#78189
AC
In the following example, the request platform software package install command is used to upgrade a consolidated package running on RP 0. The force option, which forces the upgrade past any prompt (such as already having the same consolidated package installed), is used in this example.
Router# request platform software package install rp 0 file bootflash:asr1000rp1- adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122-33.XNA.bin force
To upgrade a consolidated package on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers using the copy command, copy the consolidated package into the bootflash: directory on the router using the copy command as you would on most other Cisco routers. After making this copy, configure the router to boot using the consolidated package file.
In the following example, the consolidated package file is copied onto the bootflash: file system from TFTP. The config-register is then set to boot using boot system commands, and the boot system commands instruct the router to boot using the consolidated package stored in the bootflash: file system. The new configuration is then saved using the copy running-config startup-config command, and the system is then reloaded to complete the process.
Router# dir bootflash:
Directory of bootflash:/
11 drwx 16384 Dec 4 2007 04:32:46 -08:00 lost+found
86401 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 06:06:24 -08:00.ssh
14401 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 06:06:36 -08:00.rollback_timer
28801 drwx 4096 Mar 18 2008 17:31:17 -07:00.prst_sync
43201 drwx 4096 Dec 4 2007 04:34:45 -08:00.installer
13 -rw- 45977 Apr 9 2008 16:48:46 -07:00 target_support_output.tgz.tgz
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 42
928862208 bytes total (712273920 bytes free)
Router# copy tftp bootflash:
Address or name of remote host []? 172.17.16.81
Source filename []? /auto/tftp-users/user/asr1000rp1-adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122- 33.XNA.bin
Destination filename [asr1000rp1-adventerprisek9.02.01.00.122-33.XNA.bin]?
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr1000/configuration/guide/chassis/asrswcfg/Packa ge_Management.html#78189
send
light_mode
delete
Question #38
Which two statements about Cisco Express Forwarding are true? (Choose two.)
- ACisco Express Forwarding tables contain reachability information and adjacency tables contain forwarding information.
- BCisco Express Forwarding tables contain forwarding information and adjacency tables contain reachability information.
- CChanging MAC header rewrite strings requires cache validation.
- DAdjacency tables and Cisco Express Forwarding tables can be built separately.
- EAdjacency tables and Cisco Express Forwarding tables require packet process-switching.
Correct Answer:
AD
Main Components of CEF -
Information conventionally stored in a route cache is stored in several data structures for Cisco Express Forwarding switching. The data structures provide optimized lookup for efficient packet forwarding. The two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding operation are the forwarding information base (FIB) and the adjacency tables.
The FIB is conceptually similar to a routing table or information base. A router uses this lookup table to make destination-based switching decisions during Cisco
Express Forwarding operation. The FIB is updated when changes occur in the network and contains all routes known at the time.
Adjacency tables maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries.
This separation of the reachability information (in the Cisco Express Forwarding table) and the forwarding information (in the adjacency table), provides a number of benefits:
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipswitch_cef/configuration/15-mt/isw- cef-15-mt-book/isw-cef-overview.html
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 43
AD
Main Components of CEF -
Information conventionally stored in a route cache is stored in several data structures for Cisco Express Forwarding switching. The data structures provide optimized lookup for efficient packet forwarding. The two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding operation are the forwarding information base (FIB) and the adjacency tables.
The FIB is conceptually similar to a routing table or information base. A router uses this lookup table to make destination-based switching decisions during Cisco
Express Forwarding operation. The FIB is updated when changes occur in the network and contains all routes known at the time.
Adjacency tables maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries.
This separation of the reachability information (in the Cisco Express Forwarding table) and the forwarding information (in the adjacency table), provides a number of benefits:
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipswitch_cef/configuration/15-mt/isw- cef-15-mt-book/isw-cef-overview.html
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 43
send
light_mode
delete
Question #39
Which TCP feature allows a client to request a specific packet that was lost?
- Aflow control
- Bsliding window
- Cfast recovery
- Dselective acknowledgment
Correct Answer:
D
The TCP Selective Acknowledgment feature improves performance if multiple packets are lost from one TCP window of data.
Prior to this feature, because of limited information available from cumulative acknowledgments, a TCP sender could learn about only one lost packet per-round- trip time. An aggressive sender could choose to resend packets early, but such re-sent segments might have already been successfully received.
The TCP selective acknowledgment mechanism helps improve performance. The receiving TCP host returns selective acknowledgment packets to the sender, informing the sender of data that has been received. In other words, the receiver can acknowledge packets received out of order. The sender can then resend only missing data segments (instead of everything since the first missing packet).
Prior to selective acknowledgment, if TCP lost packets 4 and 7 out of an 8-packet window, TCP would receive acknowledgment of only packets 1, 2, and 3.
Packets 4 through 8 would need to be re-sent. With selective acknowledgment, TCP receives acknowledgment of packets 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 8. Only packets 4 and
7 must be re-sent.
TCP selective acknowledgment is used only when multiple packets are dropped within one TCP window. There is no performance impact when the feature is enabled but not used. Use the ip tcp selective-ack command in global configuration mode to enable TCP selective acknowledgment.
Refer to RFC 2018 for more details about TCP selective acknowledgment.
D
The TCP Selective Acknowledgment feature improves performance if multiple packets are lost from one TCP window of data.
Prior to this feature, because of limited information available from cumulative acknowledgments, a TCP sender could learn about only one lost packet per-round- trip time. An aggressive sender could choose to resend packets early, but such re-sent segments might have already been successfully received.
The TCP selective acknowledgment mechanism helps improve performance. The receiving TCP host returns selective acknowledgment packets to the sender, informing the sender of data that has been received. In other words, the receiver can acknowledge packets received out of order. The sender can then resend only missing data segments (instead of everything since the first missing packet).
Prior to selective acknowledgment, if TCP lost packets 4 and 7 out of an 8-packet window, TCP would receive acknowledgment of only packets 1, 2, and 3.
Packets 4 through 8 would need to be re-sent. With selective acknowledgment, TCP receives acknowledgment of packets 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 8. Only packets 4 and
7 must be re-sent.
TCP selective acknowledgment is used only when multiple packets are dropped within one TCP window. There is no performance impact when the feature is enabled but not used. Use the ip tcp selective-ack command in global configuration mode to enable TCP selective acknowledgment.
Refer to RFC 2018 for more details about TCP selective acknowledgment.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #40
Which two solutions can reduce UDP latency? (Choose two.)
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 44
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 44
- Afast retransmission
- Bfast recovery
- Cfast start
- Dlow-latency queuing
- EIP service level agreements
- Fcongestion-avoidance algorithm
Correct Answer:
DE
IP SLA uses active traffic monitoring, which generates traffic in a continuous, reliable, and predictable manner to measure network performance. IP SLA sends data across the network to measure performance between multiple network locations or across multiple network paths. It simulates network data and IP services, and collects network performance information in real time.
This information is collected:
LLQ uses the priority command. The priority command allows you to set up classes based on a variety of criteria (not just User Datagram Ports (UDP) ports) and assign priority to them, and is available for use on serial interfaces and ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). A similar command, the ip rtp priority command, allows you to stipulate priority flows based only on UDP port numbers.
Note: All the other answer choices can be used to improve TCP performance, but not UDP.
References:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/xr12000/software/xr12k_r4-
2/system_monitoring/configuration/guide/b_sysmon_cg42xr12k/b_sysmon_cg42xr12k_chapter_01 1.html http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/fsllq26.html
DE
IP SLA uses active traffic monitoring, which generates traffic in a continuous, reliable, and predictable manner to measure network performance. IP SLA sends data across the network to measure performance between multiple network locations or across multiple network paths. It simulates network data and IP services, and collects network performance information in real time.
This information is collected:
LLQ uses the priority command. The priority command allows you to set up classes based on a variety of criteria (not just User Datagram Ports (UDP) ports) and assign priority to them, and is available for use on serial interfaces and ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). A similar command, the ip rtp priority command, allows you to stipulate priority flows based only on UDP port numbers.
Note: All the other answer choices can be used to improve TCP performance, but not UDP.
References:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/xr12000/software/xr12k_r4-
2/system_monitoring/configuration/guide/b_sysmon_cg42xr12k/b_sysmon_cg42xr12k_chapter_01 1.html http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/fsllq26.html
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages