Cisco® 350-601 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (526 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
The engineer must configure SPAN on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch to get a capture of the traffic from these applications for an in-depth packet analysis.
Which two SPAN characteristics must be considered? (Choose two.)
Which two SPAN characteristics must be considered? (Choose two.)
- ASPAN source ports can be monitored in multiple SPAN sessions.
- BThe Ethernet, FC, vFC, port channel, SAN port channel can be used as SPAN source ports.Most Voted
- CA SPAN source port cannot be a destination SPAN port.Most Voted
- DOnly Ethernet, FC, vFC, port channel port types can be used as SPAN source ports.
- EThe rx/tx option is available for VLAN or VSAN SPAN sessions.
Correct Answer:
BC
A source port, also called a monitored port, is a switched interface that you monitor for network traffic analysis. The switch supports any number of ingress source ports (up to the maximum number of available ports on the switch) and any number of source VLANs or VSANs.
A source port has these characteristics:
✑ Can be of any port type: Ethernet, Fibre Channel, virtual Fibre Channel, port channel, SAN port channel, VLAN, and VSAN.
Cannot be monitored in multiple SPAN sessions.

✑ Cannot be a destination port.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli_rel_4_1/
Cisco_Nexus_5000_Series_Switch_CLI_Software_Configuration_Guide_chapter50.html
BC
A source port, also called a monitored port, is a switched interface that you monitor for network traffic analysis. The switch supports any number of ingress source ports (up to the maximum number of available ports on the switch) and any number of source VLANs or VSANs.
A source port has these characteristics:
✑ Can be of any port type: Ethernet, Fibre Channel, virtual Fibre Channel, port channel, SAN port channel, VLAN, and VSAN.
Cannot be monitored in multiple SPAN sessions.

✑ Cannot be a destination port.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli_rel_4_1/
Cisco_Nexus_5000_Series_Switch_CLI_Software_Configuration_Guide_chapter50.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Host1 is in VLAN100 located in DataCenter1 and Host2 is in VLAN200 located in DataCenter2.
Which OTV VLAN mapping configuration allows Layer 2 connectivity between these two hosts?
A.

B.

C.

D.

Which OTV VLAN mapping configuration allows Layer 2 connectivity between these two hosts?
A.

B.

C.

D.

Correct Answer:
B
You can map a VLAN on the local site to a VLAN with a different VLAN ID on the remote site. When you map two VLANs with different VLAN IDs across sites, they get mapped to a common VLAN called the transport VLAN. For example, when you map VLAN 1 on Site A to VLAN 2 on Site B, both VLANs are mapped to a transport VLAN. All traffic originating from VLAN 1 on Site A is translated as going from the transport VLAN. All traffic arriving at Site B from the transport VLAN is translated to VLAN 2.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/nexus-7000-series-switches/200998-Nexus-7000-OTV-VLAN-Mapping-on-Overlay.html? dtid=osscdc000283
B
You can map a VLAN on the local site to a VLAN with a different VLAN ID on the remote site. When you map two VLANs with different VLAN IDs across sites, they get mapped to a common VLAN called the transport VLAN. For example, when you map VLAN 1 on Site A to VLAN 2 on Site B, both VLANs are mapped to a transport VLAN. All traffic originating from VLAN 1 on Site A is translated as going from the transport VLAN. All traffic arriving at Site B from the transport VLAN is translated to VLAN 2.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/nexus-7000-series-switches/200998-Nexus-7000-OTV-VLAN-Mapping-on-Overlay.html? dtid=osscdc000283
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
Refer to the exhibit.

What is configured as a result of running these commands?

What is configured as a result of running these commands?
- Aloose unicast RPF
- Bstrict unicast RPF
- CIP Source Guard
- Dreverse lookup for outbound packets
Correct Answer:
B
The ג€ip verify unicast source reachable-via rxג€ command enables Unicast RPF in strict mode. To enable loose mode, administrators can use the any option to enforce the requirement that the source IP address for a packet must appear in the routing table.
Reference:
https://www.examtopics.com/discussions/cisco/view/62014-exam-350-601-topic-1-question-13-discussion/
B
The ג€ip verify unicast source reachable-via rxג€ command enables Unicast RPF in strict mode. To enable loose mode, administrators can use the any option to enforce the requirement that the source IP address for a packet must appear in the routing table.
Reference:
https://www.examtopics.com/discussions/cisco/view/62014-exam-350-601-topic-1-question-13-discussion/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
Which configuration implements static ingress replication?
A.

B.

C.

D.

A.

B.

C.

D.

Correct Answer:
D
The following enables static ingress replication for peers.
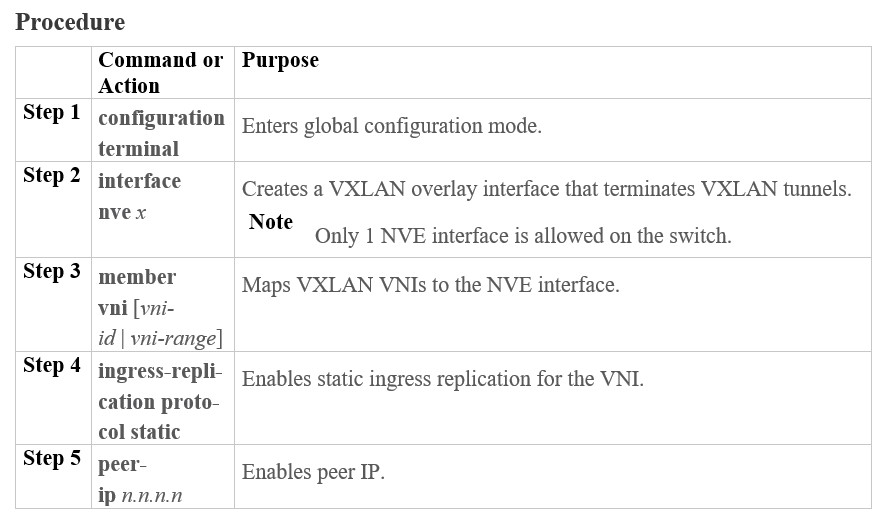
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus9000/sw/7-x/vxlan/configuration/guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-
OS_VXLAN_Configuration_Guide_7x/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_VXLAN_Configuration_Guide_7x_chapter_011.html
D
The following enables static ingress replication for peers.

Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus9000/sw/7-x/vxlan/configuration/guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-
OS_VXLAN_Configuration_Guide_7x/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_VXLAN_Configuration_Guide_7x_chapter_011.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
Refer to the exhibit.
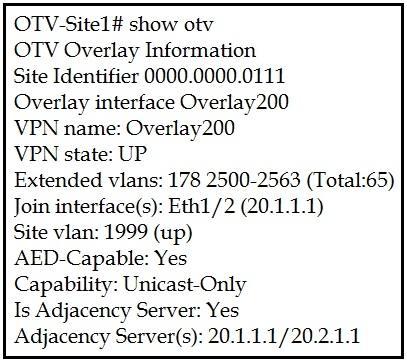
A network engineer is setting up a multihomed OTV network. The first site has been set up with a primary and secondary adjacency server.
Which configuration must be added on the remote OTV AEDs site?
A.

B.

C.

D.


A network engineer is setting up a multihomed OTV network. The first site has been set up with a primary and secondary adjacency server.
Which configuration must be added on the remote OTV AEDs site?
A.

B.

C.

D.

Correct Answer:
C
We need to add both IP's for the primary and secondary adjacency server when using a unicast only design.
C
We need to add both IP's for the primary and secondary adjacency server when using a unicast only design.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #16
A customer has a requirement to deploy a cloud service and needs to have full control over the underlying OS, data and applications.
Which cloud model meets this requirement?
Which cloud model meets this requirement?
- AMaaS
- BPaaS
- CSaaS
- DIaaS
Correct Answer:
D
Traditional IT is responsible for Application, Data, Runtime, Middleware, OS, Virtualization, Servers, Storage, Networking.
IaaS = Infrastructure as a Service ג€" The customer is responsible for OS, Virtualization, Servers, Storage, Networking.
SaaS = Software as a Service - The software is deployed by the cloud provider ג€" Customer is responsible for nothing.
PaaS = Platform as a Service - Software can be deployed by the customer building their own application | is responsible for Data and Application.
D
Traditional IT is responsible for Application, Data, Runtime, Middleware, OS, Virtualization, Servers, Storage, Networking.
IaaS = Infrastructure as a Service ג€" The customer is responsible for OS, Virtualization, Servers, Storage, Networking.
SaaS = Software as a Service - The software is deployed by the cloud provider ג€" Customer is responsible for nothing.
PaaS = Platform as a Service - Software can be deployed by the customer building their own application | is responsible for Data and Application.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
Refer to the exhibit.

A flapping link issue has been reported on the vPC keepalive link. A packet capture has been activated on the Cisco Nexus switch.
What is the destination IP address of the vPC keepalive packets that are sent by the switch?

A flapping link issue has been reported on the vPC keepalive link. A packet capture has been activated on the Cisco Nexus switch.
What is the destination IP address of the vPC keepalive packets that are sent by the switch?
- A192.168.254.4Most Voted
- B192.168.254.1
- C192.168.254.2
- D239.255.70.83
Correct Answer:
A
3200 is the default UDP port for keepalive packets. Just look for the first line with port 3200 and note the destination IP, which is 192.168.254.4.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus3000/sw/interfaces/92x/b-cisco-nexus-3000-nx-os-interfaces-configuration-guide-
92x/b-cisco-nexus-3000-nx-os-interfaces-configuration-guide-92x_chapter_0110.html
A
3200 is the default UDP port for keepalive packets. Just look for the first line with port 3200 and note the destination IP, which is 192.168.254.4.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus3000/sw/interfaces/92x/b-cisco-nexus-3000-nx-os-interfaces-configuration-guide-
92x/b-cisco-nexus-3000-nx-os-interfaces-configuration-guide-92x_chapter_0110.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
Due to a major version change, an engineer must perform a software upgrade on a Cisco Nexus Series switch.
Which two technologies should be implemented to reduce disruptions to the network during the upgrade? (Choose two.)
Which two technologies should be implemented to reduce disruptions to the network during the upgrade? (Choose two.)
- AvPCMost Voted
- BHSRPMost Voted
- CVDC
- DMLAG
- EPAgP
Correct Answer:
AB
vPC leverages both hardware and software redundancy aspects:
ג— vPC uses all port-channel member links available so that in case an individual link fails, hashing algorithm will redirect all flows to the remaining links.
ג— vPC domain is composed of two peer devices. Each peer device processes half of the traffic coming from the access layer. In case a peer device fails, the other peer device will absorb all the traffic with minimal convergence time impact.
Best Practices for HSRP/VRRP and vPC
This section describes best practices for using HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) or VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) with vPC.
HSRP/VRRP active/active with vPC
ג€¢ HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) and VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) are both network protocols that provides high availability for servers IP default gateway.
ג€¢ vPC domain at aggregation layer usually performs L2/L3 boundary so each vPC peer device is configure with interface VLAN (or SVI) and HSRP or VRRP runs on top of this interface.
ג€¢ HSRP and VRRP in the context of vPC have been improved from a functional and implementation standpoint to take full benefits of the L2 dual-active peer devices nature offered by vPC technology.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/design/vpc_design/vpc_best_practices_design_guide.pdf
AB
vPC leverages both hardware and software redundancy aspects:
ג— vPC uses all port-channel member links available so that in case an individual link fails, hashing algorithm will redirect all flows to the remaining links.
ג— vPC domain is composed of two peer devices. Each peer device processes half of the traffic coming from the access layer. In case a peer device fails, the other peer device will absorb all the traffic with minimal convergence time impact.
Best Practices for HSRP/VRRP and vPC
This section describes best practices for using HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) or VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) with vPC.
HSRP/VRRP active/active with vPC
ג€¢ HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) and VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) are both network protocols that provides high availability for servers IP default gateway.
ג€¢ vPC domain at aggregation layer usually performs L2/L3 boundary so each vPC peer device is configure with interface VLAN (or SVI) and HSRP or VRRP runs on top of this interface.
ג€¢ HSRP and VRRP in the context of vPC have been improved from a functional and implementation standpoint to take full benefits of the L2 dual-active peer devices nature offered by vPC technology.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/design/vpc_design/vpc_best_practices_design_guide.pdf
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
Refer to the exhibit.

What is the result of running the command presented?

What is the result of running the command presented?
- AMulticast traffic forwarding is suspended.
- BMRIB is flushed.
- CThe PIM database is deleted.Most Voted
- DPIM join messages are suspended.
Correct Answer:
C
When you restart PIM, the following tasks are performed:
✑ The PIM database is deleted.
✑ The MRIB and MFIB are unaffected and forwarding of traffic continues.
✑ The multicast route ownership is verified through the MRIB.
✑ Periodic PIM join and prune messages from neighbors are used to repopulate the database.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus9000/sw/6-x/multicast/configuration/guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-
OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide_chapter_011.html
C
When you restart PIM, the following tasks are performed:
✑ The PIM database is deleted.
✑ The MRIB and MFIB are unaffected and forwarding of traffic continues.
✑ The multicast route ownership is verified through the MRIB.
✑ Periodic PIM join and prune messages from neighbors are used to repopulate the database.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus9000/sw/6-x/multicast/configuration/guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-
OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide_chapter_011.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
Refer to the exhibit.
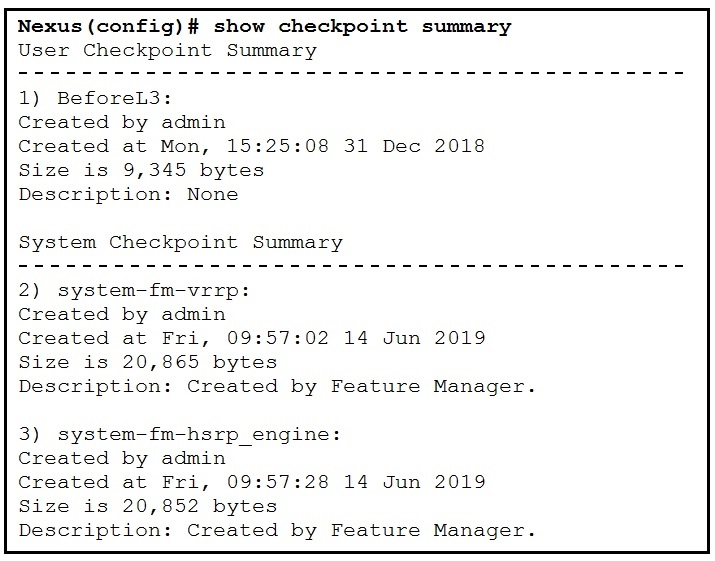
What is the reason the system-fm-vrrp checkpoint was created?

What is the reason the system-fm-vrrp checkpoint was created?
- AThe VRRP process crashed and the checkpoint was automatically created.
- BThe VRRP service restarted and the checkpoint was automatically created.
- CThe network administrator manually created it.
- DThe VRRP-enabled feature has been disabled.Most Voted
Correct Answer:
D
Reasons that could trigger automated system checkpoints are highlighted below:
✑ License expiration of a feature
✑ Disabling a feature with the no feature command
✑ Removing an instance of a Layer 3 protocol
The system-generated checkpoint name convention has the format system-fm-feature. To help illustrate this automated feature we attempted to disable the VRRP feature on our Nexus 5000 therefore triggering the system to create a checkpoint. First we confirm the VRRP feature is enabled by issuing the show feature | include vrrp command then disable it and then verify it has been disabled:
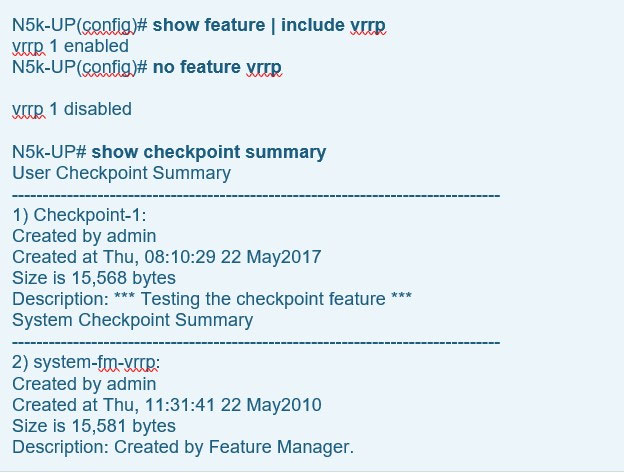
Notice that the system now shows a second checkpoint system-fm-vrrp which did not previously exist. This second checkpoint was created automatically by the
Nexus as soon as we disabled the vrrp feature.
Reference:
https://www.firewall.cx/cisco-technical-knowledgebase/cisco-data-center/1202-cisco-nexus-checkpoint-rollback-feature.html
D
Reasons that could trigger automated system checkpoints are highlighted below:
✑ License expiration of a feature
✑ Disabling a feature with the no feature command
✑ Removing an instance of a Layer 3 protocol
The system-generated checkpoint name convention has the format system-fm-feature. To help illustrate this automated feature we attempted to disable the VRRP feature on our Nexus 5000 therefore triggering the system to create a checkpoint. First we confirm the VRRP feature is enabled by issuing the show feature | include vrrp command then disable it and then verify it has been disabled:

Notice that the system now shows a second checkpoint system-fm-vrrp which did not previously exist. This second checkpoint was created automatically by the
Nexus as soon as we disabled the vrrp feature.
Reference:
https://www.firewall.cx/cisco-technical-knowledgebase/cisco-data-center/1202-cisco-nexus-checkpoint-rollback-feature.html
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
