Cisco® 200-310 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (776 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #41
DRAG DROP -
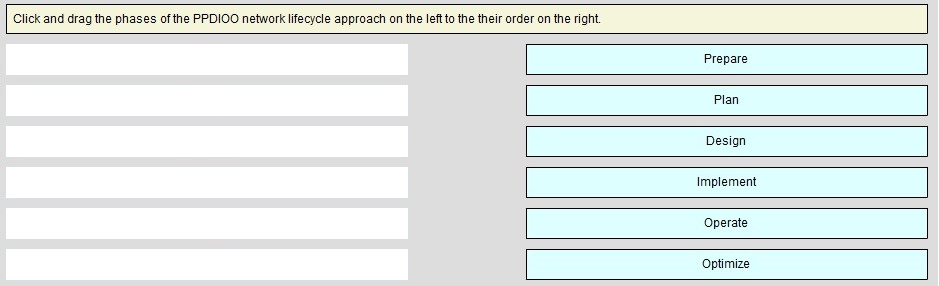
Click and drag the phases of the PPDIOO network lifecycle approach on the left to their order on the right.
Select and Place:

Click and drag the phases of the PPDIOO network lifecycle approach on the left to their order on the right.
Select and Place:

send
light_mode
delete
Question #42
Characterizing an existing network requires gathering as much information about the network as possible. Which of these choices describes the preferred order for the information-gathering process?
- Asite and network audits, traffic analysis, existing documentation and organizational input
- Bexisting documentation and organizational input, site and network audits, traffic analysis
- Ctraffic analysis, existing documentation and organizational input, site and network audits
- Dsite and network audits, existing documentation and organizational input, traffic analysis
Correct Answer:
B
This section describes the steps necessary to characterize the existing network infrastructure and all sites. This process requires three steps:
Step 1. Gather existing documentation about the network, and query the organization to discover additional information. Organization input, a network audit, and traffic analysis provide the key information you need. (Note that existing documentation may be inaccurate.)
Step 2. Perform a network audit that adds detail to the description of the network. If possible, use traffic-analysis information to augment organizational input when you are describing the applications and protocols used in the network.
Step 3. Based on your network characterization, write a summary report that describes the health of the network. With this information, you can propose hardware and software upgrades to support the network requirements and the organizational requirements.
B
This section describes the steps necessary to characterize the existing network infrastructure and all sites. This process requires three steps:
Step 1. Gather existing documentation about the network, and query the organization to discover additional information. Organization input, a network audit, and traffic analysis provide the key information you need. (Note that existing documentation may be inaccurate.)
Step 2. Perform a network audit that adds detail to the description of the network. If possible, use traffic-analysis information to augment organizational input when you are describing the applications and protocols used in the network.
Step 3. Based on your network characterization, write a summary report that describes the health of the network. With this information, you can propose hardware and software upgrades to support the network requirements and the organizational requirements.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #43
Which three terms describe the primary functions of the distribution layer of the campus network design hierarchy? (Choose three.)
- Aprovides end-user connectivity
- Bprovides high speed transport
- Cprovides QoS services
- Denforces security policies
- Eprovides WAN connections
- Fconnects access devices to the core backbone
Correct Answer:
CDF
Link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/campover.html#wp708979
CDF
Link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/campover.html#wp708979
send
light_mode
delete
Question #44
Refer to the exhibit.
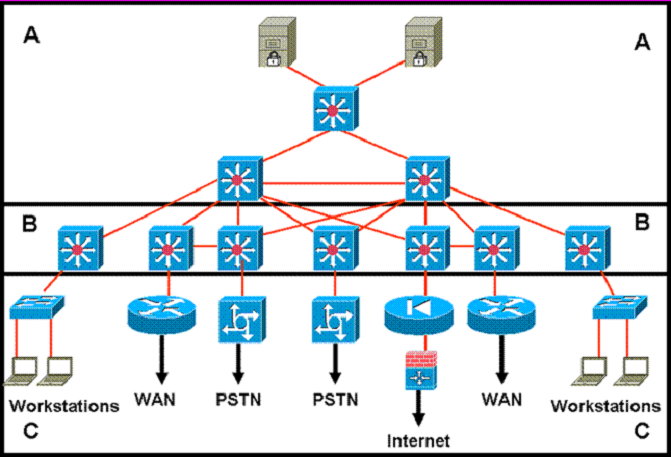
Which statement accurately represents the characteristics of the core layer in this design?

Which statement accurately represents the characteristics of the core layer in this design?
- AQoS should only be performed only in the core.
- BLoad balancing should never be implemented or used.
- CAccess lists should be used in the core to perform packet manipulation.
- DPartial mesh should be used as long as it is connected to each device by multiple paths.
- EPolicy-based traffic control should be implemented to enable prioritization and ensure the best performance for all time-critical applications. D
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Explanation
send
light_mode
delete
Question #45
Which two of the following are benefits of using a modular approach to network design? (Choose two.)
- Aimproves flexibility
- Bfacilitates implementation
- Clowers implementation costs
- Dimproves customer participation in the design process
Correct Answer:
AB
AB
send
light_mode
delete
Question #46
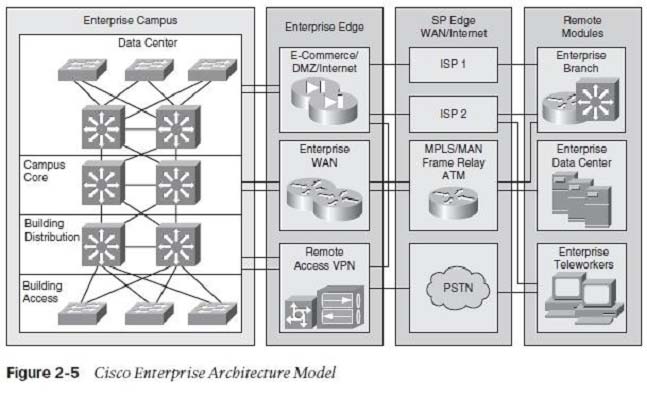
Which three modular components are part of the Cisco Enterprise Edge Architecture? (Choose three.)
- Ae-commerce module
- BInternet connectivity module
- Cserver farm module
- Dremote access and VPN module
- EPSTN services module
- Fenterprise branch module
- Gbuilding distribution module
Correct Answer:
ABD
ABD

send
light_mode
delete
Question #47
Which of the following is a component within the Cisco Enterprise Campus module?
- ATeleworker
- BE-Commerce
- CInternet Connectivity
- DBuilding Distribution
- EWAN/MAN Site-to-Site VPN
Correct Answer:
D
D
send
light_mode
delete
Question #48
What are the three primary functions of the distribution layer of the campus network design hierarchy? (Choose three.)
- Aprovide end-user connectivity
- Bprovide high speed transport
- Cprovide QoS services
- Denforce security policies
- Eprovide WAN connections
- Fconnect access devices to the core backbone
Correct Answer:
CDF
CDF
send
light_mode
delete
Question #49
DRAG DROP -
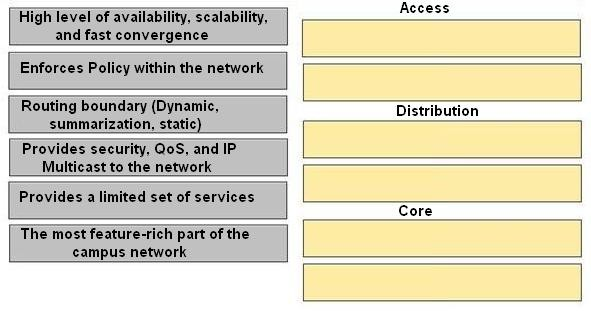
Drag the characteristics of the traditional campus network on the left to the most appropriate hierarchical network layer on the right.
Select and Place:
Drag the characteristics of the traditional campus network on the left to the most appropriate hierarchical network layer on the right.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
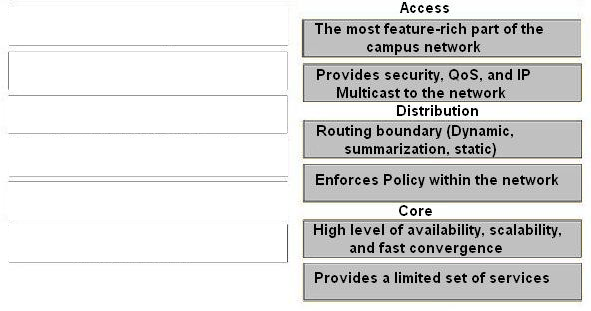
Access -
✑ The most feature-rich part of the campus network
✑ Provides security, QoS, and IP Multicast to the network
Distribution -
✑ Routing boundary (Dynamic, summarization, static)
✑ Enforces Policy within the network
Core -
✑ High level of availability, scalability, and fast convergence
✑ Provides a limited set of services
Large-Building LANs -
Large-building LANs are segmented by floors or departments. The building-access component serves one or more departments or floors. The building-distribution component serves one or more building-access components. Campus and building backbone devices connect the data center, building-distribution components, and the enterprise edge-distribution component. The access layer typically uses Layer 2 switches to contain costs, with more expensive Layer 3 switches in the distribution layer to provide policy enforcement. Current best practice is to also deploy multilayer switches in the campus and building backbone.
Cisco Enterprise Architecture Model
Core -
✑ Fast transport
✑ High reliability
✑ Redundancy
✑ Fault tolerance
✑ Low latency and good manageability
✑ Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes
✑ Limited and consistent diameter
✑ Quality of service (QoS)
Distribution -
✑ Policy-based connectivity
✑ Redundancy and load balancing
✑ Aggregation of LAN wiring closets
✑ Aggregation of WAN connections
✑ QoS
✑ Security filtering
✑ Address or area aggregation or summarization
✑ Departmental or workgroup access
✑ Broadcast or multicast domain definition
✑ Routing between virtual LANs (VLAN)
✑ Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)
✑ Redistribution between routing domains (for example, between two different routing protocols)
✑ Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols
Access -
✑ Layer 2 switching
✑ High availability
✑ Port security
✑ Broadcast suppression
✑ QoS
✑ Rate limiting
✑ Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection
✑ Virtual access control lists (VACL)
✑ Spanning tree
✑ Trust classification
Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP
Cisco Press CCDA 640-864 Official Certification Guide Fourth Edition, Chapter 3

Access -
✑ The most feature-rich part of the campus network
✑ Provides security, QoS, and IP Multicast to the network
Distribution -
✑ Routing boundary (Dynamic, summarization, static)
✑ Enforces Policy within the network
Core -
✑ High level of availability, scalability, and fast convergence
✑ Provides a limited set of services
Large-Building LANs -
Large-building LANs are segmented by floors or departments. The building-access component serves one or more departments or floors. The building-distribution component serves one or more building-access components. Campus and building backbone devices connect the data center, building-distribution components, and the enterprise edge-distribution component. The access layer typically uses Layer 2 switches to contain costs, with more expensive Layer 3 switches in the distribution layer to provide policy enforcement. Current best practice is to also deploy multilayer switches in the campus and building backbone.
Cisco Enterprise Architecture Model
Core -
✑ Fast transport
✑ High reliability
✑ Redundancy
✑ Fault tolerance
✑ Low latency and good manageability
✑ Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes
✑ Limited and consistent diameter
✑ Quality of service (QoS)
Distribution -
✑ Policy-based connectivity
✑ Redundancy and load balancing
✑ Aggregation of LAN wiring closets
✑ Aggregation of WAN connections
✑ QoS
✑ Security filtering
✑ Address or area aggregation or summarization
✑ Departmental or workgroup access
✑ Broadcast or multicast domain definition
✑ Routing between virtual LANs (VLAN)
✑ Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)
✑ Redistribution between routing domains (for example, between two different routing protocols)
✑ Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols
Access -
✑ Layer 2 switching
✑ High availability
✑ Port security
✑ Broadcast suppression
✑ QoS
✑ Rate limiting
✑ Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection
✑ Virtual access control lists (VACL)
✑ Spanning tree
✑ Trust classification
Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP
Cisco Press CCDA 640-864 Official Certification Guide Fourth Edition, Chapter 3
send
light_mode
delete
Question #50
DRAG DROP -
Drag the network function on the left to the functional area or module where it is most likely to be performed in the enterprise campus infrastructure on the right.
Select and Place:
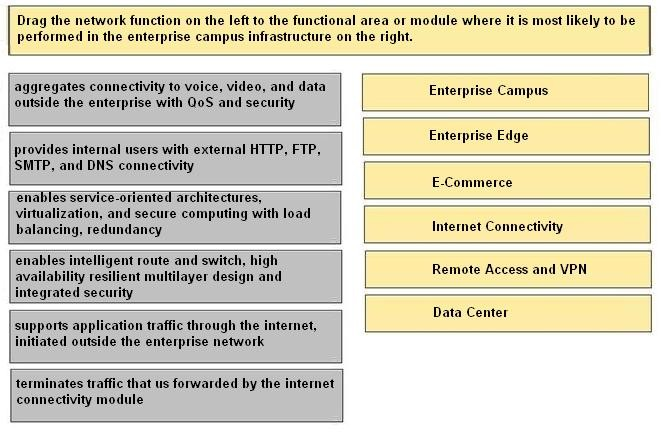
Drag the network function on the left to the functional area or module where it is most likely to be performed in the enterprise campus infrastructure on the right.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
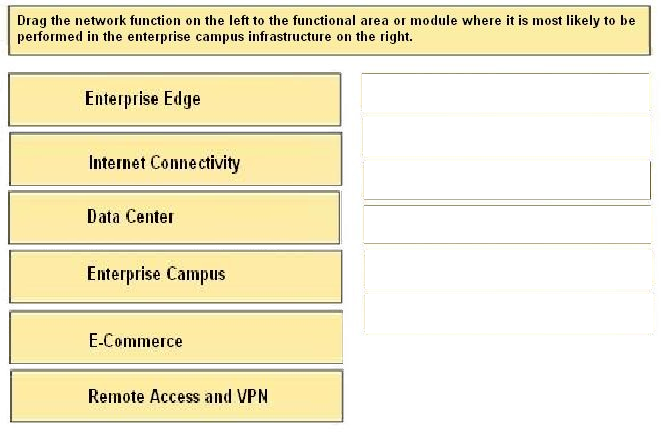
1 Enterprise Edge
2 Internet Connectivity
3 Data Center
4 Enterprise Campus
5 E-Commerce
6 Remote Access and VPN
please refer to link.
Link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/campover.html#wp708979
CCDA Study Guide: Diane Teare

1 Enterprise Edge
2 Internet Connectivity
3 Data Center
4 Enterprise Campus
5 E-Commerce
6 Remote Access and VPN
please refer to link.
Link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/campover.html#wp708979
CCDA Study Guide: Diane Teare
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages