Cisco® 200-310 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (776 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
Which four services does the architecture for Media Services contain? (Choose four.)
- Aaccess services
- Btransport services
- Cstorage services
- Dforwarding services
- Esession control services
- Fsecurity services
- Gfiltering services
- Hremote access services
Correct Answer:
ABCE
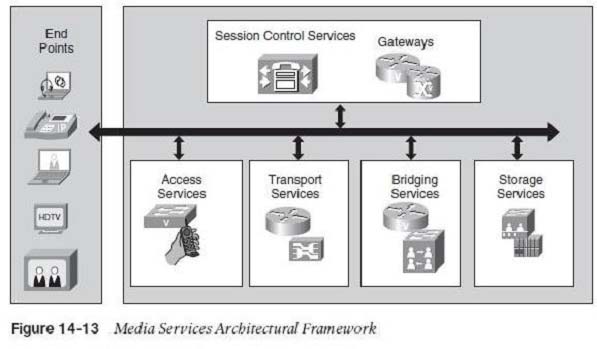
An architecture framework for media services supports different models of video models. As shown in Figure 14-13, the network provides service to video media in the Media Services Framework. Those services are access services, transport services, bridging services, storage servers, and session control services, which arc provided to endpoints.
✑ Access services provide identity of end devices, mobility, and location services.
✑ Transport services provide QoS for reliable packet delivery.
✑ Bridging services provide transcoding, conferencing, and recording services of media streams.
✑ Storage services provide capture and storage of media streams and content management and distribution.
Session control services provide session signaling and control and gateway services.

ABCE
An architecture framework for media services supports different models of video models. As shown in Figure 14-13, the network provides service to video media in the Media Services Framework. Those services are access services, transport services, bridging services, storage servers, and session control services, which arc provided to endpoints.
✑ Access services provide identity of end devices, mobility, and location services.
✑ Transport services provide QoS for reliable packet delivery.
✑ Bridging services provide transcoding, conferencing, and recording services of media streams.
✑ Storage services provide capture and storage of media streams and content management and distribution.
Session control services provide session signaling and control and gateway services.


send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Refer to the exhibit.
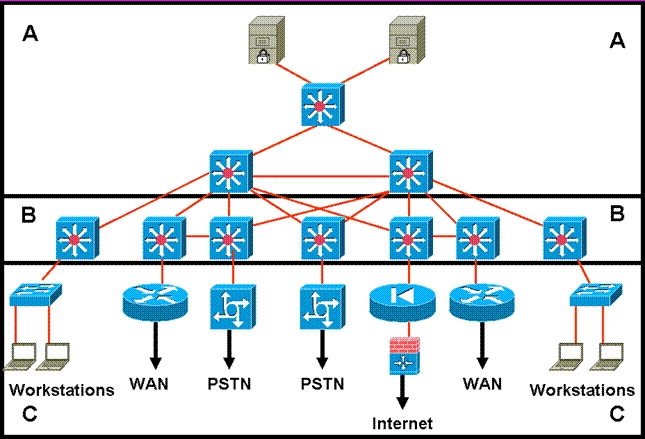
Which layer is the distribution layer?

Which layer is the distribution layer?
- ALayer A
- BLayer B
- CLayer C
- DLayers A and B form a consolidated core and distribution layer
Correct Answer:
B
B
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
Which IPv6 feature enables routing to distribute connection requests to the nearest content server?
- ALink-local
- BSite-local
- CAnycast
- DMulticast
- EGlobal aggregatable
Correct Answer:
C
Any cast is a network addressing and routing methodology in which data grams from a single sender are routed to the topologically nearest node in a group of potential receivers all identified by the same destination address.
Link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anycast
C
Any cast is a network addressing and routing methodology in which data grams from a single sender are routed to the topologically nearest node in a group of potential receivers all identified by the same destination address.
Link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anycast
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
What is the recommended spanning tree protocol to use for all Layer 2 deployments in a branch office environment?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
Refer to the exhibit.
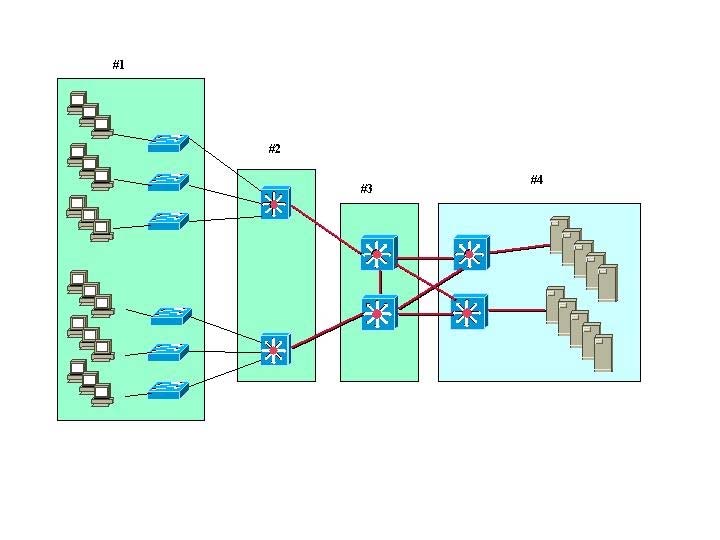
A standard, Layer 2 campus network design is pictured. Which numbered box represents the distribution layer?

A standard, Layer 2 campus network design is pictured. Which numbered box represents the distribution layer?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #16
Which two are types of network virtualization? (Choose two.)
- AVSS: Virtual Switching System
- BVRF: virtual routing and forwarding
- CVCI: virtual channel identifier
- DVLSM: variable length subnet masking
- EVM: virtual machine
- FVMP: Virtual Memory Pool
Correct Answer:
AB
Network virtualization encompasses logical isolated network segments that share the same physical infrastructure. Each segment operates independently and is logically separate from the other segments. Each network segment appears with its own privacy, security, independent set of policies, QoS levels, and independent routing paths.
Here are some examples of network virtualization technologies:
VLAN: Virtual local-area network
VSAN: Virtual storage-area network
VRF: Virtual routing and forwarding
VPN: Virtual private network
VPC: Virtual Port Channel
AB
Network virtualization encompasses logical isolated network segments that share the same physical infrastructure. Each segment operates independently and is logically separate from the other segments. Each network segment appears with its own privacy, security, independent set of policies, QoS levels, and independent routing paths.
Here are some examples of network virtualization technologies:
VLAN: Virtual local-area network
VSAN: Virtual storage-area network
VRF: Virtual routing and forwarding
VPN: Virtual private network
VPC: Virtual Port Channel
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
You are tasked with designing a new branch office that will support 75 users with possible expansion in the future and will need a highly available network. Which of the branch design profiles should be implemented?
- Alarge branch design
- Bmedium branch design
- Cteleworker design
- Dsmall branch design
Correct Answer:
B
Medium Branch Design -
The medium branch design is recommended for branch offices of 50 to 100 users, which is similar to the small branch but with an additional access router in the
WAN edge (slightly larger) allowing for redundancy services. Typically, two 2921 or 2951 routers are used to support the WAN, and separate access switches are used to provide LAN connectivity.
B
Medium Branch Design -
The medium branch design is recommended for branch offices of 50 to 100 users, which is similar to the small branch but with an additional access router in the
WAN edge (slightly larger) allowing for redundancy services. Typically, two 2921 or 2951 routers are used to support the WAN, and separate access switches are used to provide LAN connectivity.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
Which two can be used as a branch office WAN solution? (Choose two.)
- Aframe relay
- BMPLS
- CMetro Ethernet
- DGPRS
- Edial-up modem
- F3G USB modems
Correct Answer:
BC
Frame relay is old 'shared' technology today's sites use some flavor or Metro E or MPLS/VPN
BC
Frame relay is old 'shared' technology today's sites use some flavor or Metro E or MPLS/VPN
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
What is the acceptable amount of one-way network delay for voice and video applications?
- A300 bytes
- B1 sec
- C150 ms
- D500 ms
Correct Answer:
C
Delay Components in VoIP Networks
The ITU's G.I 14 recommendation specifics that the one-way delay between endpoints should not exceed 150 ms to be acceptable, commercial voice quality. In private networks, somewhat longer delays might be acceptable for economic reasons. The ITU G.114 recommendation specifics that 151-ms to 400-ms one-way delay might be acceptable provided that organizations are aware that the transmission time will affect the quality of user applications. One-way delays of above
400 ms are unacceptable for general network planning purposes.
C
Delay Components in VoIP Networks
The ITU's G.I 14 recommendation specifics that the one-way delay between endpoints should not exceed 150 ms to be acceptable, commercial voice quality. In private networks, somewhat longer delays might be acceptable for economic reasons. The ITU G.114 recommendation specifics that 151-ms to 400-ms one-way delay might be acceptable provided that organizations are aware that the transmission time will affect the quality of user applications. One-way delays of above
400 ms are unacceptable for general network planning purposes.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
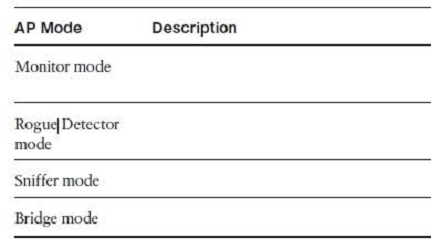
Which mode is used to exclusively look for unauthorized access points?
- Amonitor mode
- Bsniffer mode
- Crogue detector mode
- Dlocal mode
Correct Answer:
C
Interference detection and avoidance: As Cisco LWAPs monitor all channels, interference is detected by a predefined threshold (10 percent by default).
Interference can be generated by rogue APs, microwaves, cordless telephones, Bluetooth devices, neighboring WLANs, or other electronic devices.
C

Interference detection and avoidance: As Cisco LWAPs monitor all channels, interference is detected by a predefined threshold (10 percent by default).
Interference can be generated by rogue APs, microwaves, cordless telephones, Bluetooth devices, neighboring WLANs, or other electronic devices.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
