Cisco® 100-105 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (724 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which RFC was created to alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses?
- ARFC 4193
- BRFC 1519
- CRFC 1518
- DRFC 1918
Correct Answer:
D
RFC 1918 references private IP addressing schemes such as NAT. RFC 1518 simply covers the usage of CIDR, or how to use address blocks more efficiently while RFC 1918 is specifically referred to as a stopgap to avert the crisis of IPv4 addresses.
D
RFC 1918 references private IP addressing schemes such as NAT. RFC 1518 simply covers the usage of CIDR, or how to use address blocks more efficiently while RFC 1918 is specifically referred to as a stopgap to avert the crisis of IPv4 addresses.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Instructions -
For both the Router and the Switch the simulated console mode needs to start and remain in enabled mode.
RouterA and SwitchA have been configured to operate in a private network which will connect to the Internet. You have been asked to review the configuration prior to cabling and implementation.
This task requires the use of various IOS commands to access and inspect the running configuration of RouterA and SwitchA. No configuration changes are necessary.
You will connect to RouterA and SwilchA via the console devices that are attached to each.
There are 4 multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all of them before leaving this item. In order to score the maximum points you will need to have accessed both SwitchA and RouterA.
NOTE: The configuration command has been disabled for both the router and switch in this simulation.
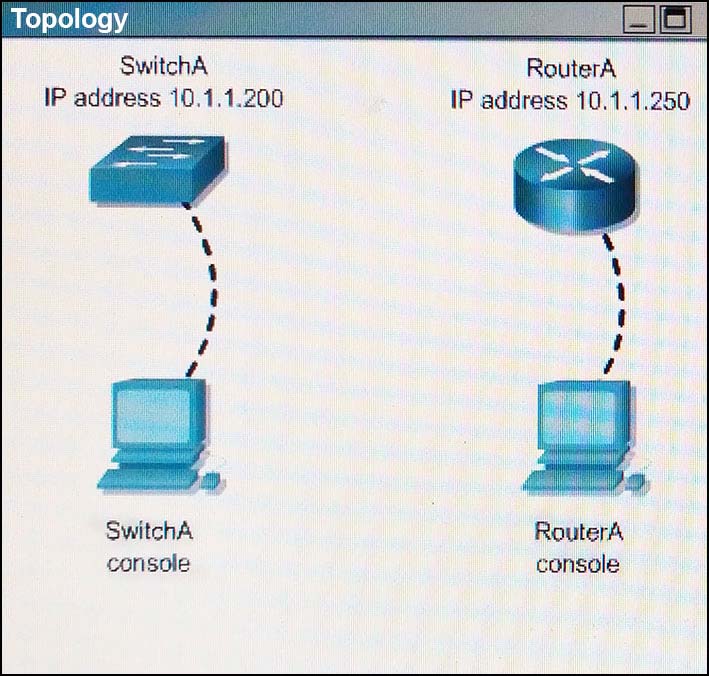
Which two of the following are true regarding the configuration of RouterA? (Choose two.)
For both the Router and the Switch the simulated console mode needs to start and remain in enabled mode.
RouterA and SwitchA have been configured to operate in a private network which will connect to the Internet. You have been asked to review the configuration prior to cabling and implementation.
This task requires the use of various IOS commands to access and inspect the running configuration of RouterA and SwitchA. No configuration changes are necessary.
You will connect to RouterA and SwilchA via the console devices that are attached to each.
There are 4 multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all of them before leaving this item. In order to score the maximum points you will need to have accessed both SwitchA and RouterA.
NOTE: The configuration command has been disabled for both the router and switch in this simulation.

Which two of the following are true regarding the configuration of RouterA? (Choose two.)
- Aat least 5 simultaneous remote connections are possible
- Bonly telnet protocol connections to RouterA are supported
- Cremote connections to RouterA using telnet will succeed
- Dconsole line connections will never time out due to inactivity
- Esince DHCP is not used on Fa0/1 there is no need to use the NAT protocol
Correct Answer:
AC
Here is the RouterA configuration:
for Router
!
!
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router1
enable secret 5 $1$14mlkm52.
ip domain-name cisco.com
ip ssh version 2
!
!
username ciscouser password 0 cisco
banner login ^c
************ welcome to router1 If you encountered any problem, please consult the administrator ************* ^c
!
line con 0
password cisco
line vty 0 4
password 4thfcvcf
no login
transport input telnet ssh
for switch
!
!
no service password-encryption
!
hostname switch1
enable password cisco
username ciscouser password 0 cisco
ip domain-name cisco.com
banner login ^c
************ welcome to router1 If you encountered any problem, please consult the administrator ************* ^c line con 0 line vty 0 4 login login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login local transport input ssh
A is correct as we can telnet from line 0 to line 4 (line vty o 4).
We can use both telnet and SSH to connect to this router (transport input telnet ssh) -> B is not correct.
C is correct as we can telnet to it.
D is not correct because by default, the timeout is set to 10 minutes on both the console and the vty ports.
E is not correct as NAT can be used even DHCP is not used.
AC
Here is the RouterA configuration:
for Router
!
!
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router1
enable secret 5 $1$14mlkm52.
ip domain-name cisco.com
ip ssh version 2
!
!
username ciscouser password 0 cisco
banner login ^c
************ welcome to router1 If you encountered any problem, please consult the administrator ************* ^c
!
line con 0
password cisco
line vty 0 4
password 4thfcvcf
no login
transport input telnet ssh
for switch
!
!
no service password-encryption
!
hostname switch1
enable password cisco
username ciscouser password 0 cisco
ip domain-name cisco.com
banner login ^c
************ welcome to router1 If you encountered any problem, please consult the administrator ************* ^c line con 0 line vty 0 4 login login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login local transport input ssh
A is correct as we can telnet from line 0 to line 4 (line vty o 4).
We can use both telnet and SSH to connect to this router (transport input telnet ssh) -> B is not correct.
C is correct as we can telnet to it.
D is not correct because by default, the timeout is set to 10 minutes on both the console and the vty ports.
E is not correct as NAT can be used even DHCP is not used.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
A workstation has just resolved a browser URL to the IP address of a server. Which protocol will the workstation now use to determine the destination MAC address to be placed into frames directed toward the sever?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
What is the default lease time for a DHCP binding?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
When a router makes a routing decision for a packet that is received from one network and destined to another, which portion of the packet does it replace?
- ALayer 2 frame header and trailer
- BLayer 3 IP address
- CLayer 5 session
- DLayer 4 protocol
Correct Answer:
A
What does a router do with a packet received from one network and destined for another network? The router performs the following three major steps:
De-encapsulates the Layer 3 packet by removing the Layer 2 frame header and trailer.
✑ Step 1.
Examines the destination IP address of the IP packet to find the best path in the routing table.
✑ Step 2.
If the router finds a path to the destination, it encapsulates the Layer 3 packet into a new Layer 2 frame and forwards the frame out the exit interface.
✑ Step 3.
Reference:
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2180208&seqNum=8
A
What does a router do with a packet received from one network and destined for another network? The router performs the following three major steps:
De-encapsulates the Layer 3 packet by removing the Layer 2 frame header and trailer.
✑ Step 1.
Examines the destination IP address of the IP packet to find the best path in the routing table.
✑ Step 2.
If the router finds a path to the destination, it encapsulates the Layer 3 packet into a new Layer 2 frame and forwards the frame out the exit interface.
✑ Step 3.
Reference:
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2180208&seqNum=8
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
Which device allows users to connect to the network using a single or double radio?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
Which entity assigns IPv6 addresses to end users?
- AICANN
- BAPNIC
- CRIR
- DISPs
Correct Answer:
D
Before going forward that far it is important to note that like IPv4, the placement of the devices that will be allocated with IPv6 addresses can affect the numbers and the method of assignment.
If the IPv6 addresses in question will be used solely for the internal purposes of a business and do not need to be directly routable to the public Internet, then the
Unique Local IPv6 range (RFC 4193) and assignment method can be used; these would be the equivalent of RFC 1918 IPv4 private address ranges. If, however, the IPv6 addresses are intended to be directly routable on the public Internet, a range must be assigned (just like with IPv4) by an Internet Service Provider (ISP), or a Regional Internet Registry (RIR) if allocating for an ISP.
As of this writing, the Unique Local address range includes all addresses that fall under the FC00::/7 prefix (they begin with 1111110 in binary), while the Global
Unicast address range includes all addresses that fall under the 2000::/3 prefix (they begin with 001 in binary). Global Unicast ranges are divided by a number of different entities; at the top of these entities is Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) who assigns addresses to the RIRs (for all regional registries except APNIC), who will in turn assign addresses to ISPs who will in turn assign addresses to End Users (EU).
D
Before going forward that far it is important to note that like IPv4, the placement of the devices that will be allocated with IPv6 addresses can affect the numbers and the method of assignment.
If the IPv6 addresses in question will be used solely for the internal purposes of a business and do not need to be directly routable to the public Internet, then the
Unique Local IPv6 range (RFC 4193) and assignment method can be used; these would be the equivalent of RFC 1918 IPv4 private address ranges. If, however, the IPv6 addresses are intended to be directly routable on the public Internet, a range must be assigned (just like with IPv4) by an Internet Service Provider (ISP), or a Regional Internet Registry (RIR) if allocating for an ISP.
As of this writing, the Unique Local address range includes all addresses that fall under the FC00::/7 prefix (they begin with 1111110 in binary), while the Global
Unicast address range includes all addresses that fall under the 2000::/3 prefix (they begin with 001 in binary). Global Unicast ranges are divided by a number of different entities; at the top of these entities is Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) who assigns addresses to the RIRs (for all regional registries except APNIC), who will in turn assign addresses to ISPs who will in turn assign addresses to End Users (EU).
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
Refer to the exhibit.
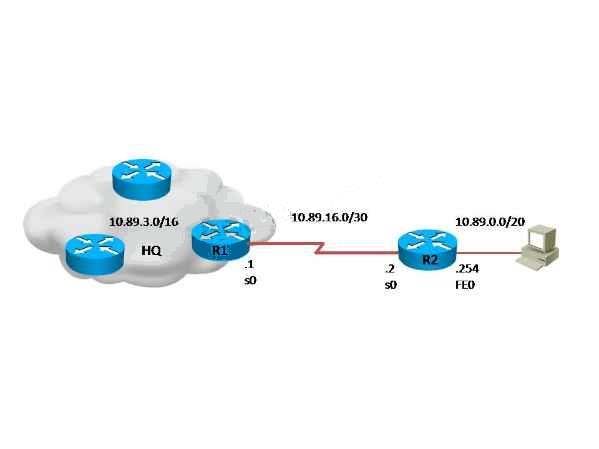
Which command is simplest to configure routing between the regional office network 10.89.0.0/20 and the corporate network?

Which command is simplest to configure routing between the regional office network 10.89.0.0/20 and the corporate network?
- Arouter2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.89.16.1
- Brouter2(config)#ip route 10.89.3.0 255.255.0.0 10.89.16.2
- Crouter1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.1
- Drouter1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.2
Correct Answer:
A
The fourth command makes it possible for all hosts beyond R2 and all hosts beyond R1 to interact with each other, hence it is the simplest technique.
A
The fourth command makes it possible for all hosts beyond R2 and all hosts beyond R1 to interact with each other, hence it is the simplest technique.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
What is one requirement for interfaces to run IPv6?
- AAn IPv6 address must be configured on the interface.
- BAn IPv4 address must be configured.
- CStateless autoconfiguration must be enabled after enabling IPv6 on the interface
- DIPv6 must be enabled with the ipv6 enable command in global configuration mode.
Correct Answer:
A
To use IPv6 on your router, you must, at a minimum, enable the protocol and assign IPv6 addresses to your interfaces.
A
To use IPv6 on your router, you must, at a minimum, enable the protocol and assign IPv6 addresses to your interfaces.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
Refer to the exhibit.
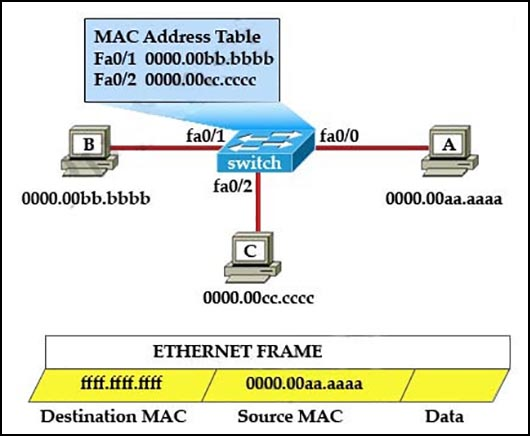
The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two.)

The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two.)
- AThe switch will not forward a frame with this destination MAC address.
- BThe frame will be forwarded out of all the ports on the switch.
- CThe MAC address of ffff.ffff.ffff will be added to the MAC address table.
- DThe frame will be forwarded out of all the active switch ports except for port fa0/0.
- EThe MAC address of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be added to the MAC Address Table.
- FThe frame will be forwarded out of fa0/0 and fa0/1 only.
Correct Answer:
DE
If the switch already has the MAC address in its table for the destination, it will forward the frame directly to the destination port. If it was not already in its MAC table, then the source MAC is added to the MAC address table and frame would have been flooded out all ports except for the port that it came from.
DE
If the switch already has the MAC address in its table for the destination, it will forward the frame directly to the destination port. If it was not already in its MAC table, then the source MAC is added to the MAC address table and frame would have been flooded out all ports except for the port that it came from.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
