Test Prep CFA® Level 3 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (362 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #41
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments.
Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS's offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried's contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return.
Fried manages the consultant's personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients' portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients' assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS's investment services as detailed in the firm's approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS's services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips.
Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips' request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy,
Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm's services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account's asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS's services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster's control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes.
Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster's average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
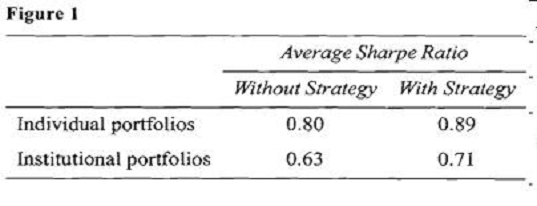
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm's portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients' (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients' trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried's order to remain unfilled.
By utilizing the futures and options strategy as suggested by DIS's economists, did Ulster violate any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS's offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried's contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return.
Fried manages the consultant's personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients' portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients' assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS's investment services as detailed in the firm's approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS's services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips.
Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips' request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy,
Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm's services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account's asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS's services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster's control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes.
Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster's average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.

At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm's portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients' (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients' trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried's order to remain unfilled.
By utilizing the futures and options strategy as suggested by DIS's economists, did Ulster violate any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
- AYes.
- BNo, because she acted in her clients best interest by reducing portfolio risk while increasing portfolio return.
- CNo, because she treated all clients fairly by applying the strategy to both individual and institutional clients.
Correct Answer:
A
Ulster has failed to recognize chat while the derivative strategy successfully lowered the volatilities of her clients' portfolios and raised the returns, the strategy may not have been suitable for all portfolios. In particular, the Jones Family Trust investment policy statement strictly forbids the use of derivative instruments, and therefore the derivatives strategy is unsuitable for the account. Ulster should not have used the strategy for the Jones Family Trust account or for any other account that would deem the strategy unsuitable and has thus violated Standard III(C) Suitability. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
A
Ulster has failed to recognize chat while the derivative strategy successfully lowered the volatilities of her clients' portfolios and raised the returns, the strategy may not have been suitable for all portfolios. In particular, the Jones Family Trust investment policy statement strictly forbids the use of derivative instruments, and therefore the derivatives strategy is unsuitable for the account. Ulster should not have used the strategy for the Jones Family Trust account or for any other account that would deem the strategy unsuitable and has thus violated Standard III(C) Suitability. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #42
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments.
Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS's offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried's contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return.
Fried manages the consultant's personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients' portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients' assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS's investment services as detailed in the firm's approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS's services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips.
Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips' request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy,
Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm's services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account's asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS's services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster's control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes.
Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster's average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
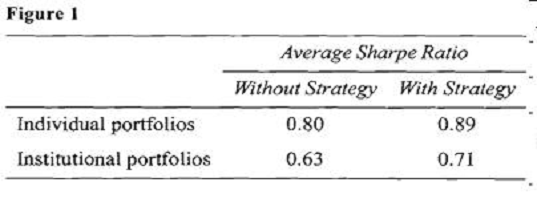
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm's portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients' (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients' trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried's order to remain unfilled.
According to CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, should Fried have taken a different course of action with respect to the limit order on the emerging market fund?
Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS's offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried's contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return.
Fried manages the consultant's personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients' portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients' assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS's investment services as detailed in the firm's approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS's services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips.
Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips' request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy,
Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm's services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account's asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS's services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster's control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes.
Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster's average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.

At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm's portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients' (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients' trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried's order to remain unfilled.
According to CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, should Fried have taken a different course of action with respect to the limit order on the emerging market fund?
- ANo.
- BYes, Fried should not have sold any shares of the emerging market fund.
- CYes, Fried should have waited to place the limit order until after the market orders were filled.
Correct Answer:
C
Fried has violated Standard VI(B) Priority of Transactions by placing his own sell order ahead of his clients' sell orders. Even though Fried has used a limit order with a 5% premium to the current stock price (and his order never gets executed), he has still acted in his own interest before acting in his clients' interest. Fried should have placed his clients' trades before placing his own. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
C
Fried has violated Standard VI(B) Priority of Transactions by placing his own sell order ahead of his clients' sell orders. Even though Fried has used a limit order with a 5% premium to the current stock price (and his order never gets executed), he has still acted in his own interest before acting in his clients' interest. Fried should have placed his clients' trades before placing his own. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #43
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Indicate whether CA's policies related to investment policy statement (IPS) reviews and notification of changes in investment style/strategy are consistent with the
Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Indicate whether CA's policies related to investment policy statement (IPS) reviews and notification of changes in investment style/strategy are consistent with the
Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- AThe IPS review policy is adequate, but the policy on communicating changes in style / strategy is inadequate.
- BBoth policies are inadequate.
- CBoth policies are consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
Correct Answer:
B
The IPS review policy is inadequate. It is good that IPS are reviewed at any lime upon client request, but it is also likely that clients may be unaware of when such a review might be appropriate. It is incumbent upon the manager 10 initiate a review of the client's IPS. The Asset Manager Code recommends such reviews on an annual basis, or whenever changes in client circumstances justify them. The notification of changes in style/strategy is also inadequate. Such notification should be made in advance, so that the client has time to consider the change and react accordingly. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
B
The IPS review policy is inadequate. It is good that IPS are reviewed at any lime upon client request, but it is also likely that clients may be unaware of when such a review might be appropriate. It is incumbent upon the manager 10 initiate a review of the client's IPS. The Asset Manager Code recommends such reviews on an annual basis, or whenever changes in client circumstances justify them. The notification of changes in style/strategy is also inadequate. Such notification should be made in advance, so that the client has time to consider the change and react accordingly. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #44
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Indicate whether CA's policies related to its IPO program, specifically allowing portfolio manager participation and employee participation, are consistent with the
Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Indicate whether CA's policies related to its IPO program, specifically allowing portfolio manager participation and employee participation, are consistent with the
Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- APolicies on both portfolio manager and employee participation in IPOs are not consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- BThe employee participation in IPOs policy is consistent with the Asset Manager Code, as is the portfolio manager's policy on participation in IPOs.
- CThe portfolio manager's policy on IPOs is not consistent with the Asset Manager Code, however the employee policy on IPOs is consistent with the Asset Manager Code.
Correct Answer:
A
The IPO program creates a substantial conflict of interest between managers and clients. Managers wanting to boost their participation in an IPO would be likely to place orders in accounts where such an investment might not be appropriate. The employee participation in and of itself might be acceptable, so long as clients' interests were placed ahead of employees'. In this case, there is no evidence of such a priority of transactions, and further, the fact that CA has no exact numbers on the program indicates that the firm is not tracking employee trading activity, which is poor policy. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
A
The IPO program creates a substantial conflict of interest between managers and clients. Managers wanting to boost their participation in an IPO would be likely to place orders in accounts where such an investment might not be appropriate. The employee participation in and of itself might be acceptable, so long as clients' interests were placed ahead of employees'. In this case, there is no evidence of such a priority of transactions, and further, the fact that CA has no exact numbers on the program indicates that the firm is not tracking employee trading activity, which is poor policy. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #45
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Participation in CA's private equity fund is limited to clients with $5 million under management. This policy:
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Participation in CA's private equity fund is limited to clients with $5 million under management. This policy:
- Adocs not violate the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- Bwould be acceptable so long as a similar investment vehicle was made available to all clients.
- Cis not consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
Correct Answer:
A
It is perfectly reasonable for CA to offer certain services or products only to clients meeting specified criteria, such as assets under management. (Study Session
2, LOS 6.b)
A
It is perfectly reasonable for CA to offer certain services or products only to clients meeting specified criteria, such as assets under management. (Study Session
2, LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #46
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
In discussing the pricing of thinly traded securities in the private equity fund, Riley suggested that CA should choose one pricing method and apply it consistently, thus avoiding the need to disclose specific pricing methods to clients. Simpson responded that using third party sources or internal valuation models was acceptable, so long as the pricing sources are fully disclosed to clients. Indicate whether Riley's comment or Simpson's response are correct or incorrect.
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
In discussing the pricing of thinly traded securities in the private equity fund, Riley suggested that CA should choose one pricing method and apply it consistently, thus avoiding the need to disclose specific pricing methods to clients. Simpson responded that using third party sources or internal valuation models was acceptable, so long as the pricing sources are fully disclosed to clients. Indicate whether Riley's comment or Simpson's response are correct or incorrect.
- ABoth Riley's comment and Simpson's response are correct.
- BRiley's comment is not correct; however Simpson's response is correct.
- CRiley is correct, while Simpson is not correct.
Correct Answer:
B
Riley was incorrect. The pricing methodology should be disclosed to clients, whether one or multiple sources are used. Simpson was correct. Multiple sources are acceptable, so long as full disclosure is made. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
B
Riley was incorrect. The pricing methodology should be disclosed to clients, whether one or multiple sources are used. Simpson was correct. Multiple sources are acceptable, so long as full disclosure is made. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #47
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Trading stocks during the last trading hour of a month to establish a fair market price:
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Trading stocks during the last trading hour of a month to establish a fair market price:
- Adoes not violate the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- Bis acceptable so long as the trade is not material relative to the overall CA position in the security.
- Cis not consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct. C
Correct Answer:
Explanation
This type of trading is clearly market manipulation. Even though the 100 shares may be insignificant, the trade sets the price for the entire position. Such trades, especially entered as buy orders, are an unethical attempt to manipulate prices higher and justify a higher return for the period. However, even a sell transaction made under similar circumstances would be market manipulation. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
Explanation
This type of trading is clearly market manipulation. Even though the 100 shares may be insignificant, the trade sets the price for the entire position. Such trades, especially entered as buy orders, are an unethical attempt to manipulate prices higher and justify a higher return for the period. However, even a sell transaction made under similar circumstances would be market manipulation. (Study Session 2, LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #48
Shirley Riley, CFA, has just been promoted, from vice president of trading to chief investment officer (CIO) at Crane & Associates, LLC (CA), a large investment management firm. Riley has been with CA for eight years, but she has much to learn as she assumes her new duties as CIO. Riley has decided to hire Denny
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Simpson has verified that CA has adequate disclosures of its soft dollar usage. Given that full disclosure is made to clients, indicate whether CA's use of soft dollars for BTN and BTR are consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
Simpson, CFA, as the new compliance officer for CA, Riley and Simpson have been reviewing procedures and policies throughout the firm and have discovered several potential issues.
Communications with Clients -
Portfolio managers are encouraged to communicate with clients on a regular basis. At a minimum, managers are expected to contact clients on a quarterly basis to review portfolio performance. Each client must have an investment policy statement (IPS) created when their account is opened, specifying the objectives and constraints for their portfolio. IPSs are reviewed at client request at any time. Any time market conditions dictate a change in the investment style or strategy of a client portfolio, the client is notified immediately by phone or email.
Employee Incentive Program -
CA offers several incentive programs to employees. One of the most popular of these programs is the CA IPO program. Whenever CA is involved in an initial public offering (IPO), portfolio managers are allowed to participate. The structure is simple""for every 100 shares purchased on behalf of a client, the manager is awarded five shares for his own account. The manager is thus rewarded for getting an IPO sold and at the same time is able to share in the results of the IPO.
Any¬time shares are remaining 72 hours before the IPO goes public, other employees are allowed to participate on a first-come, first-serve basis. Employees seem to appreciate this opportunity, but CA does not have exact numbers on employee participation in the program.
Private Equity Fund -
CA has a private equity fund that is internally managed. This fund is made available only to clients with more than $5 million in assets managed by CA, a policy that is fully disclosed in CA's marketing materials. Roughly one-third of the fund's assets are invested in companies that are either very small capitalization or thinly traded (or both). The pricing of these securities for monthly account statements is often difficult. CA support staff get information from different sources"" sometimes using third party services, sometimes using CA valuation models. In some instances, a manager of the private equity fund will enter an order during the last trading hour of the month to purchase 100 shares of one of these small securities at a modest premium to the last trade price. If the trade gets executed, that price can then be used on the account statements. The small size of these trades does not significantly affect the fund's overall position in any particular company holding, which is typically several thousand shares.
Soft Dollar Usage -
Several different managers at CA use independent research in developing investment ideas. One of the more popular research services among CA managers is
"Beneath the Numbers (BTN)," which focuses on potential accounting abuses at prominent companies. This service often provides early warnings of problems with a stock, allowing CA managers the opportunity to sell their clients' positions before a negative surprise lowers the price. Stocks covered by BTN are typically widely held in CA client accounts. Managers at CA have been so happy with BTN that they have also subscribed to a new research product provided by the same authors"""Beneath the Radar (BTR)." BTR recommends small capitalization securities that are not large enough to attract much attention from large institutional investors. The results of BTR's recommendations are mixed thus far, but CA managers are willing to be patient.
As they discuss these issues, Riley informs Simpson that she is determined to bring CA into full compliance with the CFA Institute's "Asset Manager Code of
Professional Conduct." The following questions should be answered with the Asset Manager Code as a guide.
Simpson has verified that CA has adequate disclosures of its soft dollar usage. Given that full disclosure is made to clients, indicate whether CA's use of soft dollars for BTN and BTR are consistent with the Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct.
- AGiven the adequate disclosures, use of soft dollars for both BTN and BTR is acceptable.
- BUse of soft dollars for BTN is acceptable, but not for BTR.
- CNeither of these publications provide direct benefit to the client, thus neither may be paid for with soft dollars.
Correct Answer:
B
BTN obviously assists in the investment decision-making process at CA. Using soft dollars to purchase BTN is acceptable. BTR might assist in the investment decision-making process, but managers have not performed any due diligence to verify the quality of the service. With no proven track record or other apparent means of verifying BTR's value, buying the service violates the managers' duty to have a reasonable basis for making investment decisions. (Study Session 2,
LOS 6.b)
B
BTN obviously assists in the investment decision-making process at CA. Using soft dollars to purchase BTN is acceptable. BTR might assist in the investment decision-making process, but managers have not performed any due diligence to verify the quality of the service. With no proven track record or other apparent means of verifying BTR's value, buying the service violates the managers' duty to have a reasonable basis for making investment decisions. (Study Session 2,
LOS 6.b)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #49
John Green, CFA, is a sell-side technology analyst at Federal Securities, a large global investment banking and advisory firm. In many of his recent conversations with executives at the firms he researches, Green has heard disturbing news. Most of these firms are lowering sales estimates for the coming year. However, the stock prices have been stable despite management's widely disseminated sales warnings. Green is preparing his quarterly industry analysis and decides to seek further input. He calls Alan Volk, CFA, a close friend who runs the Initial Public Offering section of the investment banking department of Federal Securities.
Volk tells Green he has seen no slowing of demand for technology IPOs. "We've got three new issues due out next week, and two of them are well oversubscribed." Green knows that Volk's department handled over 200 IPOs last year, so he is confident that Volk's opinion is reliable. Green prepares his industry report, which is favorable. Among other conclusions, the report states that "the future is still bright, based on the fact that 67% of technology IPOs are oversubscribed." Privately, Green recommends to Federal portfolio managers that they begin selling all existing technology issues, which have "stagnated," and buy the IPOs in their place.
After carefully evaluating Federal's largest institutional client's portfolio, Green contacts the client and recommends selling all of his existing technology stocks and buying two of the upcoming IPOs, similar to the recommendation given to Federal's portfolio managers. Green's research has allowed him to conclude that only these two IPOs would be appropriate for this particular client's portfolio. Investing in these IPOs and selling the current technology holdings would, according to
Green, "double the returns that your portfolio experienced last year."
Federal Securities has recently hired Dirks Bentley, a CFA candidate who has passed Level 2 and is currently preparing to take the Level 3 CFA® exam, to reorganize Federal's compliance department. Bentley tells Green that he may be subject to CFA Institute sanctions due to inappropriate contact between analysts and investment bankers within Federal Securities. Bentley has recommended that Green implement a firewall to rectify the situation and has outlined the key characteristics for such a system. Bentley's suggestions are as follows:
1. Any communication between the departments of Federal Securities must be channeled through the compliance department for review and eventual delivery.
The firm must create and maintain watch, restricted, and rumor lists to be used in the review of employee trading.
2. All beneficial ownership, whether direct or indirect, of recommended securities must be disclosed in writing.
3. The firm must increase the level of review or restriction of proprietary trading activities during periods in which the firm has knowledge of information that is both material and nonpublic.
Bentley has identified two of Green's analysts, neither of whom have non-compete contracts, who are preparing to leave Federal Securities and go into competition. The first employee, James Ybarra, CFA, has agreed to take a position with one of Federal's direct competitors. Ybarra has contacted existing Federal clients using a client list he created with public records. None of the contacted clients have agreed to move their accounts as Ybarra has requested. The second employee, Martha Cliff, CFA, has registered the name Cliff Investment Consulting (CIC), which she plans to use for her independent consulting business. For the new business venture, Cliff has developed and professionally printed marketing literature that compares the new firm's services to that of Federal Securities and highlights the significant cost savings that will be realized by switching to CIC. After she leaves Federal, Cliff plans to target many of the same prospects that
Federal Securities is targeting, using an address list she purchased from a third-party vendor. Bentley decides to call a meeting with Green to discuss his findings.
After discussing the departing analysts. Green asks Bentley how to best handle the disclosure of the following items: (1) although not currently a board member.
Green has served in the past on the board of directors of a company he researches and expects that he will do so again in the near future; and (2) Green recently inherited put options on a company for which he has an outstanding buy recommendation. Bentley is contemplating his response to Green.
According to Standard 11(A) Material Nonpublic Information, when Green contacted Volk, he:
Volk tells Green he has seen no slowing of demand for technology IPOs. "We've got three new issues due out next week, and two of them are well oversubscribed." Green knows that Volk's department handled over 200 IPOs last year, so he is confident that Volk's opinion is reliable. Green prepares his industry report, which is favorable. Among other conclusions, the report states that "the future is still bright, based on the fact that 67% of technology IPOs are oversubscribed." Privately, Green recommends to Federal portfolio managers that they begin selling all existing technology issues, which have "stagnated," and buy the IPOs in their place.
After carefully evaluating Federal's largest institutional client's portfolio, Green contacts the client and recommends selling all of his existing technology stocks and buying two of the upcoming IPOs, similar to the recommendation given to Federal's portfolio managers. Green's research has allowed him to conclude that only these two IPOs would be appropriate for this particular client's portfolio. Investing in these IPOs and selling the current technology holdings would, according to
Green, "double the returns that your portfolio experienced last year."
Federal Securities has recently hired Dirks Bentley, a CFA candidate who has passed Level 2 and is currently preparing to take the Level 3 CFA® exam, to reorganize Federal's compliance department. Bentley tells Green that he may be subject to CFA Institute sanctions due to inappropriate contact between analysts and investment bankers within Federal Securities. Bentley has recommended that Green implement a firewall to rectify the situation and has outlined the key characteristics for such a system. Bentley's suggestions are as follows:
1. Any communication between the departments of Federal Securities must be channeled through the compliance department for review and eventual delivery.
The firm must create and maintain watch, restricted, and rumor lists to be used in the review of employee trading.
2. All beneficial ownership, whether direct or indirect, of recommended securities must be disclosed in writing.
3. The firm must increase the level of review or restriction of proprietary trading activities during periods in which the firm has knowledge of information that is both material and nonpublic.
Bentley has identified two of Green's analysts, neither of whom have non-compete contracts, who are preparing to leave Federal Securities and go into competition. The first employee, James Ybarra, CFA, has agreed to take a position with one of Federal's direct competitors. Ybarra has contacted existing Federal clients using a client list he created with public records. None of the contacted clients have agreed to move their accounts as Ybarra has requested. The second employee, Martha Cliff, CFA, has registered the name Cliff Investment Consulting (CIC), which she plans to use for her independent consulting business. For the new business venture, Cliff has developed and professionally printed marketing literature that compares the new firm's services to that of Federal Securities and highlights the significant cost savings that will be realized by switching to CIC. After she leaves Federal, Cliff plans to target many of the same prospects that
Federal Securities is targeting, using an address list she purchased from a third-party vendor. Bentley decides to call a meeting with Green to discuss his findings.
After discussing the departing analysts. Green asks Bentley how to best handle the disclosure of the following items: (1) although not currently a board member.
Green has served in the past on the board of directors of a company he researches and expects that he will do so again in the near future; and (2) Green recently inherited put options on a company for which he has an outstanding buy recommendation. Bentley is contemplating his response to Green.
According to Standard 11(A) Material Nonpublic Information, when Green contacted Volk, he:
- Aviolated CFA Institute Standards.
- Bviolated of CFA Institute Standards unless the contact was disclosed to his clients.
- Cdid not violate CFA Institute Standards since he was conducting a legitimate research activity.
Correct Answer:
C
There is no evidence co suggest that the contact was inappropriate. Green is crying co gauge investor sentiment relative to technology stocks. While a fire wall within the firm would be advisable, since no company-specific information was exchanged, the contact was relatively harmless. Also, there is no violation of
Standard 11(A) Material Nonpublic Information because there was no inside information discussed. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
C
There is no evidence co suggest that the contact was inappropriate. Green is crying co gauge investor sentiment relative to technology stocks. While a fire wall within the firm would be advisable, since no company-specific information was exchanged, the contact was relatively harmless. Also, there is no violation of
Standard 11(A) Material Nonpublic Information because there was no inside information discussed. (Study Session 1, LOS 2.a)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #50
John Green, CFA, is a sell-side technology analyst at Federal Securities, a large global investment banking and advisory firm. In many of his recent conversations with executives at the firms he researches, Green has heard disturbing news. Most of these firms are lowering sales estimates for the coming year. However, the stock prices have been stable despite management's widely disseminated sales warnings. Green is preparing his quarterly industry analysis and decides to seek further input. He calls Alan Volk, CFA, a close friend who runs the Initial Public Offering section of the investment banking department of Federal Securities.
Volk tells Green he has seen no slowing of demand for technology IPOs. "We've got three new issues due out next week, and two of them are well oversubscribed." Green knows that Volk's department handled over 200 IPOs last year, so he is confident that Volk's opinion is reliable. Green prepares his industry report, which is favorable. Among other conclusions, the report states that "the future is still bright, based on the fact that 67% of technology IPOs are oversubscribed." Privately, Green recommends to Federal portfolio managers that they begin selling all existing technology issues, which have "stagnated," and buy the IPOs in their place.
After carefully evaluating Federal's largest institutional client's portfolio, Green contacts the client and recommends selling all of his existing technology stocks and buying two of the upcoming IPOs, similar to the recommendation given to Federal's portfolio managers. Green's research has allowed him to conclude that only these two IPOs would be appropriate for this particular client's portfolio. Investing in these IPOs and selling the current technology holdings would, according to
Green, "double the returns that your portfolio experienced last year."
Federal Securities has recently hired Dirks Bentley, a CFA candidate who has passed Level 2 and is currently preparing to take the Level 3 CFA® exam, to reorganize Federal's compliance department. Bentley tells Green that he may be subject to CFA Institute sanctions due to inappropriate contact between analysts and investment bankers within Federal Securities. Bentley has recommended that Green implement a firewall to rectify the situation and has outlined the key characteristics for such a system. Bentley's suggestions are as follows:
1. Any communication between the departments of Federal Securities must be channeled through the compliance department for review and eventual delivery.
The firm must create and maintain watch, restricted, and rumor lists to be used in the review of employee trading.
2. All beneficial ownership, whether direct or indirect, of recommended securities must be disclosed in writing.
3. The firm must increase the level of review or restriction of proprietary trading activities during periods in which the firm has knowledge of information that is both material and nonpublic.
Bentley has identified two of Green's analysts, neither of whom have non-compete contracts, who are preparing to leave Federal Securities and go into competition. The first employee, James Ybarra, CFA, has agreed to take a position with one of Federal's direct competitors. Ybarra has contacted existing Federal clients using a client list he created with public records. None of the contacted clients have agreed to move their accounts as Ybarra has requested. The second employee, Martha Cliff, CFA, has registered the name Cliff Investment Consulting (CIC), which she plans to use for her independent consulting business. For the new business venture, Cliff has developed and professionally printed marketing literature that compares the new firm's services to that of Federal Securities and highlights the significant cost savings that will be realized by switching to CIC. After she leaves Federal, Cliff plans to target many of the same prospects that
Federal Securities is targeting, using an address list she purchased from a third-party vendor. Bentley decides to call a meeting with Green to discuss his findings.
After discussing the departing analysts. Green asks Bentley how to best handle the disclosure of the following items: (1) although not currently a board member.
Green has served in the past on the board of directors of a company he researches and expects that he will do so again in the near future; and (2) Green recently inherited put options on a company for which he has an outstanding buy recommendation. Bentley is contemplating his response to Green.
According to CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, which of the following statements regarding Green's recommendation to Federal Securities' clients is TRUE?
Volk tells Green he has seen no slowing of demand for technology IPOs. "We've got three new issues due out next week, and two of them are well oversubscribed." Green knows that Volk's department handled over 200 IPOs last year, so he is confident that Volk's opinion is reliable. Green prepares his industry report, which is favorable. Among other conclusions, the report states that "the future is still bright, based on the fact that 67% of technology IPOs are oversubscribed." Privately, Green recommends to Federal portfolio managers that they begin selling all existing technology issues, which have "stagnated," and buy the IPOs in their place.
After carefully evaluating Federal's largest institutional client's portfolio, Green contacts the client and recommends selling all of his existing technology stocks and buying two of the upcoming IPOs, similar to the recommendation given to Federal's portfolio managers. Green's research has allowed him to conclude that only these two IPOs would be appropriate for this particular client's portfolio. Investing in these IPOs and selling the current technology holdings would, according to
Green, "double the returns that your portfolio experienced last year."
Federal Securities has recently hired Dirks Bentley, a CFA candidate who has passed Level 2 and is currently preparing to take the Level 3 CFA® exam, to reorganize Federal's compliance department. Bentley tells Green that he may be subject to CFA Institute sanctions due to inappropriate contact between analysts and investment bankers within Federal Securities. Bentley has recommended that Green implement a firewall to rectify the situation and has outlined the key characteristics for such a system. Bentley's suggestions are as follows:
1. Any communication between the departments of Federal Securities must be channeled through the compliance department for review and eventual delivery.
The firm must create and maintain watch, restricted, and rumor lists to be used in the review of employee trading.
2. All beneficial ownership, whether direct or indirect, of recommended securities must be disclosed in writing.
3. The firm must increase the level of review or restriction of proprietary trading activities during periods in which the firm has knowledge of information that is both material and nonpublic.
Bentley has identified two of Green's analysts, neither of whom have non-compete contracts, who are preparing to leave Federal Securities and go into competition. The first employee, James Ybarra, CFA, has agreed to take a position with one of Federal's direct competitors. Ybarra has contacted existing Federal clients using a client list he created with public records. None of the contacted clients have agreed to move their accounts as Ybarra has requested. The second employee, Martha Cliff, CFA, has registered the name Cliff Investment Consulting (CIC), which she plans to use for her independent consulting business. For the new business venture, Cliff has developed and professionally printed marketing literature that compares the new firm's services to that of Federal Securities and highlights the significant cost savings that will be realized by switching to CIC. After she leaves Federal, Cliff plans to target many of the same prospects that
Federal Securities is targeting, using an address list she purchased from a third-party vendor. Bentley decides to call a meeting with Green to discuss his findings.
After discussing the departing analysts. Green asks Bentley how to best handle the disclosure of the following items: (1) although not currently a board member.
Green has served in the past on the board of directors of a company he researches and expects that he will do so again in the near future; and (2) Green recently inherited put options on a company for which he has an outstanding buy recommendation. Bentley is contemplating his response to Green.
According to CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, which of the following statements regarding Green's recommendation to Federal Securities' clients is TRUE?
- AGreen violated the Standards by making a material misrepresentation in his report to Federal Securities' clients.
- BGreen violated the Standards by failing to preserve the confidentiality of Federal Securities' investment banking clients.
- CGreen did not violate the Standards since he made a suitable recommendation in the best interest of Federal Securities' clients.
Correct Answer:
A
Green has taken a small number of oversubscribed IPOs to represent the entire market for technology IPOs. This is clearly a misrepresentation of the true market situation. Thus, Green has violated Standard 1(C) Misrepresentations which prohibits such misstatements of fact. Also, IPOs may not be suitable for all accounts, but Green has recommended that all of Federal Securities' portfolio managers add the IPO shares to their portfolios. Green did not violate the confidentiality of the investment banking clients since he was unaware of, and did not disclose, any details of the upcoming IPOs, Also, Green was not in possession of any material nonpublic information. (Study Session I, LOS2.a)
A
Green has taken a small number of oversubscribed IPOs to represent the entire market for technology IPOs. This is clearly a misrepresentation of the true market situation. Thus, Green has violated Standard 1(C) Misrepresentations which prohibits such misstatements of fact. Also, IPOs may not be suitable for all accounts, but Green has recommended that all of Federal Securities' portfolio managers add the IPO shares to their portfolios. Green did not violate the confidentiality of the investment banking clients since he was unaware of, and did not disclose, any details of the upcoming IPOs, Also, Green was not in possession of any material nonpublic information. (Study Session I, LOS2.a)
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
