Microsoft AZ-203 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (150 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #6
DRAG DROP -
You are preparing to deploy a medical records application to an Azure virtual machine (VM). The application will be deployed by using a VHD produced by an on- premises build server.
You need to ensure that both the application and related data are encrypted during and after deployment to Azure.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You are preparing to deploy a medical records application to an Azure virtual machine (VM). The application will be deployed by using a VHD produced by an on- premises build server.
You need to ensure that both the application and related data are encrypted during and after deployment to Azure.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Step 1: Encrypt the on-premises VHD by using BitLocker without a TPM. Upload the VM to Azure Storage
Step 2: Run the Azure PowerShell command Set-AzureRMVMOSDisk
To use an existing disk instead of creating a new disk you can use the Set-AzureRMVMOSDisk command.
Example:
$osDiskName = $vmname+'_osDisk'
$osDiskCaching = 'ReadWrite'
$osDiskVhdUri = "https://$stoname.blob.core.windows.net/vhds/"+$vmname+"_os.vhd"
$vm = Set-AzureRmVMOSDisk -VM $vm -VhdUri $osDiskVhdUri -name $osDiskName -Create
Step 3: Run the Azure PowerShell command Set-AzureRmVMDiskEncryptionExtension
Use the Set-AzVMDiskEncryptionExtension cmdlet to enable encryption on a running IaaS virtual machine in Azure.
Incorrect:
Not TPM: BitLocker can work with or without a TPM. A TPM is a tamper resistant security chip on the system board that will hold the keys for encryption and check the integrity of the boot sequence and allows the most secure BitLocker implementation. A VM does not have a TPM.
References:
https://www.itprotoday.com/iaaspaas/use-existing-vhd-azurerm-vm
Explanation
Step 1: Encrypt the on-premises VHD by using BitLocker without a TPM. Upload the VM to Azure Storage
Step 2: Run the Azure PowerShell command Set-AzureRMVMOSDisk
To use an existing disk instead of creating a new disk you can use the Set-AzureRMVMOSDisk command.
Example:
$osDiskName = $vmname+'_osDisk'
$osDiskCaching = 'ReadWrite'
$osDiskVhdUri = "https://$stoname.blob.core.windows.net/vhds/"+$vmname+"_os.vhd"
$vm = Set-AzureRmVMOSDisk -VM $vm -VhdUri $osDiskVhdUri -name $osDiskName -Create
Step 3: Run the Azure PowerShell command Set-AzureRmVMDiskEncryptionExtension
Use the Set-AzVMDiskEncryptionExtension cmdlet to enable encryption on a running IaaS virtual machine in Azure.
Incorrect:
Not TPM: BitLocker can work with or without a TPM. A TPM is a tamper resistant security chip on the system board that will hold the keys for encryption and check the integrity of the boot sequence and allows the most secure BitLocker implementation. A VM does not have a TPM.
References:
https://www.itprotoday.com/iaaspaas/use-existing-vhd-azurerm-vm
send
light_mode
delete
Question #7
DRAG DROP -
You plan to create a Docker image that runs as ASP.NET Core application named ContosoApp. You have a setup script named setupScript.ps1 and a series of application files including ContosoApp.dll.
You need to create a Dockerfile document that meets the following requirements:
✑ Call setupScript.ps1 when the container is built.
✑ Run ContosoApp.dll when the container starts.
The Docker document must be created in the same folder where ContosoApp.dll and setupScript.ps1 are stored.
Which four commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You plan to create a Docker image that runs as ASP.NET Core application named ContosoApp. You have a setup script named setupScript.ps1 and a series of application files including ContosoApp.dll.
You need to create a Dockerfile document that meets the following requirements:
✑ Call setupScript.ps1 when the container is built.
✑ Run ContosoApp.dll when the container starts.
The Docker document must be created in the same folder where ContosoApp.dll and setupScript.ps1 are stored.
Which four commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Step 1: WORKDIR /apps/ContosoApp
Step 2: COPY ./-
The Docker document must be created in the same folder where ContosoApp.dll and setupScript.ps1 are stored.
Step 3: EXPOSE ./ContosApp/ /app/ContosoApp
Step 4: CMD powershell ./setupScript.ps1
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "ContosoApp.dll"]
You need to create a Dockerfile document that meets the following requirements:
✑ Call setupScript.ps1 when the container is built.
✑ Run ContosoApp.dll when the container starts.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/containers/tutorial-custom-docker-image
Explanation
Step 1: WORKDIR /apps/ContosoApp
Step 2: COPY ./-
The Docker document must be created in the same folder where ContosoApp.dll and setupScript.ps1 are stored.
Step 3: EXPOSE ./ContosApp/ /app/ContosoApp
Step 4: CMD powershell ./setupScript.ps1
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "ContosoApp.dll"]
You need to create a Dockerfile document that meets the following requirements:
✑ Call setupScript.ps1 when the container is built.
✑ Run ContosoApp.dll when the container starts.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/containers/tutorial-custom-docker-image
send
light_mode
delete
Question #8
DRAG DROP -
You are creating a script that will run a large workload on an Azure Batch pool. Resources will be reused and do not need to be cleaned up after use.
You have the following parameters:

You need to write an Azure CLI script that will create the jobs, tasks, and the pool.
In which order should you arrange the commands to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of command segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You are creating a script that will run a large workload on an Azure Batch pool. Resources will be reused and do not need to be cleaned up after use.
You have the following parameters:

You need to write an Azure CLI script that will create the jobs, tasks, and the pool.
In which order should you arrange the commands to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of command segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Step 1: az batch pool create -
# Create a new Linux pool with a virtual machine configuration. az batch pool create \
--id mypool \
--vm-size Standard_A1 \
--target-dedicated 2 \
--image canonical:ubuntuserver:16.04-LTS \
--node-agent-sku-id "batch.node.ubuntu 16.04"
Step 2: az batch job create -
# Create a new job to encapsulate the tasks that are added.
az batch job create \
--id myjob \
--pool-id mypool
Step 3: az batch task create -
# Add tasks to the job. Here the task is a basic shell command. az batch task create \
--job-id myjob \
--task-id task1 \
--command-line "/bin/bash -c 'printenv AZ_BATCH_TASK_WORKING_DIR'"
Step 4: for i in {1..$numberOfJobs} do
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-latn-ba/azure/batch/scripts/batch-cli-sample-run-job
Explanation
Step 1: az batch pool create -
# Create a new Linux pool with a virtual machine configuration. az batch pool create \
--id mypool \
--vm-size Standard_A1 \
--target-dedicated 2 \
--image canonical:ubuntuserver:16.04-LTS \
--node-agent-sku-id "batch.node.ubuntu 16.04"
Step 2: az batch job create -
# Create a new job to encapsulate the tasks that are added.
az batch job create \
--id myjob \
--pool-id mypool
Step 3: az batch task create -
# Add tasks to the job. Here the task is a basic shell command. az batch task create \
--job-id myjob \
--task-id task1 \
--command-line "/bin/bash -c 'printenv AZ_BATCH_TASK_WORKING_DIR'"
Step 4: for i in {1..$numberOfJobs} do
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-latn-ba/azure/batch/scripts/batch-cli-sample-run-job
send
light_mode
delete
Question #9
HOTSPOT -
You are developing an Azure Function App by using Visual Studio. The app will process orders input by an Azure Web App. The web app places the order information into Azure Queue Storage.
You need to review the Azure Function App code shown below.
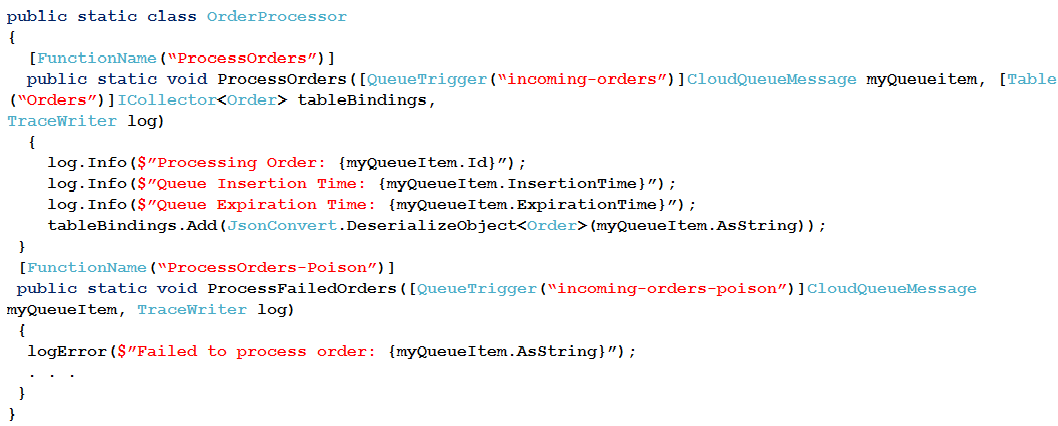
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

You are developing an Azure Function App by using Visual Studio. The app will process orders input by an Azure Web App. The web app places the order information into Azure Queue Storage.
You need to review the Azure Function App code shown below.

NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Box 1: No -
ExpirationTime - The time that the message expires.
InsertionTime - The time that the message was added to the queue.
Box 2: Yes -
maxDequeueCount - The number of times to try processing a message before moving it to the poison queue. Default value is 5.
Box 3: Yes -
When there are multiple queue messages waiting, the queue trigger retrieves a batch of messages and invokes function instances concurrently to process them.
By default, the batch size is 16. When the number being processed gets down to 8, the runtime gets another batch and starts processing those messages. So the maximum number of concurrent messages being processed per function on one virtual machine (VM) is 24.
Box 4: Yes -
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-bindings-storage-queue

Box 1: No -
ExpirationTime - The time that the message expires.
InsertionTime - The time that the message was added to the queue.
Box 2: Yes -
maxDequeueCount - The number of times to try processing a message before moving it to the poison queue. Default value is 5.
Box 3: Yes -
When there are multiple queue messages waiting, the queue trigger retrieves a batch of messages and invokes function instances concurrently to process them.
By default, the batch size is 16. When the number being processed gets down to 8, the runtime gets another batch and starts processing those messages. So the maximum number of concurrent messages being processed per function on one virtual machine (VM) is 24.
Box 4: Yes -
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-bindings-storage-queue
send
light_mode
delete
Question #10
DRAG DROP -
You are developing a Docker/Go using Azure App Service Web App for Containers. You plan to run the container in an App Service on Linux. You identify a
Docker container image to use.
None of your current resource groups reside in a location that supports Linux. You must minimize the number of resource groups required.
You need to create the application and perform an initial deployment.
Which three Azure CLI commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

You are developing a Docker/Go using Azure App Service Web App for Containers. You plan to run the container in an App Service on Linux. You identify a
Docker container image to use.
None of your current resource groups reside in a location that supports Linux. You must minimize the number of resource groups required.
You need to create the application and perform an initial deployment.
Which three Azure CLI commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:

You can host native Linux applications in the cloud by using Azure Web Apps. To create a Web App for Containers, you must run Azure CLI commands that create a group, then a service plan, and finally the web app itself.
Step 1: az group create -
In the Cloud Shell, create a resource group with the az group create command.
Step 2: az appservice plan create
In the Cloud Shell, create an App Service plan in the resource group with the az appservice plan create command.
Step 3: az webapp create -
In the Cloud Shell, create a web app in the myAppServicePlan App Service plan with the az webapp create command. Don't forget to replace with a unique app name, and <docker-ID> with your Docker ID.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/mt-mt/azure/app-service/containers/quickstart-docker-go?view=sql-server-ver15

You can host native Linux applications in the cloud by using Azure Web Apps. To create a Web App for Containers, you must run Azure CLI commands that create a group, then a service plan, and finally the web app itself.
Step 1: az group create -
In the Cloud Shell, create a resource group with the az group create command.
Step 2: az appservice plan create
In the Cloud Shell, create an App Service plan in the resource group with the az appservice plan create command.
Step 3: az webapp create -
In the Cloud Shell, create a web app in the myAppServicePlan App Service plan with the az webapp create command. Don't forget to replace with a unique app name, and <docker-ID> with your Docker ID.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/mt-mt/azure/app-service/containers/quickstart-docker-go?view=sql-server-ver15
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
