Microsoft AZ-203 Exam Practice Questions (P. 1)
- Full Access (150 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #1
HOTSPOT -
You have an Azure Batch project that processes and converts files and stores the files in Azure storage. You are developing a function to start the batch job.
You add the following parameters to the function.

You must ensure that converted files are placed in the container referenced by the outputContainerSasUrl parameter. Files which fail to convert are placed in the container referenced by the failedContainerSasUrl parameter.
You need to ensure the files are correctly processed.
How should you complete the code segment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
You have an Azure Batch project that processes and converts files and stores the files in Azure storage. You are developing a function to start the batch job.
You add the following parameters to the function.

You must ensure that converted files are placed in the container referenced by the outputContainerSasUrl parameter. Files which fail to convert are placed in the container referenced by the failedContainerSasUrl parameter.
You need to ensure the files are correctly processed.
How should you complete the code segment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Box 1: CreateJob -
Box 2: TaskSuccess -
TaskSuccess: Upload the file(s) only after the task process exits with an exit code of 0.
Incorrect: TaskCompletion: Upload the file(s) after the task process exits, no matter what the exit code was.
Box 3: TaskFailure -
TaskFailure:Upload the file(s) only after the task process exits with a nonzero exit code.
Box 4: OutputFiles -
To specify output files for a task, create a collection of OutputFile objects and assign it to the CloudTask.OutputFiles property when you create the task.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.azure.batch.protocol.models.outputfileuploadcondition https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/batch-task-output-files
Explanation
Box 1: CreateJob -
Box 2: TaskSuccess -
TaskSuccess: Upload the file(s) only after the task process exits with an exit code of 0.
Incorrect: TaskCompletion: Upload the file(s) after the task process exits, no matter what the exit code was.
Box 3: TaskFailure -
TaskFailure:Upload the file(s) only after the task process exits with a nonzero exit code.
Box 4: OutputFiles -
To specify output files for a task, create a collection of OutputFile objects and assign it to the CloudTask.OutputFiles property when you create the task.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.azure.batch.protocol.models.outputfileuploadcondition https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/batch-task-output-files
send
light_mode
delete
Question #2
You are writing code to create and run an Azure Batch job.
You have created a pool of compute nodes.
You need to choose the right class and its method to submit a batch job to the Batch service.
Which method should you use?
You have created a pool of compute nodes.
You need to choose the right class and its method to submit a batch job to the Batch service.
Which method should you use?
- AJobOperations.EnableJobAsync(String, IEnumerable<BatchClientBehavior>,CancellationToken)
- BJobOperations.CreateJob()
- CCloudJob.Enable(IEnumerable<BatchClientBehavior>)
- DJobOperations.EnableJob(String,IEnumerable<BatchClientBehavior>)
- ECloudJob.CommitAsync(IEnumerable<BatchClientBehavior>, CancellationToken)
Correct Answer:
E
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the
BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
The Commit method submits the job to the Batch service. Initially the job has no tasks.
{
CloudJob job = batchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob();
job.Id = JobId;
job.PoolInformation = new PoolInformation { PoolId = PoolId }; job.Commit();
}
...
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet
E
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the
BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
The Commit method submits the job to the Batch service. Initially the job has no tasks.
{
CloudJob job = batchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob();
job.Id = JobId;
job.PoolInformation = new PoolInformation { PoolId = PoolId }; job.Commit();
}
...
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet
send
light_mode
delete
Question #3
DRAG DROP -
You are developing Azure WebJobs.
You need to recommend a WebJob type for each scenario.
Which WebJob type should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate WebJob types to the correct scenarios. Each WebJob type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

You are developing Azure WebJobs.
You need to recommend a WebJob type for each scenario.
Which WebJob type should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate WebJob types to the correct scenarios. Each WebJob type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:

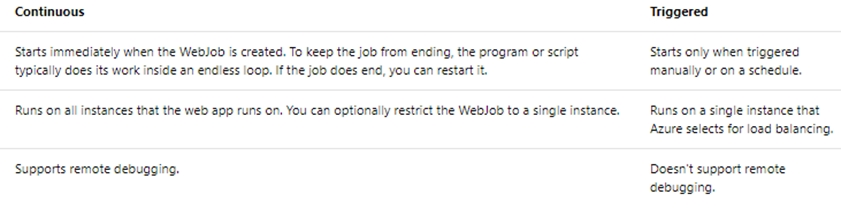
Box 1: Continuous -
Continuous runs on all instances that the web app runs on. You can optionally restrict the WebJob to a single instance.
Box 2: Triggered -
Triggered runs on a single instance that Azure selects for load balancing.
Box 3: Continuous -
Continuous supports remote debugging.
Note:
The following table describes the differences between continuous and triggered WebJobs.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/web-sites-create-web-jobs

Box 1: Continuous -
Continuous runs on all instances that the web app runs on. You can optionally restrict the WebJob to a single instance.
Box 2: Triggered -
Triggered runs on a single instance that Azure selects for load balancing.
Box 3: Continuous -
Continuous supports remote debugging.
Note:
The following table describes the differences between continuous and triggered WebJobs.

References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/web-sites-create-web-jobs
send
light_mode
delete
Question #4
You are developing a software solution for an autonomous transportation system. The solution uses large data sets and Azure Batch processing to simulate navigation sets for entire fleets of vehicles.
You need to create compute nodes for the solution on Azure Batch.
What should you do?
You need to create compute nodes for the solution on Azure Batch.
What should you do?
- AIn the Azure portal, add a Job to a Batch account.
- BIn a .NET method, call the method: BatchClient.PoolOperations.CreateJob
- CIn Python, implement the class: JobAddParameter
- DIn Azure CLI, run the command: az batch pool create
- EIn a .NET method, call the method: BatchClient.PoolOperations.CreatePool
- FIn Python, implement the class: TaskAddParameter
- GIn the Azure CLI, run the command: az batch account create
Correct Answer:
B
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the
BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
Note:
Step 1: Create a pool of compute nodes. When you create a pool, you specify the number of compute nodes for the pool, their size, and the operating system.
When each task in your job runs, it's assigned to execute on one of the nodes in your pool.
Step 2: Create a job. A job manages a collection of tasks. You associate each job to a specific pool where that job's tasks will run.
Step 3: Add tasks to the job. Each task runs the application or script that you uploaded to process the data files it downloads from your Storage account. As each task completes, it can upload its output to Azure Storage.
Incorrect Answers:
C, F: To create a Batch pool in Python, the app uses the PoolAddParameter class to set the number of nodes, VM size, and a pool configuration.
E: BatchClient.PoolOperations does not have a CreateJob method.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-python
B
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the
BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
Note:
Step 1: Create a pool of compute nodes. When you create a pool, you specify the number of compute nodes for the pool, their size, and the operating system.
When each task in your job runs, it's assigned to execute on one of the nodes in your pool.
Step 2: Create a job. A job manages a collection of tasks. You associate each job to a specific pool where that job's tasks will run.
Step 3: Add tasks to the job. Each task runs the application or script that you uploaded to process the data files it downloads from your Storage account. As each task completes, it can upload its output to Azure Storage.
Incorrect Answers:
C, F: To create a Batch pool in Python, the app uses the PoolAddParameter class to set the number of nodes, VM size, and a pool configuration.
E: BatchClient.PoolOperations does not have a CreateJob method.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-python
send
light_mode
delete
Question #5
DRAG DROP -
You are deploying an Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS) cluster that will use multiple containers.
You need to create the cluster and verify that the services for the containers are configured correctly and available.
Which four commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate command segments from the list of command segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
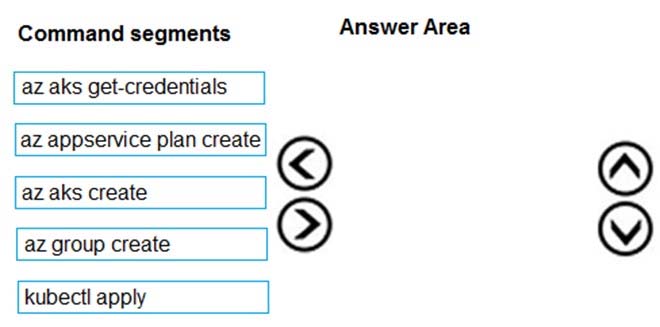
You are deploying an Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS) cluster that will use multiple containers.
You need to create the cluster and verify that the services for the containers are configured correctly and available.
Which four commands should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate command segments from the list of command segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
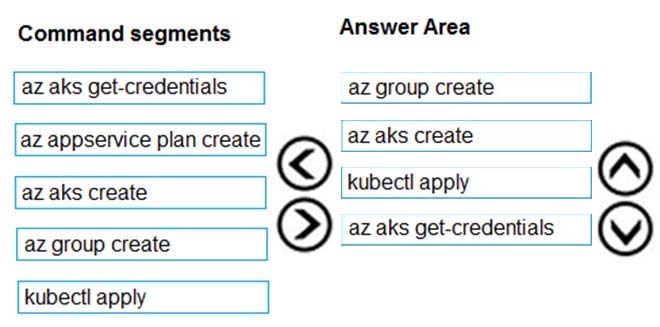
Step 1: az group create -
Create a resource group with the az group create command. An Azure resource group is a logical group in which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
Example: The following example creates a resource group named myAKSCluster in the eastus location. az group create --name myAKSCluster --location eastus
Step 2 : az aks create -
Use the az aks create command to create an AKS cluster.
Step 3: kubectl apply -
To deploy your application, use the kubectl apply command. This command parses the manifest file and creates the defined Kubernetes objects.
Step 4: az aks get-credentials -
Configure it with the credentials for the new AKS cluster. Example: az aks get-credentials --name aks-cluster --resource-group aks-resource-group
References:
https://docs.bitnami.com/azure/get-started-aks/

Step 1: az group create -
Create a resource group with the az group create command. An Azure resource group is a logical group in which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
Example: The following example creates a resource group named myAKSCluster in the eastus location. az group create --name myAKSCluster --location eastus
Step 2 : az aks create -
Use the az aks create command to create an AKS cluster.
Step 3: kubectl apply -
To deploy your application, use the kubectl apply command. This command parses the manifest file and creates the defined Kubernetes objects.
Step 4: az aks get-credentials -
Configure it with the credentials for the new AKS cluster. Example: az aks get-credentials --name aks-cluster --resource-group aks-resource-group
References:
https://docs.bitnami.com/azure/get-started-aks/
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
