Microsoft 70-767 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (142 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) projects. The project consists of several packages that load data warehouse tables.
You need to extend the control flow design for each package to use the following control flow while minimizing development efforts and maintenance:
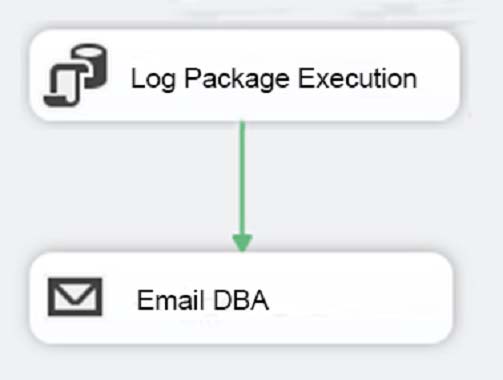
Solution: You add the control flow to an ASP.NET assembly. You add a script task that references this assembly to each data warehouse load package.
Does the solution meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) projects. The project consists of several packages that load data warehouse tables.
You need to extend the control flow design for each package to use the following control flow while minimizing development efforts and maintenance:

Solution: You add the control flow to an ASP.NET assembly. You add a script task that references this assembly to each data warehouse load package.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
A package consists of a control flow and, optionally, one or more data flows. You create the control flow in a package by using the Control Flow tab in SSIS
Designer.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/control-flow/control-flow
B
A package consists of a control flow and, optionally, one or more data flows. You create the control flow in a package by using the Control Flow tab in SSIS
Designer.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/control-flow/control-flow
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) projects. The project consists of several packages that load data warehouse tables.
You need to extend the control flow design for each package to use the following control flow while minimizing development efforts and maintenance:
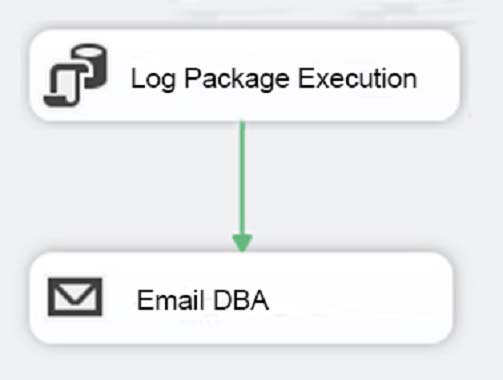
Solution: You add the control flow to a control flow package part. You add an instance of the control flow package part to each data warehouse load package.
Does the solution meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) projects. The project consists of several packages that load data warehouse tables.
You need to extend the control flow design for each package to use the following control flow while minimizing development efforts and maintenance:

Solution: You add the control flow to a control flow package part. You add an instance of the control flow package part to each data warehouse load package.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
A
A package consists of a control flow and, optionally, one or more data flows. You create the control flow in a package by using the Control Flow tab in SSIS
Designer.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/control-flow/control-flow
A
A package consists of a control flow and, optionally, one or more data flows. You create the control flow in a package by using the Control Flow tab in SSIS
Designer.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/control-flow/control-flow
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.

✑ Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
✑ Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.
✑ Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to implement partitioning for the Fact.Ticket table.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, drag the appropriate actions to the correct locations. Each action may be used once, more than once or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: More than one combination of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct combinations you select.
Select and Place:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.

✑ Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
✑ Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.
✑ Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to implement partitioning for the Fact.Ticket table.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, drag the appropriate actions to the correct locations. Each action may be used once, more than once or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: More than one combination of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct combinations you select.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
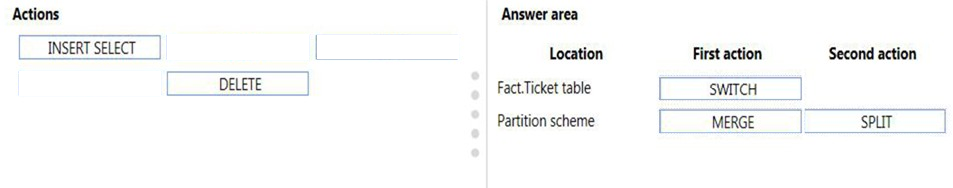
From scenario: - Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
The detailed steps for the recurring partition maintenance tasks are:
Step 1: Fact.Ticket Table, First action
SWITCH OUT: Create a staging table and then switch a partition between the history table and the staging table using the ALTER TABLE (Transact-SQL) statement with the SWITCH PARTITION argument
Step 2: Partition.Scheme, First action
MERGE RANGE: Merge the empty partition 1 with partition 2 using the ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION (Transact-SQL) with MERGE RANGE
Step 2: Partition.Scheme, Second action
SPLIT RANGE: Create a new empty partition using the ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION (Transact-SQL) with SPLIT RANGE.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/tables/manage-retention-of-historical-data-in-system-versioned-temporal-tables

From scenario: - Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
The detailed steps for the recurring partition maintenance tasks are:
Step 1: Fact.Ticket Table, First action
SWITCH OUT: Create a staging table and then switch a partition between the history table and the staging table using the ALTER TABLE (Transact-SQL) statement with the SWITCH PARTITION argument
Step 2: Partition.Scheme, First action
MERGE RANGE: Merge the empty partition 1 with partition 2 using the ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION (Transact-SQL) with MERGE RANGE
Step 2: Partition.Scheme, Second action
SPLIT RANGE: Create a new empty partition using the ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION (Transact-SQL) with SPLIT RANGE.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/tables/manage-retention-of-historical-data-in-system-versioned-temporal-tables
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
✑ Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.
✑ Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.

✑ Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to configure the Fact.Order table.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
✑ Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.
✑ Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.

✑ Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to configure the Fact.Order table.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
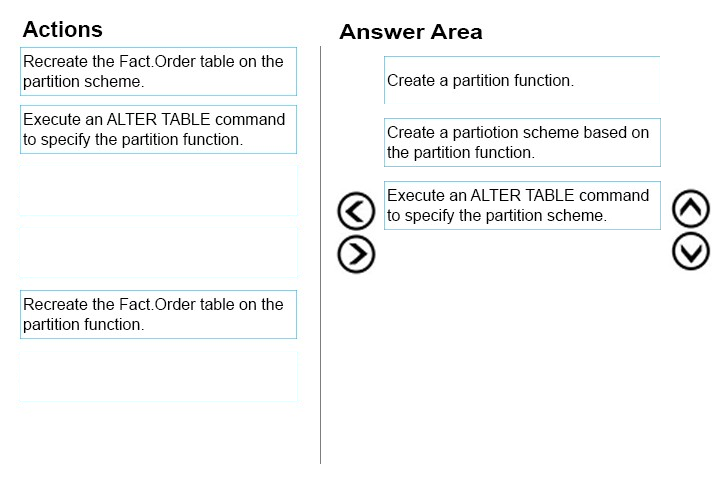
From scenario: Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data. Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the
Fact.Order partition.
Step 1: Create a partition function.
Using CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION is the first step in creating a partitioned table or index.
Step 2: Create a partition scheme based on the partition function.
To migrate SQL Server partition definitions to SQL Data Warehouse simply:
✑ Eliminate the SQL Server partition scheme.
✑ Add the partition function definition to your CREATE TABLE.
Step 3: Execute an ALTER TABLE command to specify the partition function.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-partition

From scenario: Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data. Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the
Fact.Order partition.
Step 1: Create a partition function.
Using CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION is the first step in creating a partitioned table or index.
Step 2: Create a partition scheme based on the partition function.
To migrate SQL Server partition definitions to SQL Data Warehouse simply:
✑ Eliminate the SQL Server partition scheme.
✑ Add the partition function definition to your CREATE TABLE.
Step 3: Execute an ALTER TABLE command to specify the partition function.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-partition
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ - Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ - Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
✑ - Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.
✑ - Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
✑ - Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.
✑ - Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ - Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to optimize data loading for the Dimension.Customer table.
Which three Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-
SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: You will not need all of the Transact-SQL segments.
Select and Place:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse instance that supports several client applications.
The data warehouse includes the following tables: Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, Dimension.Date, Fact.Ticket, and Fact.Order. The
Dimension.SalesTerritory and Dimension.Customer tables are frequently updated. The Fact.Order table is optimized for weekly reporting, but the company wants to change it to daily. The Fact.Order table is loaded by using an ETL process. Indexes have been added to the table over time, but the presence of these indexes slows data loading.
All data in the data warehouse is stored on a shared SAN. All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment. The data warehouse has grown and the cost of storage has increased. Data older than one year is accessed infrequently and is considered historical.
You have the following requirements:
✑ Implement table partitioning to improve the manageability of the data warehouse and to avoid the need to repopulate all transactional data each night. Use a partitioning strategy that is as granular as possible.
✑ - Partition the Fact.Order table and retain a total of seven years of data.
✑ - Partition the Fact.Ticket table and retain seven years of data. At the end of each month, the partition structure must apply a sliding window strategy to ensure that a new partition is available for the upcoming month, and that the oldest month of data is archived and removed.
✑ - Optimize data loading for the Dimension.SalesTerritory, Dimension.Customer, and Dimension.Date tables.
✑ - Incrementally load all tables in the database and ensure that all incremental changes are processed.
✑ - Maximize the performance during the data loading process for the Fact.Order partition.
✑ - Ensure that historical data remains online and available for querying.
✑ - Reduce ongoing storage costs while maintaining query performance for current data.
You are not permitted to make changes to the client applications.
You need to optimize data loading for the Dimension.Customer table.
Which three Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-
SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: You will not need all of the Transact-SQL segments.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:

Step 1: USE DB1 -
From Scenario: All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment.
Step 2: EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db
Before you can enable a table for change data capture, the database must be enabled. To enable the database, use the sys.sp_cdc_enable_db stored procedure. sys.sp_cdc_enable_db has no parameters.
Step 3: EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source schema = N 'schema' etc.
Sys.sp_cdc_enable_table enables change data capture for the specified source table in the current database.
Partial syntax:
sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
[ @source_schema = ] 'source_schema',
[ @source_name = ] 'source_name' , [,[ @capture_instance = ] 'capture_instance' ]
[,[ @supports_net_changes = ] supports_net_changes ]
Etc.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sys-sp-cdc-enable-table-transact-sql https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sys-sp-cdc-enable-db-transact-sql

Step 1: USE DB1 -
From Scenario: All tables are in a database named DB1. You have a second database named DB2 that contains copies of production data for a development environment.
Step 2: EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db
Before you can enable a table for change data capture, the database must be enabled. To enable the database, use the sys.sp_cdc_enable_db stored procedure. sys.sp_cdc_enable_db has no parameters.
Step 3: EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source schema = N 'schema' etc.
Sys.sp_cdc_enable_table enables change data capture for the specified source table in the current database.
Partial syntax:
sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
[ @source_schema = ] 'source_schema',
[ @source_name = ] 'source_name' , [,[ @capture_instance = ] 'capture_instance' ]
[,[ @supports_net_changes = ] supports_net_changes ]
Etc.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sys-sp-cdc-enable-table-transact-sql https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sys-sp-cdc-enable-db-transact-sql
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
