Microsoft 70-764 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (342 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have an on-premises server that runs Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Standard Edition.
You need to identify missing indexes.
What should you use?
You have an on-premises server that runs Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Standard Edition.
You need to identify missing indexes.
What should you use?
- AActivity Monitor
- BSp_who3
- CSQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) Object Explorer
- DSQL Server Data Collector
- ESQL Server Data Tools (SSDT)
- FSQL Server Configuration Manager
Correct Answer:
D
Data Collector can gather performance information from multiple SQL Server instances and store it in a single repository. It has three built-in data collecting specifications (data collectors) designed to collect the most important performance metrics. The information collected by default is about disk usage, query statistics, and server activity.
The Query Statistics data collection set collects information about query statistics, activity, execution plans and text on the SQL Server instance.
Missing indexes can be found with the execution plans.
References: https://www.sqlshack.com/sql-server-performance-monitoring-data-collector/
D
Data Collector can gather performance information from multiple SQL Server instances and store it in a single repository. It has three built-in data collecting specifications (data collectors) designed to collect the most important performance metrics. The information collected by default is about disk usage, query statistics, and server activity.
The Query Statistics data collection set collects information about query statistics, activity, execution plans and text on the SQL Server instance.
Missing indexes can be found with the execution plans.
References: https://www.sqlshack.com/sql-server-performance-monitoring-data-collector/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
HOTSPOT -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
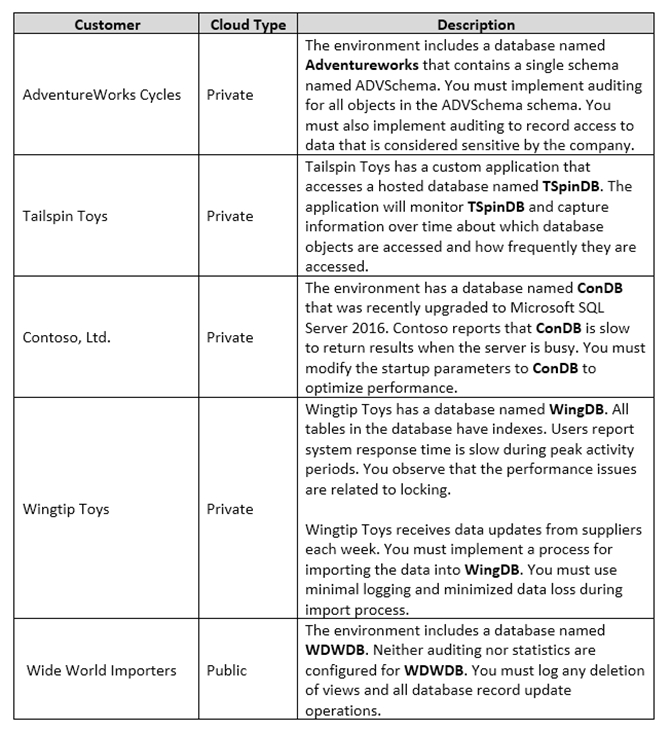
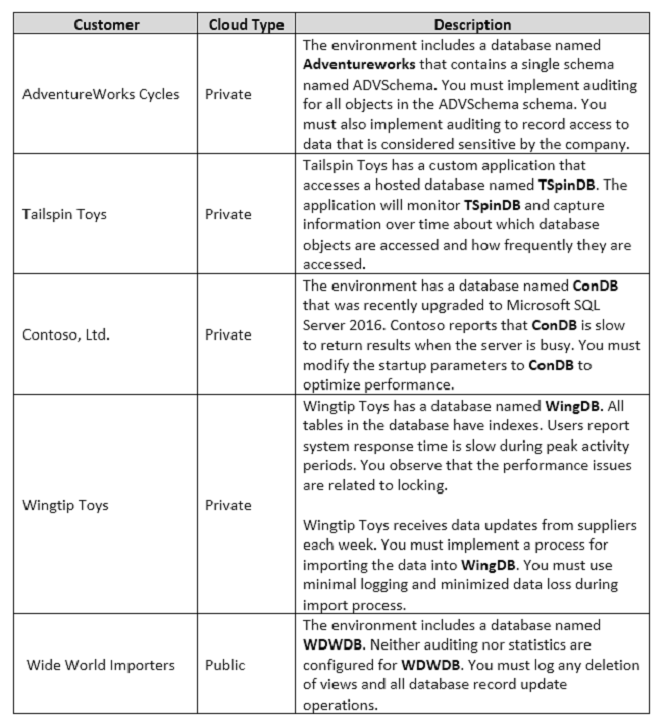
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
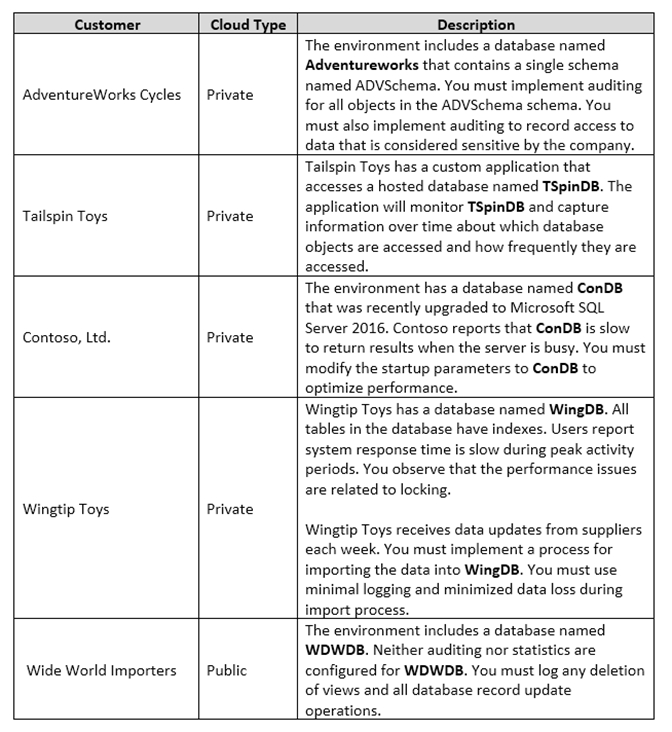
You need to configure monitoring for Tailspin Toys.
In the table below, identify the monitoring tool that you must use for each activity.
NOTE: Make only one selection in each column.
Hot Area:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to configure monitoring for Tailspin Toys.
In the table below, identify the monitoring tool that you must use for each activity.
NOTE: Make only one selection in each column.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
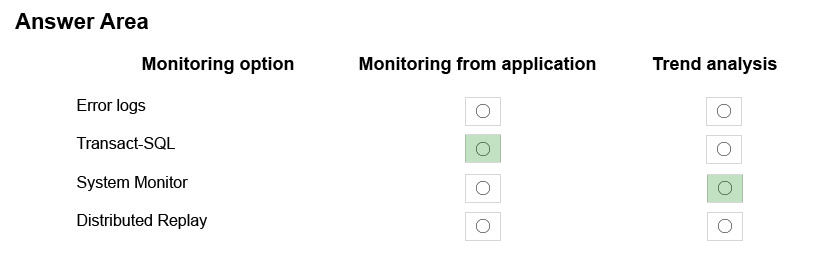
Monitoring from application: Transact-SQL
Transact-SQL can be used to monitor a customized application.
Trend analysis: System Monitor -
System Monitor can provide trend analysis.
From question:
Tailspin Toys has a custom application that accesses a hosted database named TSpinDB. The application will monitor TSpinDB and capture information over time about which database objects are accessed and how frequently they are accessed.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/performance/performance-monitoring-and-tuning-tools

Monitoring from application: Transact-SQL
Transact-SQL can be used to monitor a customized application.
Trend analysis: System Monitor -
System Monitor can provide trend analysis.
From question:
Tailspin Toys has a custom application that accesses a hosted database named TSpinDB. The application will monitor TSpinDB and capture information over time about which database objects are accessed and how frequently they are accessed.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/performance/performance-monitoring-and-tuning-tools
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
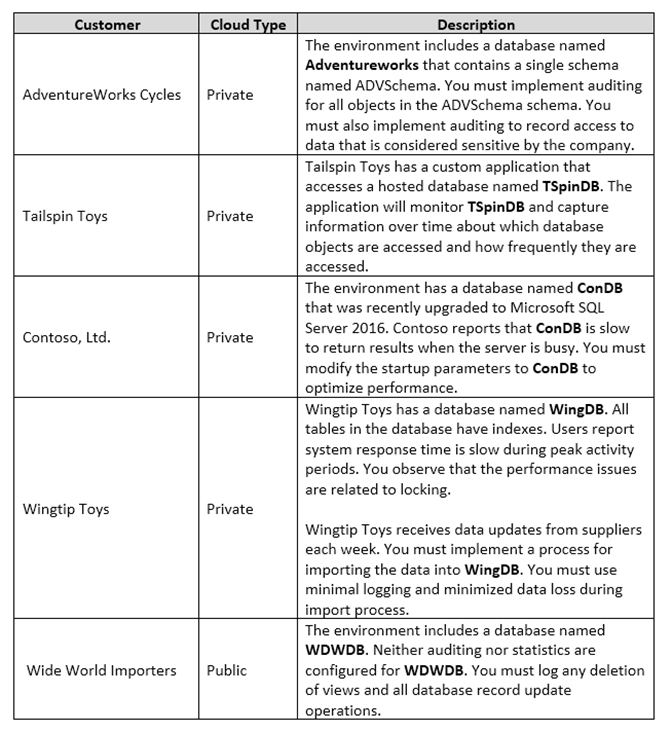
You need to implement a process for importing data into WingDB.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to implement a process for importing data into WingDB.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
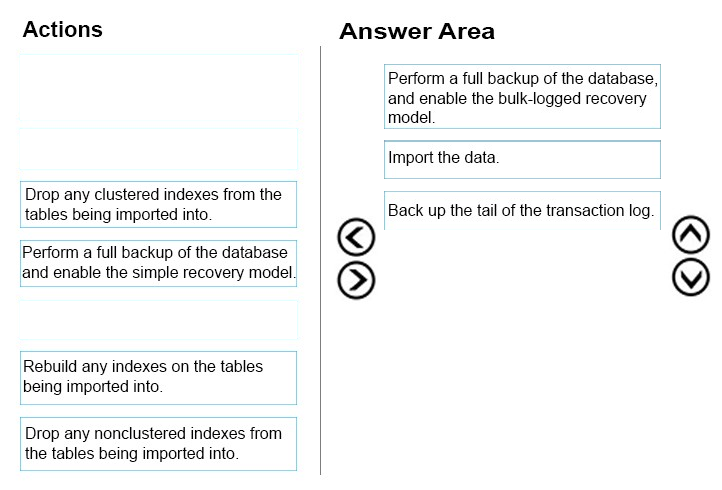
Step 1: Perform a full backup of the database and enable the bulk-logged recovery model.
Not: Simple recovery model.
With the Simple recovery model we cannot minimize data loss.
Step 2: Import the data -
Step 3: Backup the tail of the transaction log.
For databases that use full and bulk-logged recovery, database backups are necessary but not sufficient. Transaction log backups are also required.
Note: Three recovery models exist: simple, full, and bulk-logged. Typically, a database uses the full recovery model or simple recovery model. A database can be switched to another recovery model at any time.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/backup-restore/recovery-models-sql-server

Step 1: Perform a full backup of the database and enable the bulk-logged recovery model.
Not: Simple recovery model.
With the Simple recovery model we cannot minimize data loss.
Step 2: Import the data -
Step 3: Backup the tail of the transaction log.
For databases that use full and bulk-logged recovery, database backups are necessary but not sufficient. Transaction log backups are also required.
Note: Three recovery models exist: simple, full, and bulk-logged. Typically, a database uses the full recovery model or simple recovery model. A database can be switched to another recovery model at any time.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/backup-restore/recovery-models-sql-server
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
HOTSPOT -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
You need to configure auditing for the Adventure Works environment.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to configure auditing for the Adventure Works environment.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Box 1: CREATE SERVER AUDIT -
Create the server audit.
You must implement auditing to record access to data that is considered sensitive by the company.
Create database audit -
Box 2: ALTER SERVER AUDIT -
Enable the server audit.
Box 3: CREATE DATABASE AUDIT -
Create the database audit specification.
Box 4: FOR SERVER AUDIIT -
You must implement auditing for all objects in the ADVSchema.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/auditing/create-a-server-audit-and-database-audit-specification

Box 1: CREATE SERVER AUDIT -
Create the server audit.
You must implement auditing to record access to data that is considered sensitive by the company.
Create database audit -
Box 2: ALTER SERVER AUDIT -
Enable the server audit.
Box 3: CREATE DATABASE AUDIT -
Create the database audit specification.
Box 4: FOR SERVER AUDIIT -
You must implement auditing for all objects in the ADVSchema.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/auditing/create-a-server-audit-and-database-audit-specification
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
HOTSPOT -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
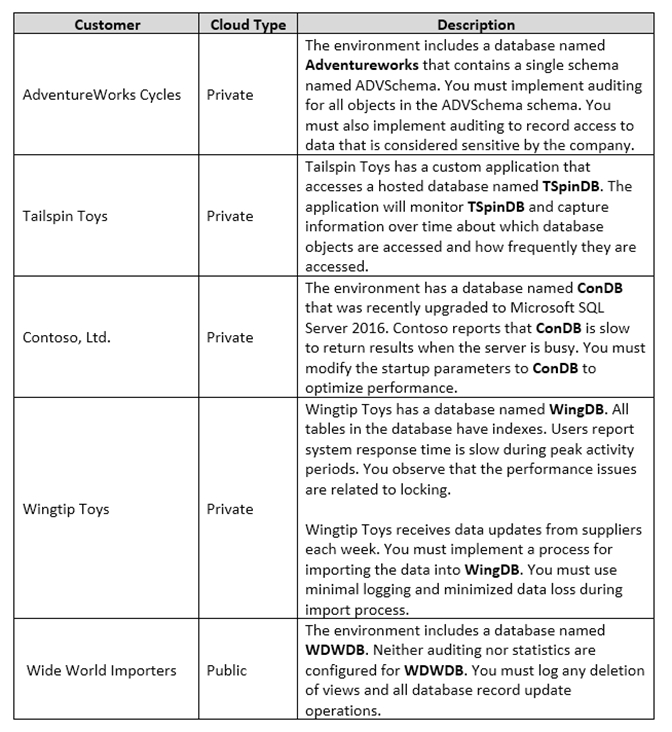
You need to configure the Contoso instance.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the answer area.
Hot Area:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to configure the Contoso instance.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the answer area.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
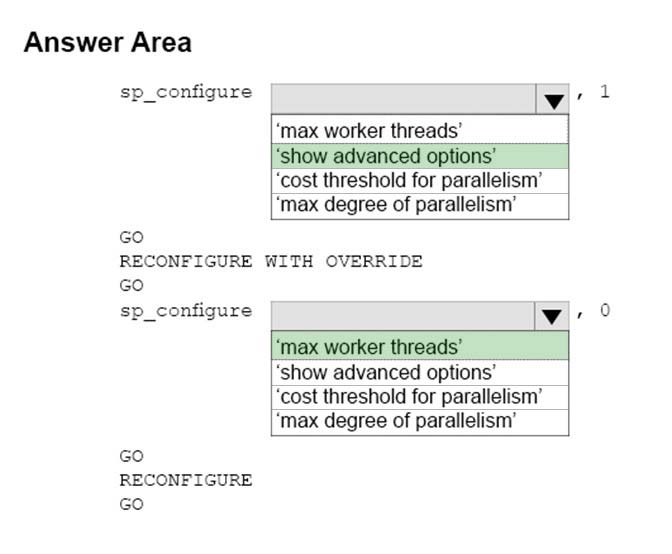
Box 1: show advanced options -
Advanced configuration options are displayed by first setting show advanced option to 1.
Box 2: max worker threads -
SQL Server uses the native thread services of the operating systems so that one or more threads support each network that SQL Server supports simultaneously, another thread handles database checkpoints, and a pool of threads handles all users. The default value for max worker threads is 0. This enables SQL Server to automatically configure the number of worker threads at startup. The default setting is best for most systems.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/configure-windows/configure-the-max-worker-threads-server-configuration-option

Box 1: show advanced options -
Advanced configuration options are displayed by first setting show advanced option to 1.
Box 2: max worker threads -
SQL Server uses the native thread services of the operating systems so that one or more threads support each network that SQL Server supports simultaneously, another thread handles database checkpoints, and a pool of threads handles all users. The default value for max worker threads is 0. This enables SQL Server to automatically configure the number of worker threads at startup. The default setting is best for most systems.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/configure-windows/configure-the-max-worker-threads-server-configuration-option
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
You need to monitor WingDB and gather information for troubleshooting issues.
What should you use?
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to monitor WingDB and gather information for troubleshooting issues.
What should you use?
- Asp_updatestats
- Bsp_lock
- Csys.dm_os_waiting_tasks
- Dsys.dm_tran_active_snapshot_database_transactions
- EActivity Monitor
Correct Answer:
B
The sp_lock system stored procedure is packaged with SQL Server and will give you insight into the locks that are happening on your system. This procedure returns much of its information from the syslock info in the master database, which is a system table that contains information on all granted, converting, and waiting lock requests.
Note: sp_lock will be removed in a future version of Microsoft SQL Server. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature. To obtain information about locks in the SQL Server Database Engine, use the sys.dm_tran_locks dynamic management view. sys.dm_tran_locks returns information about currently active lock manager resources in SQL Server 2008and later. Each row represents a currently active request to the lock manager for a lock that has been granted or is waiting to be granted.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sp-lock-transact-sql
B
The sp_lock system stored procedure is packaged with SQL Server and will give you insight into the locks that are happening on your system. This procedure returns much of its information from the syslock info in the master database, which is a system table that contains information on all granted, converting, and waiting lock requests.
Note: sp_lock will be removed in a future version of Microsoft SQL Server. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature. To obtain information about locks in the SQL Server Database Engine, use the sys.dm_tran_locks dynamic management view. sys.dm_tran_locks returns information about currently active lock manager resources in SQL Server 2008and later. Each row represents a currently active request to the lock manager for a lock that has been granted or is waiting to be granted.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sp-lock-transact-sql
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
HOTSPOT -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.
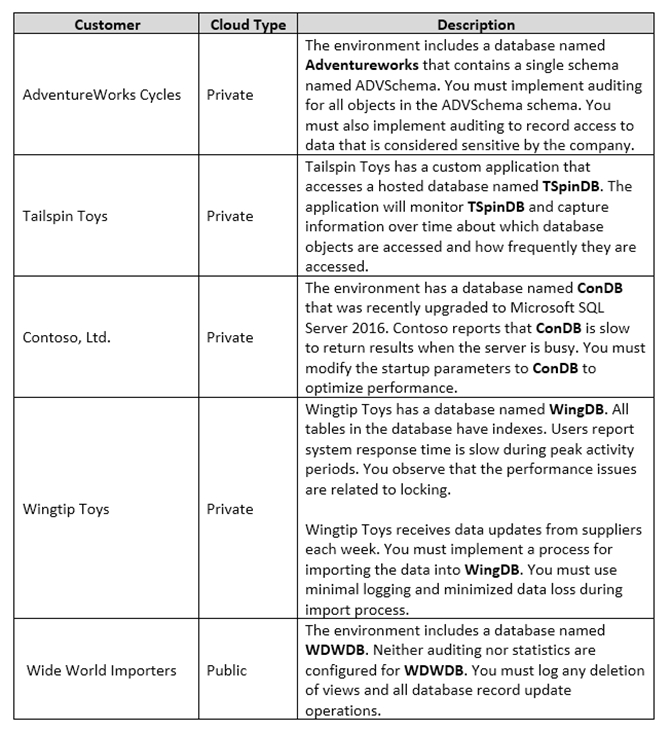
You need to configure auditing for WDWDB.
In the table below, identify the event type that you must audit for each activity.
Hot Area:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are a database administrator for a company that has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server environment and Microsoft Azure SQL Database instances. The environment hosts several customer databases, and each customer uses a dedicated instance. The environments that you manage are shown in the following table.

You need to configure auditing for WDWDB.
In the table below, identify the event type that you must audit for each activity.
Hot Area:

send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
HOTSPOT -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
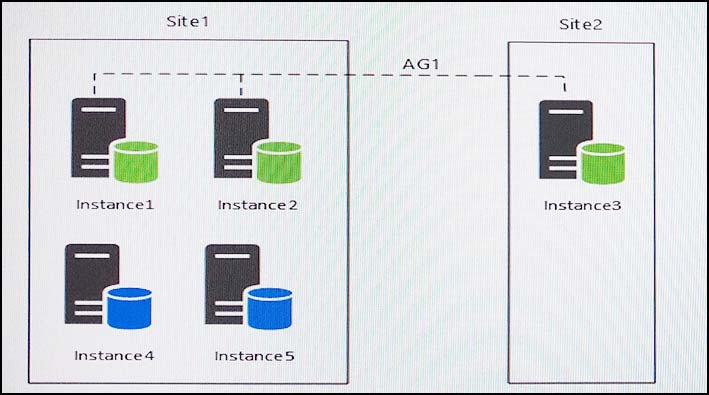
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.
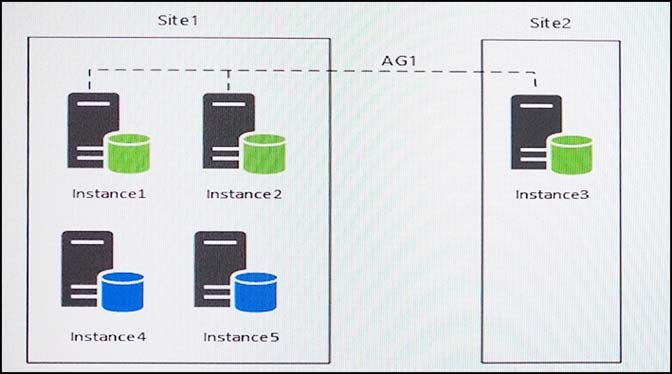
You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.
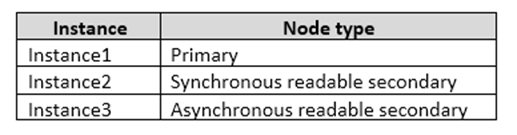
Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
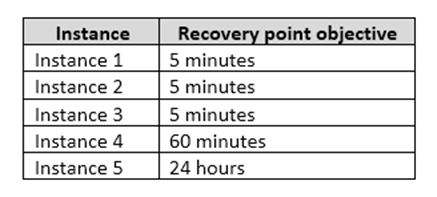
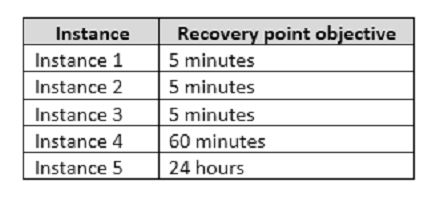
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.
Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
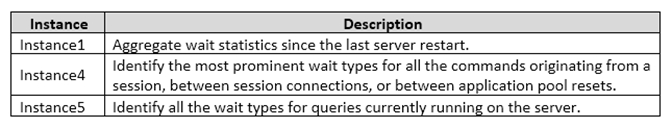
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.
You need to create the connection strings for the operations and reporting systems.
In the table below, identify the option that must be specified in each connection string.
NOTE: Make only one selection in each column.
Hot Area:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.

You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.

Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.

Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.

You need to create the connection strings for the operations and reporting systems.
In the table below, identify the option that must be specified in each connection string.
NOTE: Make only one selection in each column.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
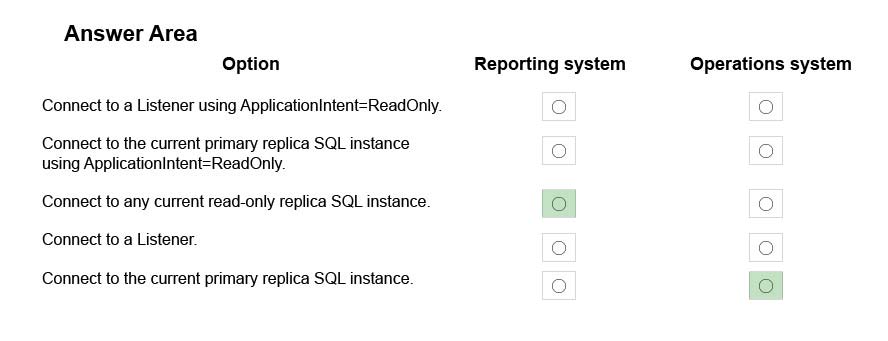
Reporting system: Connect to any current read-only replica instance
We configure Read-OnlyAccess on an Availability Replica. We select Read-intent only. Only read-only connections are allowed to secondary databases of this replica. The secondary database(s) are all available for read access.
From Scenario: Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role.
The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
Operating system: Connect to the current primary replica SQL instance
By default, both read-write and read-intent access are allowed to the primary replica and no connections are allowed to secondary replicas of an Always On availability group.
From scenario: Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/availability-groups/windows/configure-read-only-access-on-an-availability-replica-sql-server

Reporting system: Connect to any current read-only replica instance
We configure Read-OnlyAccess on an Availability Replica. We select Read-intent only. Only read-only connections are allowed to secondary databases of this replica. The secondary database(s) are all available for read access.
From Scenario: Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role.
The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
Operating system: Connect to the current primary replica SQL instance
By default, both read-write and read-intent access are allowed to the primary replica and no connections are allowed to secondary replicas of an Always On availability group.
From scenario: Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/availability-groups/windows/configure-read-only-access-on-an-availability-replica-sql-server
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.
You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.

Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.
Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.

You need to propose a new process for the StagedExternal database.
Which five actions should you recommended be performed in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.

You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.

Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.

Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.

You need to propose a new process for the StagedExternal database.
Which five actions should you recommended be performed in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
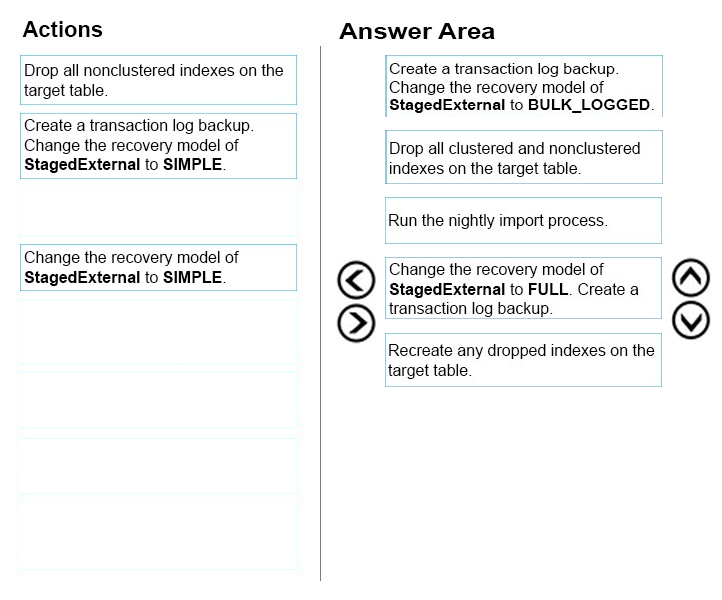
From scenario: Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternaldatabase log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
All databases use the full recovery model.
References: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190421(v=sql.105).aspx

From scenario: Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternaldatabase log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
All databases use the full recovery model.
References: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190421(v=sql.105).aspx
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
DRAG DROP -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.
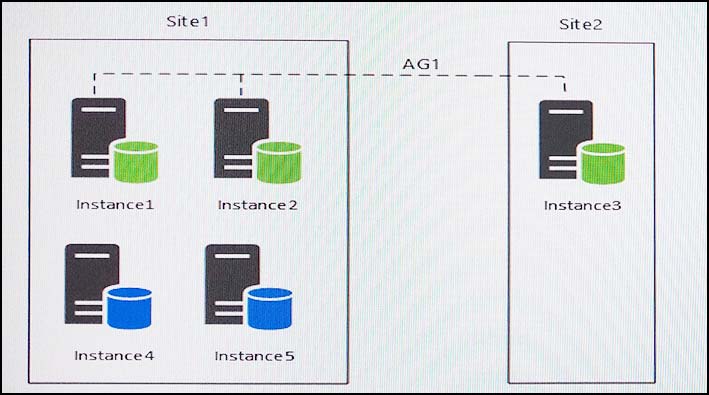
You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.

Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.
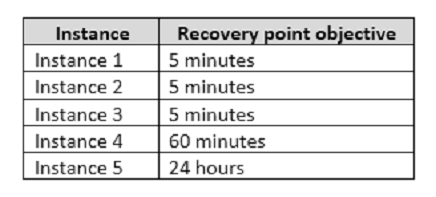
Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.

You need to analyze the wait type and statistics for specific instanced in the environment.
Which object should you use to gather information about each instance? To answer, drag the appropriate objects to the correct instances. Each object may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
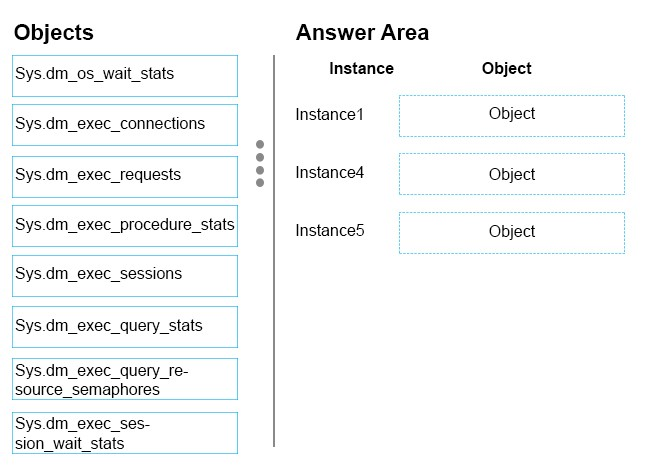
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have five servers that run Microsoft Windows 2012 R2. Each server hosts a Microsoft SQL Server instance. The topology for the environment is shown in the following diagram.

You have an Always On Availability group named AG1. The details for AG1 are shown in the following table.

Instance1 experiences heavy read-write traffic. The instance hosts a database named OperationsMain that is four terabytes (TB) in size. The database has multiple data files and filegroups. One of the filegroups is read_only and is half of the total database size.
Instance4 and Instance5 are not part of AG1. Instance4 is engaged in heavy read-write I/O.
Instance5 hosts a database named StagedExternal. A nightly BULK INSERT process loads data into an empty table that has a rowstore clustered index and two nonclustered rowstore indexes.
You must minimize the growth of the StagedExternal database log file during the BULK INSERT operations and perform point-in-time recovery after the BULK
INSERT transaction. Changes made must not interrupt the log backup chain.
You plan to add a new instance named Instance6 to a datacenter that is geographically distant from Site1 and Site2. You must minimize latency between the nodes in AG1.
All databases use the full recovery model. All backups are written to the network location \\SQLBackup\. A separate process copies backups to an offsite location.
You should minimize both the time required to restore the databases and the space required to store backups. The recovery point objective (RPO) for each instance is shown in the following table.

Full backups of OperationsMain take longer than six hours to complete. All SQL Server backups use the keyword COMPRESSION.
You plan to deploy the following solutions to the environment. The solutions will access a database named DB1 that is part of AG1.
✑ Reporting system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader role. The user has
EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries make no changes to the data. The queries must be load balanced over variable read-only replicas.
✑ Operations system: This solution accesses data inDB1with a login that is mapped to a database user that is a member of the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles. The user has EXECUTE permissions on the database. Queries from the operations system will perform both DDL and DML operations.
The wait statistics monitoring requirements for the instances are described in the following table.

You need to analyze the wait type and statistics for specific instanced in the environment.
Which object should you use to gather information about each instance? To answer, drag the appropriate objects to the correct instances. Each object may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
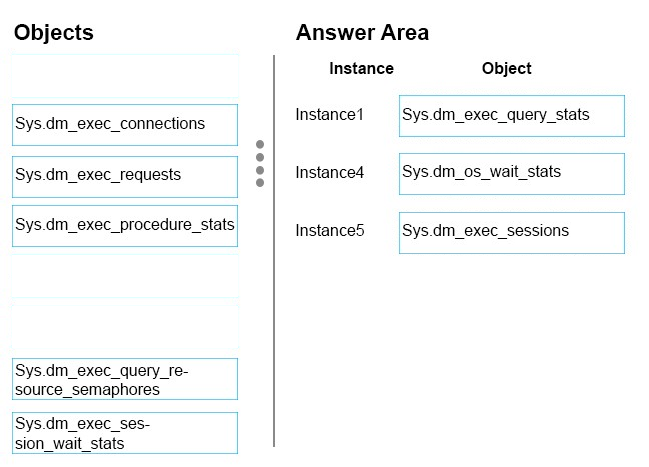
Instance 1: sys.dm_exec_query_stats
From Scenario: Instance1 requirement: Aggregate statistics since last server restart. sys.dm_exec_query_stats returns aggregate performance statistics for cachedquery plans in SQL Server.
Instance 4: sys.dm_os_wait_stats
sys.dm_os_wait_statsreturns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed.
From Scenario: Instance4 requirement: Identify the most prominent wait types.

Instance 5:sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats
From Scenario: Instance5 requirement: Identify all wait types for queries currently running on the server. sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats returns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed for each session.

Instance 1: sys.dm_exec_query_stats
From Scenario: Instance1 requirement: Aggregate statistics since last server restart. sys.dm_exec_query_stats returns aggregate performance statistics for cachedquery plans in SQL Server.
Instance 4: sys.dm_os_wait_stats
sys.dm_os_wait_statsreturns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed.
From Scenario: Instance4 requirement: Identify the most prominent wait types.

Instance 5:sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats
From Scenario: Instance5 requirement: Identify all wait types for queries currently running on the server. sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats returns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed for each session.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages

