GIAC GCPM Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (355 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which of the following techniques is described in the statement below?
"It evaluates the abstract early start and finish dates and late start and finish dates for all activities devoid of any resource limitations by performing a forward and backward pass analysis through the schedule network."
"It evaluates the abstract early start and finish dates and late start and finish dates for all activities devoid of any resource limitations by performing a forward and backward pass analysis through the schedule network."
- AResource utilization
- BCritical Chain methodMost Voted
- CResource leveling heuristic
- DCritical path method
Correct Answer:
C
Answer option C is correct.
The Critical Path method evaluates the abstract early start and finish dates and late start and finish dates for all activities devoid of any resource limitations by performing a forward and backward pass analysis through the schedule network.
Critical Path Method, abbreviated CPM, or Critical Path Analysis, is a mathematically based algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is an important tool for effective project management. It provides the following benefits:
✑ Provides the graphical view of the project
✑ Predicts the time required to complete the project
✑ Shows which activities are critical to maintain the schedule and which are not
CPM models the activities and events of a project as a network. Activities are depicted as nodes on the network, and events that signify the beginning or ending of activities are depicted as arcs or lines between the nodes.
Answer option B is incorrect. The Critical Chain method is a project management technique in which schedule network analysis is used for the purpose of modifying and determining a set of project schedules to account for more inadequate than estimated project financial resources. This method tends to keep the resources levelly loaded, but requires the resources to be flexible in their start times and to quickly switch between tasks and task chains to keep the whole project on schedule. In the Critical Chain method, projects are completed more rapidly and with better scheduling consistency.
Answer option A is incorrect. Resource utilization simply means that the resource is scheduled for work.
Answer option C is incorrect. A resource leveling heuristic is a guideline, such as a maximum of 35 hours per week, per resource. It is a rule that usually signals the maximum amount of hours a resource may be utilized on the project.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Critical Path Scheduling
C
Answer option C is correct.
The Critical Path method evaluates the abstract early start and finish dates and late start and finish dates for all activities devoid of any resource limitations by performing a forward and backward pass analysis through the schedule network.
Critical Path Method, abbreviated CPM, or Critical Path Analysis, is a mathematically based algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is an important tool for effective project management. It provides the following benefits:
✑ Provides the graphical view of the project
✑ Predicts the time required to complete the project
✑ Shows which activities are critical to maintain the schedule and which are not
CPM models the activities and events of a project as a network. Activities are depicted as nodes on the network, and events that signify the beginning or ending of activities are depicted as arcs or lines between the nodes.
Answer option B is incorrect. The Critical Chain method is a project management technique in which schedule network analysis is used for the purpose of modifying and determining a set of project schedules to account for more inadequate than estimated project financial resources. This method tends to keep the resources levelly loaded, but requires the resources to be flexible in their start times and to quickly switch between tasks and task chains to keep the whole project on schedule. In the Critical Chain method, projects are completed more rapidly and with better scheduling consistency.
Answer option A is incorrect. Resource utilization simply means that the resource is scheduled for work.
Answer option C is incorrect. A resource leveling heuristic is a guideline, such as a maximum of 35 hours per week, per resource. It is a rule that usually signals the maximum amount of hours a resource may be utilized on the project.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Critical Path Scheduling
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Billy is the project manager of the PQW Project and she has an assigned project budget of $655,000. Currently she is 80 percent complete with the project though she was scheduled to be 100 percent done by this date. She has spent $490,000 to date and other than the project schedule, which was delayed because of a vendor, the project is going well. What should Billy report as her schedule performance index for this project?
- A100 percent because the vendor caused her lateness
- B$524,000
- C80
- D1.23
Correct Answer:
C
Answer option C is correct.
Schedule performance index (SPI) is the measure of schedule efficiency on a project. It is used in trend analysis to predict future performance. SPI is the ratio of earned value to planned value. The SPI is calculated based on the following formula:
SPI = Earned value (EV) / Planned value (PV)
If the SPI value is greater than 1, it indicates better than expected performance, whereas if the value is less than 1, it shows poor performance. The SPI value of 1 indicates that the project is right on target. You can find the planned value by multiplying where Billy should be in the project, 100 percent, by the project's budget.
In this instance the planned value is $655,000 because she is to be 100 percent complete.
Answer option A is incorrect. The SPI simply reports a value not an explanation.
Answer option D is incorrect. 1.23 is the cost performance index for the project.
Answer option B is incorrect. $524,000 is the earned value for the project.
Reference: The Project Management Body of Knowledge, Fifth edition, Section 7.4.2.1, Page 217
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Earned Value Analysis and Forecasting
C
Answer option C is correct.
Schedule performance index (SPI) is the measure of schedule efficiency on a project. It is used in trend analysis to predict future performance. SPI is the ratio of earned value to planned value. The SPI is calculated based on the following formula:
SPI = Earned value (EV) / Planned value (PV)
If the SPI value is greater than 1, it indicates better than expected performance, whereas if the value is less than 1, it shows poor performance. The SPI value of 1 indicates that the project is right on target. You can find the planned value by multiplying where Billy should be in the project, 100 percent, by the project's budget.
In this instance the planned value is $655,000 because she is to be 100 percent complete.
Answer option A is incorrect. The SPI simply reports a value not an explanation.
Answer option D is incorrect. 1.23 is the cost performance index for the project.
Answer option B is incorrect. $524,000 is the earned value for the project.
Reference: The Project Management Body of Knowledge, Fifth edition, Section 7.4.2.1, Page 217
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Earned Value Analysis and Forecasting
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
You work as a project manager for HRM Inc. Your organization has developed a product and is facing problems with current suppliers. Which of the following techniques will help your organization in the above issue?
- ARisk analysis
- BMake-or-buy analysis
- CChecklist analysis
- DBreak-even analysis
Correct Answer:
B
Answer option B is correct.
A make-or-buy analysis is used to verify whether a particular work can best be accomplished by the project team or must be purchased from outside sources. The budget constraints can influence the make-or-buy decisions. A make-or-buy analysis must consider all related costs; both direct and indirect support costs. A make-or-buy analysis takes place when an organization that has developed a product or part, or significantly modified a product or part, is facing problems with current suppliers, or has reduced capacity or varying demand.
Answer option A is incorrect. Risk analysis is the science of risks and their probability and evaluation in a business or a process. It is an important factor in security enhancement and prevention in a system. Risk analysis should be performed as part of the risk management process for each project. The outcome of the risk analysis would be the creation or review of the risk register to identify and quantify risk elements to the project and their potential impact.
Risk analysis includes the following three types of analysis:
✑ Risk assessment determines money, time, and effort needed for providing protection.
✑ Business impact analysis identifies assets to be protected.
✑ Threat analysis determines factors against which protection should be provided.
Answer option C is incorrect. The checklist analysis approach is a risk identification process. It is an organized approach built on the past knowledge incorporated in checklist questions. Checklist analysis is used for high-level or comprehensive analysis, as well as for root cause analysis. It is relevant to any activity or system, including equipment issues and human factors issues and is generally performed by an individual trained to understand the checklist questions. Checklist analysis is sometimes performed by a small group, not necessarily risk analysis experts.
Answer option D is incorrect. Break-even analysis is a method of price determination. In this method, the demand for a product and the cost of overproduction of the product are taken into consideration. The analysis of cost behavior and its impact on profit is known as break-even analysis. Its main advantage is that it shows different levels of profits at different levels of output.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Make vs. Buy Analysis
B
Answer option B is correct.
A make-or-buy analysis is used to verify whether a particular work can best be accomplished by the project team or must be purchased from outside sources. The budget constraints can influence the make-or-buy decisions. A make-or-buy analysis must consider all related costs; both direct and indirect support costs. A make-or-buy analysis takes place when an organization that has developed a product or part, or significantly modified a product or part, is facing problems with current suppliers, or has reduced capacity or varying demand.
Answer option A is incorrect. Risk analysis is the science of risks and their probability and evaluation in a business or a process. It is an important factor in security enhancement and prevention in a system. Risk analysis should be performed as part of the risk management process for each project. The outcome of the risk analysis would be the creation or review of the risk register to identify and quantify risk elements to the project and their potential impact.
Risk analysis includes the following three types of analysis:
✑ Risk assessment determines money, time, and effort needed for providing protection.
✑ Business impact analysis identifies assets to be protected.
✑ Threat analysis determines factors against which protection should be provided.
Answer option C is incorrect. The checklist analysis approach is a risk identification process. It is an organized approach built on the past knowledge incorporated in checklist questions. Checklist analysis is used for high-level or comprehensive analysis, as well as for root cause analysis. It is relevant to any activity or system, including equipment issues and human factors issues and is generally performed by an individual trained to understand the checklist questions. Checklist analysis is sometimes performed by a small group, not necessarily risk analysis experts.
Answer option D is incorrect. Break-even analysis is a method of price determination. In this method, the demand for a product and the cost of overproduction of the product are taken into consideration. The analysis of cost behavior and its impact on profit is known as break-even analysis. Its main advantage is that it shows different levels of profits at different levels of output.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Make vs. Buy Analysis
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
You work as a project manager for HRM Inc. You are working with your team on calculating the project's critical path. You have calculated that one of the activities on the critical path is going to be delayed by six days due to a vendor fault. How will this condition affect the project's completion date?
- AThe project will be early by six days.
- BThe project may be late depending on the amount of float available for the critical path.
- CThe project manager should check to see if float is available for other activities and shift the delayed work to another path.
- DThe project will be late by six days.
Correct Answer:
B
Answer option B is correct.
If a task on the critical path is delayed by six days, then the project will be late.
Answer option A is incorrect. The project won't be early, as a critical path activity is late.
Answer option D is incorrect. The critical path does not have float.
Answer option C is incorrect. Work typically cannot be moved from path to path in the network diagram, as the network diagram illustrates the flow of the project work.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Critical Path Scheduling
B
Answer option B is correct.
If a task on the critical path is delayed by six days, then the project will be late.
Answer option A is incorrect. The project won't be early, as a critical path activity is late.
Answer option D is incorrect. The critical path does not have float.
Answer option C is incorrect. Work typically cannot be moved from path to path in the network diagram, as the network diagram illustrates the flow of the project work.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Time and Cost Management
Objective: Critical Path Scheduling
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
You work as a project manager for HRM Inc. You have to address the following information on the business case justifying the project, including return on investment. Which of the following documents will you use to address the above information?
- ARisk register
- BProject charter
- CStakeholder register
- DProject scope statement
Correct Answer:
B
Answer option B is correct.
A project charter is a document that officially recognizes and acknowledges that a project exists. It helps define requirements and expectations to all involved in the project. It is issued by the project sponsor. It can be as simple as a one-page form for a very small project, briefly describing the project and listing the responsibilities and authority of the project manager. Charters can be much longer, however, depending on the size of the project. In addition to formally authorizing a project, the charter provides the project manager with the authority to apply organizational resources to project activities. Project charters are important to the success of a project.
It's a good idea to have a project manager assigned to the project prior to the start of planning, and preferably while the project charter is being developed. Here's an example of a project charter.
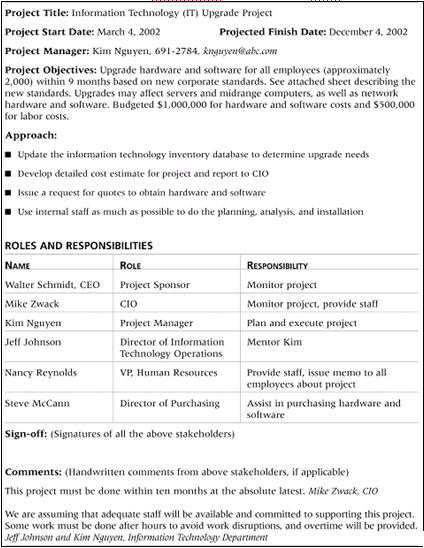
Answer option A is incorrect. A risk register is a document that contains the results of qualitative risk analysis, quantitative risk analysis, and risk response planning. Description, category, cause, probability of occurring, impact on objectives, proposed responses, owner, and the current status of all identified risks are put in the risk register.
Answer option C is incorrect. The stakeholder register is a project management document that contains a list of the stakeholders associated with the project. It assesses how they are involved in the project and identifies what role they play in the organization. The information in this document can be very perceptive and is meant for limited exchange only. It also contains relevant information about the stakeholders, such as their requirements, expectations, and influence on the project.
Answer option D is incorrect. Project scope statement is the narrative description of the project scope. It includes major deliverables, project assumptions, project constraints, and a description of work. It helps developing a common understanding of project scope among the stakeholders. It is a documented description of the project to answer questions such as What is being produced?, How is it being produced?, What is included?, etc.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Project Charter and Scope Management
Objective: Project Charters
B
Answer option B is correct.
A project charter is a document that officially recognizes and acknowledges that a project exists. It helps define requirements and expectations to all involved in the project. It is issued by the project sponsor. It can be as simple as a one-page form for a very small project, briefly describing the project and listing the responsibilities and authority of the project manager. Charters can be much longer, however, depending on the size of the project. In addition to formally authorizing a project, the charter provides the project manager with the authority to apply organizational resources to project activities. Project charters are important to the success of a project.
It's a good idea to have a project manager assigned to the project prior to the start of planning, and preferably while the project charter is being developed. Here's an example of a project charter.

Answer option A is incorrect. A risk register is a document that contains the results of qualitative risk analysis, quantitative risk analysis, and risk response planning. Description, category, cause, probability of occurring, impact on objectives, proposed responses, owner, and the current status of all identified risks are put in the risk register.
Answer option C is incorrect. The stakeholder register is a project management document that contains a list of the stakeholders associated with the project. It assesses how they are involved in the project and identifies what role they play in the organization. The information in this document can be very perceptive and is meant for limited exchange only. It also contains relevant information about the stakeholders, such as their requirements, expectations, and influence on the project.
Answer option D is incorrect. Project scope statement is the narrative description of the project scope. It includes major deliverables, project assumptions, project constraints, and a description of work. It helps developing a common understanding of project scope among the stakeholders. It is a documented description of the project to answer questions such as What is being produced?, How is it being produced?, What is included?, etc.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Project Charter and Scope Management
Objective: Project Charters
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
Virginia is the project manager for her organization. She has hired a subject matter expert to interview the project stakeholders on certain identified risks within the project. The subject matter expert will assess the risk event with what specific goal in mind?
- ATo determine the validity of each risk event
- BTo determine the level of probability and impact for each risk event
- CTo determine the probability and schedule of the risk event
- DTo determine the bias of the risk event based on each person interviewed
Correct Answer:
B
Answer option B is correct.
During the risk assessment process, the goal is to determine the level of probability and impact for each risk event.
Answer option A is incorrect. The validity of each risk event is not a valid result of the risk probability and assessment technique.
Answer option D is incorrect. The bias towards certain risk events may come to light during the risk assessment technique, but this is not the primary goal of the process.
Answer option C is incorrect. The probability and impact are determined, not the probability and schedule during the risk assessment technique.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide)"
Chapter: Quality and Risk Management
Objective: Risk Probability and Impact Matrices
B
Answer option B is correct.
During the risk assessment process, the goal is to determine the level of probability and impact for each risk event.
Answer option A is incorrect. The validity of each risk event is not a valid result of the risk probability and assessment technique.
Answer option D is incorrect. The bias towards certain risk events may come to light during the risk assessment technique, but this is not the primary goal of the process.
Answer option C is incorrect. The probability and impact are determined, not the probability and schedule during the risk assessment technique.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide)"
Chapter: Quality and Risk Management
Objective: Risk Probability and Impact Matrices
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
You are the project manager of the TRT Project. During the execution phase of your project, Rick, a team member, complains that other team members are isolating him and this isolation is bothering him. Which of the following is NOT a recommended step to resolve the issue?
- AGet feedback on Rick from other team members.
- BShift Rick to another project.
- CGet more feedback from Rick.
- DApply team building measures to improve the team's effectiveness.
Correct Answer:
B
Answer option B is correct.
Shifting Rick to another project is a bad approach towards resolving the issue. Rick is a part of team and you must get more information from other resources before taking any decision. Furthermore, it should be one of your professional abilities to improve the team's effectiveness.
Answer options D, C, and A are incorrect. You should take all these steps to resolve such issues.
Reference: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK Guide), Fifth Edition, ISBN:9781933890517, Section 9.4.
Chapter: Communications and Human Resources
Objective: Team Building
B
Answer option B is correct.
Shifting Rick to another project is a bad approach towards resolving the issue. Rick is a part of team and you must get more information from other resources before taking any decision. Furthermore, it should be one of your professional abilities to improve the team's effectiveness.
Answer options D, C, and A are incorrect. You should take all these steps to resolve such issues.
Reference: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK Guide), Fifth Edition, ISBN:9781933890517, Section 9.4.
Chapter: Communications and Human Resources
Objective: Team Building
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
Which of the following forecasting methods is described in the statement below?
"It is based on the assumption that it is possible to identify some factors that might influence the variable that is being forecasted."
"It is based on the assumption that it is possible to identify some factors that might influence the variable that is being forecasted."
- ACausal/econometric method
- BJudgmental method
- CEnsemble forecasting
- DTime series method
Correct Answer:
A
Answer option A is correct.
Forecasting is the process of estimating or predicting in unknown situations. Forecasting is about predicting the future as accurately as possible with the help of all the information available, including historical data and knowledge of any future events that might impact forecasts. The forecasting methods are categorized as follows:
✑ Time series method: It uses historical data as the basis for estimating future outcomes.
✑ Causal/econometric method: This forecasting method is based on the assumption that it is possible to identify some factors that might influence the variable that is being forecasted. If the causes are understood, projections of the influencing variables can be made and used in the forecast.
✑ Judgmental method: Judgmental forecasting methods incorporate intuitive judgments, opinions, and subjective probability estimates.
✑ Other methods: Other methods may include probabilistic forecasting, simulation, and ensemble forecasting.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Forecasting and Integrated Change Control
A
Answer option A is correct.
Forecasting is the process of estimating or predicting in unknown situations. Forecasting is about predicting the future as accurately as possible with the help of all the information available, including historical data and knowledge of any future events that might impact forecasts. The forecasting methods are categorized as follows:
✑ Time series method: It uses historical data as the basis for estimating future outcomes.
✑ Causal/econometric method: This forecasting method is based on the assumption that it is possible to identify some factors that might influence the variable that is being forecasted. If the causes are understood, projections of the influencing variables can be made and used in the forecast.
✑ Judgmental method: Judgmental forecasting methods incorporate intuitive judgments, opinions, and subjective probability estimates.
✑ Other methods: Other methods may include probabilistic forecasting, simulation, and ensemble forecasting.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Forecasting and Integrated Change Control
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
FILL BLANK -
Fill in the blank with the appropriate term.
_____________________(also called contractor conferences, vendor conferences, and pre-bid conferences) are meetings with prospective sellers prior to preparation of a bid or proposal.
Fill in the blank with the appropriate term.
_____________________(also called contractor conferences, vendor conferences, and pre-bid conferences) are meetings with prospective sellers prior to preparation of a bid or proposal.
Correct Answer:
Bidder conferences
Bidder conferences (also called contractor conferences, vendor conferences, and pre-bid conferences) are meetings with prospective sellers prior to preparation of a bid or proposal. They are used to ensure that all prospective sellers have a clear, common understanding of the procurement. All potential sellers are given equal standing during this initial buyer and seller interaction to produce the best bid. The meeting can discuss the request for quote, request for proposal, or the invitation for bid - all dependent on what the customer has requested.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Monitoring Your Projects Progress
Bidder conferences
Bidder conferences (also called contractor conferences, vendor conferences, and pre-bid conferences) are meetings with prospective sellers prior to preparation of a bid or proposal. They are used to ensure that all prospective sellers have a clear, common understanding of the procurement. All potential sellers are given equal standing during this initial buyer and seller interaction to produce the best bid. The meeting can discuss the request for quote, request for proposal, or the invitation for bid - all dependent on what the customer has requested.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Procurement and Project Integration
Objective: Monitoring Your Projects Progress
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
Identify Risks is the process of determining which risks may affect the project. Which of the following are inputs of the Identify risks process?
- ARisk management plan
- BRisk register
- CScope baseline
- DProject documents
Correct Answer:
ACD
Answer options C, D, and A are correct.
Identify risks is one of the five processes related to the risks in a project. In this process, those risks are determined that may affect the project. In this process, the characteristics of these identified risks are documented.
Inputs -
There are eleven inputs in the Identify risks process:
✑ Risk management plan
✑ Activity cost estimates
✑ Activity duration estimates
✑ Scope baseline
✑ Stakeholder register
✑ Cost management plan
✑ Schedule management plan
✑ Quality management plan
✑ Project documents
✑ Enterprise environmental factors
✑ Organizational process assets
Outputs -

The risk identification process covers the total scope of a project and produces only one output, the risk register.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Quality and Risk Management
Objective: Risk Identification and Assessment
ACD
Answer options C, D, and A are correct.
Identify risks is one of the five processes related to the risks in a project. In this process, those risks are determined that may affect the project. In this process, the characteristics of these identified risks are documented.
Inputs -
There are eleven inputs in the Identify risks process:
✑ Risk management plan
✑ Activity cost estimates
✑ Activity duration estimates
✑ Scope baseline
✑ Stakeholder register
✑ Cost management plan
✑ Schedule management plan
✑ Quality management plan
✑ Project documents
✑ Enterprise environmental factors
✑ Organizational process assets
Outputs -

The risk identification process covers the total scope of a project and produces only one output, the risk register.
Reference: "Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Fourth edition"
Chapter: Quality and Risk Management
Objective: Risk Identification and Assessment
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
