Cisco® 642-885 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (131 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
Which type of BGP session behaves like an EBGP session during session establishment but behaves like an IBGP session when propagating routing updates where the local preference, multi-exit discriminator, and next-hop attributes are not changed?
- ABGP sessions between a route reflector and its clients
- BBGP sessions between a route reflector and its non-client IBGP peers
- CBGP sessions between a route reflector and another route reflector
- DIntra-confederation IBGP sessions
- EIntra-confederation EBGP sessions
Correct Answer:
E
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.7/routing/configuration/guide/rc37bgp.html#wp1191371
BGP Routing Domain Confederation
One way to reduce the iBGP mesh is to divide an autonomous system into multiple subautonomous systems and group them into a single confederation. To the outside world, the confederation looks like a single autonomous system. Each autonomous system is fully meshed within itself and has a few connections to other autonomous systems in the same confederation. Although the peers in different autonomous systems have eBGP sessions, they exchange routing information as if they were iBGP peers. Specifically, the next hop, MED, and local preference information is preserved. This feature allows you to retain a single IGP for all of the autonomous systems.
E
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.7/routing/configuration/guide/rc37bgp.html#wp1191371
BGP Routing Domain Confederation
One way to reduce the iBGP mesh is to divide an autonomous system into multiple subautonomous systems and group them into a single confederation. To the outside world, the confederation looks like a single autonomous system. Each autonomous system is fully meshed within itself and has a few connections to other autonomous systems in the same confederation. Although the peers in different autonomous systems have eBGP sessions, they exchange routing information as if they were iBGP peers. Specifically, the next hop, MED, and local preference information is preserved. This feature allows you to retain a single IGP for all of the autonomous systems.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
You noticed a recent change to the BGP configuration on a PE router, the bgp scan time has been changed from the default value to 30s. Which three effects will this change have? (Choose three.)
- AThe BGP table will be examined and verified more frequently
- BThe BGP keepalive messages will be sent to the BGP peers at a faster rate
- CThe BGP table will be modified more quickly in the event that a next-hop address becomes unreachable
- DThe CPU load of the router will increase
- EThe minimum time interval between sending EBGP and IBGP routing updates will decrease
- FThe BGP convergence time will increase
Correct Answer:
ACD
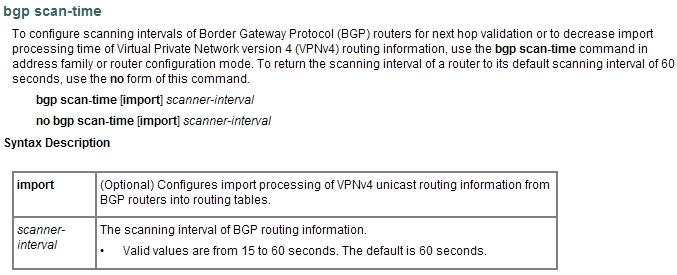
ACD

send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
On Cisco IOS-XR, which BGP process can be distributed into multiple instances?
- ABGP process manager
- BBGP RIB process
- CBGP speaker process
- DBGP scanner process
- EBGP dampening process
Correct Answer:
C
Cisco IOS XR allows you to control the configuration of the number of distributed speakers and enables you to selectively assign neighbors to specific speakers.
On the CRS-1 platform, multiple speaker processes up to 15 may be configured. However, configuring all the different speakers on the primary route processor simply adds to the load on the single RP.
Distributed speaker functionality is useful if Distributed Route Processor (DRP) hardware is available to take advantage of process placement. Later sections in this chapter depict distributed
BGP and placement of BGP process speakers on DRPs on a CRS-1 router.
In addition to the speaker process, BPM starts the bRIB process once BGP is configured. bRIB process is responsible for performing the best-path calculation based on partial best paths received from the speaker processes. The best route is installed into the bRIB and is advertised back to all speakers. The bRIB process is also responsible for installing routes
C
Cisco IOS XR allows you to control the configuration of the number of distributed speakers and enables you to selectively assign neighbors to specific speakers.
On the CRS-1 platform, multiple speaker processes up to 15 may be configured. However, configuring all the different speakers on the primary route processor simply adds to the load on the single RP.
Distributed speaker functionality is useful if Distributed Route Processor (DRP) hardware is available to take advantage of process placement. Later sections in this chapter depict distributed
BGP and placement of BGP process speakers on DRPs on a CRS-1 router.
In addition to the speaker process, BPM starts the bRIB process once BGP is configured. bRIB process is responsible for performing the best-path calculation based on partial best paths received from the speaker processes. The best route is installed into the bRIB and is advertised back to all speakers. The bRIB process is also responsible for installing routes
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
Refer to the configuration exhibit, taken from a Cisco IOS-XR router.
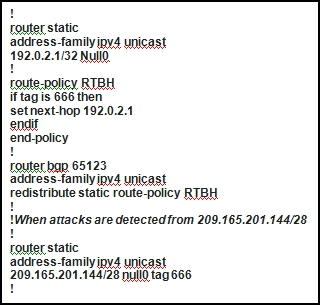
Which configuration change is required to properly enable this router as the signaling router for implementing source-based RTBH filtering?

Which configuration change is required to properly enable this router as the signaling router for implementing source-based RTBH filtering?
- ASet community (no-export) in the route policy
- BPass in the route policy
- CSet local-preference 1000 in the route policy
- DThe 192.0.2.1/32 static route should be tagged as 666 (tag 666)
Correct Answer:
A
A
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
Refer to the Cisco IOS-XR BGP configuration exhibit.

Identify two configuration errors. (Choose two.)

Identify two configuration errors. (Choose two.)
- AThe neighbor-group efg is missing the ebgp-multihop 2 configuration
- BThe ttl-security configuration command is missing the option to set the number of hops
- CThe passall route policy is wrong
- DThe route-policy passall in and route-policy passall out commands should be configured under the neighbor-group efg instead of the af-group abc
- EThe maximum-prefix 10 configuration should be configured under the af-group abc instead of the neighbor-group efg
Correct Answer:
CE
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_configuration_example09186a008010a28a.shtml
CE
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_configuration_example09186a008010a28a.shtml
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
