Cisco® 300-115 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (992 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
After the implementation of several different types of switches from different vendors, a network engineer notices that directly connected devices that use Cisco
Discovery Protocol are not visible. Which vendor-neutral protocol could be used to resolve this issue?
Discovery Protocol are not visible. Which vendor-neutral protocol could be used to resolve this issue?
- ALocal Area Mobility
- BLink Layer Discovery Protocol
- CNetFlow
- DDirected Response Protocol
Correct Answer:
B
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on an IEEE 802 local area network, principally wired Ethernet. LLDP performs functions similar to several proprietary protocols, such as the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP).
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Link_Layer_Discovery_Protocol
B
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on an IEEE 802 local area network, principally wired Ethernet. LLDP performs functions similar to several proprietary protocols, such as the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP).
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Link_Layer_Discovery_Protocol
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Several new switches have been added to the existing network as VTP clients. All of the new switches have been configured with the same VTP domain, password, and version. However, VLANs are not passing from the VTP server (existing network) to the VTP clients. What must be done to fix this?
- ARemove the VTP domain name from all switches with "null" and then replace it with the new domain name.
- BConfigure a different native VLAN on all new switches that are configured as VTP clients.
- CProvision one of the new switches to be the VTP server and duplicate information from the existing network.
- DEnsure that all switch interconnects are configured as trunks to allow VTP information to be transferred.
Correct Answer:
D
VTP allows switches to advertise VLAN information between other members of the same VTP domain. VTP allows a consistent view of the switched network across all switches. There are several reasons why the VLAN information can fail to be exchanged.
Verify these items if switches that run VTP fail to exchange VLAN information:
✑ VTP information only passes through a trunk port. Make sure that all ports that interconnect switches are configured as trunks and are actually trunking.
Make sure that if EtherChannels are created between two switches, only Layer 2 EtherChannels propagate VLAN information.
✑ Make sure that the VLANs are active in all the devices.
✑ One of the switches must be the VTP server in a VTP domain. All VLAN changes must be done on this switch in order to have them propagated to the VTP clients.
✑ The VTP domain name must match and it is case sensitive. CISCO and cisco are two different domain names.
✑ Make sure that no password is set between the server and client. If any password is set, make sure that the password is the same on both sides.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk689/technologies_tech_note09186a0080890613.shtml
D
VTP allows switches to advertise VLAN information between other members of the same VTP domain. VTP allows a consistent view of the switched network across all switches. There are several reasons why the VLAN information can fail to be exchanged.
Verify these items if switches that run VTP fail to exchange VLAN information:
✑ VTP information only passes through a trunk port. Make sure that all ports that interconnect switches are configured as trunks and are actually trunking.
Make sure that if EtherChannels are created between two switches, only Layer 2 EtherChannels propagate VLAN information.
✑ Make sure that the VLANs are active in all the devices.
✑ One of the switches must be the VTP server in a VTP domain. All VLAN changes must be done on this switch in order to have them propagated to the VTP clients.
✑ The VTP domain name must match and it is case sensitive. CISCO and cisco are two different domain names.
✑ Make sure that no password is set between the server and client. If any password is set, make sure that the password is the same on both sides.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk689/technologies_tech_note09186a0080890613.shtml
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
After implementing VTP, the extended VLANs are not being propagated to other VTP switches. What should be configured for extended VLANs?
- AVTP does not support extended VLANs and should be manually added to all switches.
- BEnable VTP version 3, which supports extended VLAN propagation.
- CVTP authentication is required when using extended VLANs because of their ability to cause network instability.
- DEnsure that all switches run the same Cisco IOS version. Extended VLANs will not propagate to different IOS versions when extended VLANs are in use.
Correct Answer:
B
✑ VTP version 1 and VTP version 2 do not propagate configuration information for extended-range VLANs (VLAN numbers 1006 to 4094). You must configure extended-range VLANs manually on each network device.
✑ VTP version 3 supports extended-range VLANs (VLAN numbers 1006 to 4094). If you convert from VTP version 3 to VTP version 2, the VLANs in the range
1006 to 4094 are removed from VTP control.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/15.1SY/config_guide/sup2T/vtp.pdf
B
✑ VTP version 1 and VTP version 2 do not propagate configuration information for extended-range VLANs (VLAN numbers 1006 to 4094). You must configure extended-range VLANs manually on each network device.
✑ VTP version 3 supports extended-range VLANs (VLAN numbers 1006 to 4094). If you convert from VTP version 3 to VTP version 2, the VLANs in the range
1006 to 4094 are removed from VTP control.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/15.1SY/config_guide/sup2T/vtp.pdf
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
Refer to the exhibit.
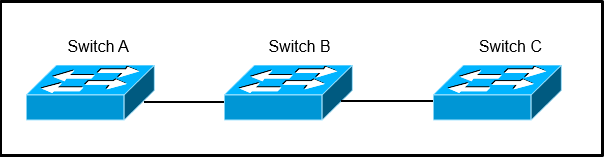
Switch A, B, and C are trunked together and have been properly configured for VTP. Switch C receives VLAN information from the VTP server Switch A, but
Switch B does not receive any VLAN information. What is the most probable cause of this behavior?

Switch A, B, and C are trunked together and have been properly configured for VTP. Switch C receives VLAN information from the VTP server Switch A, but
Switch B does not receive any VLAN information. What is the most probable cause of this behavior?
- ASwitch B is configured in transparent mode.
- BSwitch B is configured with an access port to Switch A, while Switch C is configured with a trunk port to Switch B.
- CThe VTP revision number of the Switch B is higher than that of Switch A.
- DThe trunk between Switch A and Switch B is misconfigured.
Correct Answer:
A
VTP transparent switches do not participate in VTP. A VTP transparent switch does not advertise its VLAN configuration and does not synchronize its VLAN configuration based on received advertisements, but transparent switches do forward VTP advertisements that they receive out their trunk ports in VTP Version 2.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk689/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094c52.shtml
A
VTP transparent switches do not participate in VTP. A VTP transparent switch does not advertise its VLAN configuration and does not synchronize its VLAN configuration based on received advertisements, but transparent switches do forward VTP advertisements that they receive out their trunk ports in VTP Version 2.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk689/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094c52.shtml
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
Refer to the exhibit.
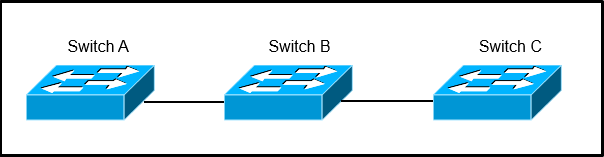
Switch A, B, and C are trunked together and have been properly configured for VTP. Switch B has all VLANs, but Switch C is not receiving traffic from certain
VLANs. What would cause this issue?

Switch A, B, and C are trunked together and have been properly configured for VTP. Switch B has all VLANs, but Switch C is not receiving traffic from certain
VLANs. What would cause this issue?
- AA VTP authentication mismatch occurred between Switch A and Switch B.
- BThe VTP revision number of Switch B is higher than that of Switch A.
- CVTP pruning is configured globally on all switches and it removed VLANs from the trunk interface that is connected to Switch C.
- DThe trunk between Switch A and Switch B is misconfigured.
Correct Answer:
C
VTP pruning increases network available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to reach the destination devices.
Without VTP pruning, a switch floods broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast traffic across all trunk links within a VTP domain even though receiving switches might discard them. VTP pruning is disabled by default.
VTP pruning blocks unneeded flooded traffic to VLANs on trunk ports that are included in the pruning-eligible list. The best explanation for why switch C is not seeing traffic from only some of the VLANs, is that VTP pruning has been configured.
C
VTP pruning increases network available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to reach the destination devices.
Without VTP pruning, a switch floods broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast traffic across all trunk links within a VTP domain even though receiving switches might discard them. VTP pruning is disabled by default.
VTP pruning blocks unneeded flooded traffic to VLANs on trunk ports that are included in the pruning-eligible list. The best explanation for why switch C is not seeing traffic from only some of the VLANs, is that VTP pruning has been configured.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #16
After the recent upgrade of the switching infrastructure, the network engineer notices that the port roles that were once "blocking" are now defined as "alternate" and "backup." What is the reason for this change?
- AThe new switches are using RSTP instead of legacy IEEE 802.1D STP.
- BIEEE 802.1D STP and PortFast have been configured by default on all newly implemented Cisco Catalyst switches.
- CThe administrator has defined the switch as the root in the STP domain.
- DThe port roles have been adjusted based on the interface bandwidth and timers of the new Cisco Catalyst switches.
Correct Answer:
A
RSTP works by adding an alternative port and a backup port compared to STP. These ports are allowed to immediately enter the forwarding state rather than passively wait for the network to converge.
RSTP bridge port roles:
* Root port A forwarding port that is the closest to the root bridge in terms of path cost
* Designated port A forwarding port for every LAN segment
* Alternate port A best alternate path to the root bridge. This path is different than using the root port. The alternative port moves to the forwarding state if there is a failure on the designated port for the segment.
* Backup port A backup/redundant path to a segment where another bridge port already connects. The backup port applies only when a single switch has two links to the same segment (collision domain). To have two links to the same collision domain, the switch must be attached to a hub.
* Disabled port Not strictly part of STP, a network administrator can manually disable a port
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/24062-146.html
A
RSTP works by adding an alternative port and a backup port compared to STP. These ports are allowed to immediately enter the forwarding state rather than passively wait for the network to converge.
RSTP bridge port roles:
* Root port A forwarding port that is the closest to the root bridge in terms of path cost
* Designated port A forwarding port for every LAN segment
* Alternate port A best alternate path to the root bridge. This path is different than using the root port. The alternative port moves to the forwarding state if there is a failure on the designated port for the segment.
* Backup port A backup/redundant path to a segment where another bridge port already connects. The backup port applies only when a single switch has two links to the same segment (collision domain). To have two links to the same collision domain, the switch must be attached to a hub.
* Disabled port Not strictly part of STP, a network administrator can manually disable a port
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/24062-146.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition using PortFast. After testing, it has been determined that several ports are not transitioning as they should. What is the reason for this?
- ARSTP has been enabled per interface and not globally.
- BThe STP root bridge selection is forcing key ports to remain in non-rapid transitioning mode.
- CSTP is unable to achieve rapid transition for trunk links.
- DThe switch does not have the processing power to ensure rapid transition for all ports.
Correct Answer:
C
RSTP can only achieve rapid transition to the forwarding state on edge ports and on point-to-point links, not on trunk links. The link type is automatically derived from the duplex mode of a port. A port that operates in full-duplex is assumed to be point-to-point, while a half-duplex port is considered as a shared port by default. This automatic link type setting can be overridden by explicit configuration. In switched networks today, most links operate in full-duplex mode and are treated as point-to-point links by RSTP. This makes them candidates for rapid transition to the forwarding state.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/24062-146.html
C
RSTP can only achieve rapid transition to the forwarding state on edge ports and on point-to-point links, not on trunk links. The link type is automatically derived from the duplex mode of a port. A port that operates in full-duplex is assumed to be point-to-point, while a half-duplex port is considered as a shared port by default. This automatic link type setting can be overridden by explicit configuration. In switched networks today, most links operate in full-duplex mode and are treated as point-to-point links by RSTP. This makes them candidates for rapid transition to the forwarding state.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/24062-146.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
Which technique automatically limits VLAN traffic to only the switches that require it?
- Aaccess lists
- BDTP in nonegotiate
- CVTP pruning
- DPBR
Correct Answer:
C
VTP pruning enhances network bandwidth use by reducing unnecessary flooded traffic, such as broadcast, multicast, unknown, and flooded unicast packets to only the switches that require it. VTP pruning increases available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to access the appropriate network devices. By default, VTP pruning is disabled.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12-2SX/configuration/guide/book/vtp.html#wp1020444
C
VTP pruning enhances network bandwidth use by reducing unnecessary flooded traffic, such as broadcast, multicast, unknown, and flooded unicast packets to only the switches that require it. VTP pruning increases available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to access the appropriate network devices. By default, VTP pruning is disabled.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12-2SX/configuration/guide/book/vtp.html#wp1020444
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
What effect does the mac address-table aging-time 180 command have on the MAC address-table?
- AThis is how long a dynamic MAC address will remain in the CAM table.
- BThe MAC address-table will be flushed every 3 minutes.
- CThe default timeout period will be 360 seconds.
- DARP requests will be processed less frequently by the switch.
- EThe MAC address-table will hold addresses 180 seconds longer than the default of 10 minutes.
Correct Answer:
A
You can configure the amount of time that an entry (the packet source MAC address and port that packet ingresses) remain in the MAC table.
To configure the aging time for all MAC addresses, perform this task:
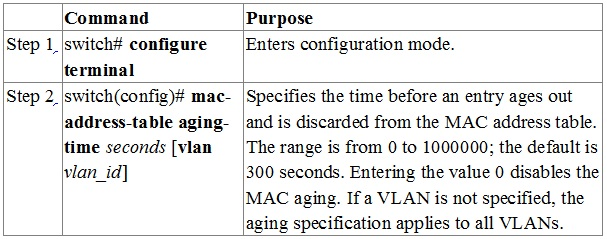
This example shows how to set the aging time for entries in the MAC address table to 600 seconds (10 minutes): switch# configure terminal switch(config)# mac-address-table aging-time 600
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli/CLIConfigurationGuide/MACAddress.html#wp1126206
A
You can configure the amount of time that an entry (the packet source MAC address and port that packet ingresses) remain in the MAC table.
To configure the aging time for all MAC addresses, perform this task:

This example shows how to set the aging time for entries in the MAC address table to 600 seconds (10 minutes): switch# configure terminal switch(config)# mac-address-table aging-time 600
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli/CLIConfigurationGuide/MACAddress.html#wp1126206
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
While working in the core network building, a technician accidently bumps the fiber connection between two core switches and damages one of the pairs of fiber.
As designed, the link was placed into a non-forwarding state due to a fault with UDLD. After the damaged cable was replaced, the link did not recover. What solution allows the network switch to automatically recover from such an issue?
As designed, the link was placed into a non-forwarding state due to a fault with UDLD. After the damaged cable was replaced, the link did not recover. What solution allows the network switch to automatically recover from such an issue?
- Amacros
- Berrdisable autorecovery
- CIP Event Dampening
- Dcommand aliases
- EBidirectional Forwarding Detection
Correct Answer:
B
There are a number of events which can disable a link on a Catalyst switch, such as the detection of a loopback, UDLD failure, or a broadcast storm. By default, manual intervention by an administrator is necessary to restore the interface to working order; this can be done by issuing shutdown followed by no shutdown on the interface. The idea behind requiring administrative action is so that a human engineer can intercede, assess, and (ideally) correct the issue. However, some configurations may be prone to accidental violations, and a steady recurrence of these can amount to a huge time sink for the administrative staff.
This is where errdisable autorecovery can be of great assistance. We can configure the switch to automatically re-enable any error-disabled interfaces after a specified timeout period. This gives the offending issue a chance to be cleared by the user (for example, by removing an unapproved device) without the need for administrative intervention.
Reference: http://packetlife.net/blog/2009/sep/14/errdisable-autorecovery/
B
There are a number of events which can disable a link on a Catalyst switch, such as the detection of a loopback, UDLD failure, or a broadcast storm. By default, manual intervention by an administrator is necessary to restore the interface to working order; this can be done by issuing shutdown followed by no shutdown on the interface. The idea behind requiring administrative action is so that a human engineer can intercede, assess, and (ideally) correct the issue. However, some configurations may be prone to accidental violations, and a steady recurrence of these can amount to a huge time sink for the administrative staff.
This is where errdisable autorecovery can be of great assistance. We can configure the switch to automatically re-enable any error-disabled interfaces after a specified timeout period. This gives the offending issue a chance to be cleared by the user (for example, by removing an unapproved device) without the need for administrative intervention.
Reference: http://packetlife.net/blog/2009/sep/14/errdisable-autorecovery/
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
