Cisco® 210-260 Exam Practice Questions (P. 1)
- Full Access (620 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #1
Which two services define cloud networks? (Choose two.)
- AInfrastructure as a Service
- BPlatform as a Service
- CSecurity as a Service
- DCompute as a Service
- ETenancy as a Service
Correct Answer:
AB
The diagram below depicts the Cloud Computing stack it shows three distinct categories within Cloud Computing: Software as a Service, Platform as a Service and Infrastructure as a Service.
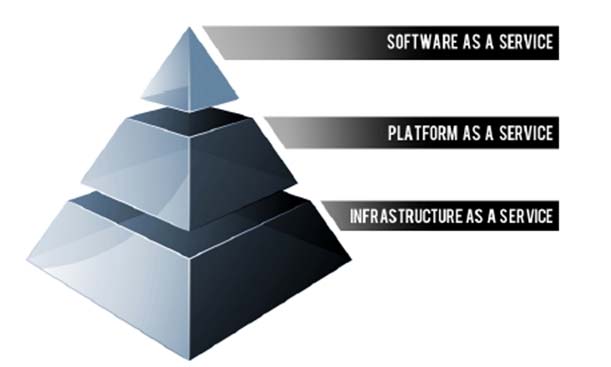
A simplified way of differentiating these flavors of Cloud Computing is as follows;
✑ SaaS applications are designed for end-users, delivered over the web
✑ PaaS is the set of tools and services designed to make coding and deploying those applications quick and efficient
✑ IaaS is the hardware and software that powers it all servers, storage, networks, operating systems
Reference: https://support.rackspace.com/white-paper/understanding-the-cloud-computing-stack-saas-paas-iaas/
AB
The diagram below depicts the Cloud Computing stack it shows three distinct categories within Cloud Computing: Software as a Service, Platform as a Service and Infrastructure as a Service.

A simplified way of differentiating these flavors of Cloud Computing is as follows;
✑ SaaS applications are designed for end-users, delivered over the web
✑ PaaS is the set of tools and services designed to make coding and deploying those applications quick and efficient
✑ IaaS is the hardware and software that powers it all servers, storage, networks, operating systems
Reference: https://support.rackspace.com/white-paper/understanding-the-cloud-computing-stack-saas-paas-iaas/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #2
In which two situations should you use out-of-band management? (Choose two.)
- Awhen a network device fails to forward packets
- Bwhen you require ROMMON access
- Cwhen management applications need concurrent access to the device
- Dwhen you require administrator access from multiple locations
- Ewhen the control plane fails to respond
Correct Answer:
AB
Out-of-band refers to an interface that allows only management protocol traffic to be forwarded or processed. An out-of-band management interface is defined by the network operator to specifically receive network management traffic. The advantage isthat forwarding (or customer) traffic cannot interfere with the management of the router, which significantly reduces the possibility of denial-of-service attacks.
Out-of-band interfaces forward traffic only between out-of-band interfaces or terminate management packets that are destined to the router. In addition, the out-of- band interfaces can participate in dynamic routing protocols. The service provider connects to the routers out-of-band interfaces and builds an independent overlay management network, with all the routing and policy tools that the router can provide.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr9000/software/asr9k_r4-0/security/configuration/guide/b_sc40asr9kbook/ b_sc40asr9kbook_chapter_0101.pdf
AB
Out-of-band refers to an interface that allows only management protocol traffic to be forwarded or processed. An out-of-band management interface is defined by the network operator to specifically receive network management traffic. The advantage isthat forwarding (or customer) traffic cannot interfere with the management of the router, which significantly reduces the possibility of denial-of-service attacks.
Out-of-band interfaces forward traffic only between out-of-band interfaces or terminate management packets that are destined to the router. In addition, the out-of- band interfaces can participate in dynamic routing protocols. The service provider connects to the routers out-of-band interfaces and builds an independent overlay management network, with all the routing and policy tools that the router can provide.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr9000/software/asr9k_r4-0/security/configuration/guide/b_sc40asr9kbook/ b_sc40asr9kbook_chapter_0101.pdf
send
light_mode
delete
Question #3
In which three ways does the TACACS protocol differ from RADIUS? (Choose three.)
- ATACACS uses TCP to communicate with the NAS.
- BTACACS can encrypt the entire packet that is sent to the NAS.
- CTACACS supports per-command authorization.
- DTACACS authenticates and authorizes simultaneously, causing fewer packets to be transmitted.
- ETACACS uses UDP to communicate with the NAS.
- FTACACS encrypts only the password field in an authentication packet.
Correct Answer:
ABC
TACACS+ uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 49 to communicate between the TACACS+ client and the TACACS+ server. An example is a Cisco switch authenticating and authorizing administrative access to the switchs IOS CLI. The switch is the TACACS+ client, and Cisco Secure ACS is the server.
TACACS+ communication between the client and server uses different message types depending on the function. In other words, different messages may be used for authentication than are used for authorization and accounting. Another very interesting point to know is that TACACS+ communication will encrypt the entire packet.
Reference: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2838882/radius-versus-tacacs.html
ABC
TACACS+ uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 49 to communicate between the TACACS+ client and the TACACS+ server. An example is a Cisco switch authenticating and authorizing administrative access to the switchs IOS CLI. The switch is the TACACS+ client, and Cisco Secure ACS is the server.
TACACS+ communication between the client and server uses different message types depending on the function. In other words, different messages may be used for authentication than are used for authorization and accounting. Another very interesting point to know is that TACACS+ communication will encrypt the entire packet.
Reference: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2838882/radius-versus-tacacs.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #4
According to Cisco best practices, which three protocols should the default ACL allow on an access port to enable wired BYOD devices to supply valid credentials and connect to the network? (Choose three.)
- ABOOTP
- BTFTP
- CDNS
- DMAB
- EHTTP
- F802.1x
Correct Answer:
ABC
ACL-DEFAULT allows DHCP, DNS, ICMP, and TFTP traffic and denies everything else.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Unified_Access/BYOD_Design_Guide/BYOD_Wired.html
ABC
ACL-DEFAULT allows DHCP, DNS, ICMP, and TFTP traffic and denies everything else.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Unified_Access/BYOD_Design_Guide/BYOD_Wired.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #5
Which two next-generation encryption algorithms does Cisco recommend? (Choose two.)
- AAES
- B3DES
- CDES
- DMD5
- EDH-1024
- FSHA-384
Correct Answer:
Answer: A, F
The following table shows the relative security level provided by the recommended and NGE algorithms. The security level is the relative strength of an algorithm. bits, the relative effort it would take to "beat"
-bit symmetric key algorithm (without reduction or other attacks). The 128-bit security level is for sensitive information and the 192-bit level is for information of higher importance.
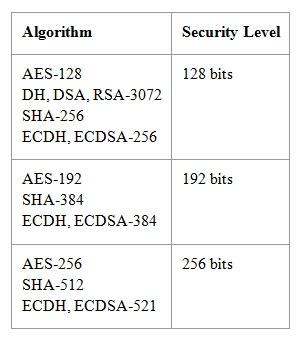
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/security-center/next-generation-cryptography.html
Answer: A, F
The following table shows the relative security level provided by the recommended and NGE algorithms. The security level is the relative strength of an algorithm. bits, the relative effort it would take to "beat"
-bit symmetric key algorithm (without reduction or other attacks). The 128-bit security level is for sensitive information and the 192-bit level is for information of higher importance.

Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/security-center/next-generation-cryptography.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #6
Which three ESP fields can be encrypted during transmission? (Choose three.)
- ASecurity Parameter Index
- BSequence Number
- CMAC Address
- DPadding
- EPad Length
- FNext Header
Correct Answer:
DEF
The remaining four parts of the ESP are all encrypted during transmission across the network. Those parts are as follows:
✑ is the actual data that is carried by the packet.
✑ , from 0 to 255 bytes of data, allows certain types of encryption algorithms to require the data to be a multiple of a certain number of bytes. The padding also ensures that the text of a message terminates ona four-byte boundary (an architectural requirement within IP).
✑ field specifies how much of the payload is padding rather than data.
✑ field, identifies the type of data carried and the protocol.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/vpn_solutions_center/2-0/ip_security/provisioning/guide/IPsecPG1.html
DEF
The remaining four parts of the ESP are all encrypted during transmission across the network. Those parts are as follows:
✑ is the actual data that is carried by the packet.
✑ , from 0 to 255 bytes of data, allows certain types of encryption algorithms to require the data to be a multiple of a certain number of bytes. The padding also ensures that the text of a message terminates ona four-byte boundary (an architectural requirement within IP).
✑ field specifies how much of the payload is padding rather than data.
✑ field, identifies the type of data carried and the protocol.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/vpn_solutions_center/2-0/ip_security/provisioning/guide/IPsecPG1.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #7
What are two default Cisco IOS privilege levels? (Choose two.)
- A0
- B1
- C5
- D7
- E10
- F15
Correct Answer:
BF
By default, the Cisco IOS software command-line interface (CLI) has two levels of access to commands: user EXEC mode (level 1) and privileged EXEC mode
(level 15). However, you can configure additional levels of access to commands, called privilege levels, to meet the needs of your users while protecting the system from unauthorized access. Up to 16 privilege levels can be configured, from level 0, which is the most restricted level, to level 15, which is the least restricted level.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/security/configuration/guide/fsecur_c/scfpass.html#wp1001016
BF
By default, the Cisco IOS software command-line interface (CLI) has two levels of access to commands: user EXEC mode (level 1) and privileged EXEC mode
(level 15). However, you can configure additional levels of access to commands, called privilege levels, to meet the needs of your users while protecting the system from unauthorized access. Up to 16 privilege levels can be configured, from level 0, which is the most restricted level, to level 15, which is the least restricted level.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/security/configuration/guide/fsecur_c/scfpass.html#wp1001016
send
light_mode
delete
Question #8
Which two authentication types does OSPF support? (Choose two.)
- Aplaintext
- BMD5
- CHMAC
- DAES 256
- ESHA-1
- FDES
Correct Answer:
AB
These are the three different types of authentication supported by OSPF.
✑ Null AuthenticationThis is also called Type 0 and it means no authentication information is included in the packet header. It is the default.
✑ Plain Text AuthenticationThis is also called Type 1 and it uses simple clear-text passwords.
✑ MD5 AuthenticationThis is also called Type 2 and it uses MD5 cryptographic passwords.
Authentication does not need to be set. However, if it is set, all peer routers on the same segment must have the same password and authentication method. The examples in this document demonstrate configurations for both plain text and MD5 authentication.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13697-25.html
AB
These are the three different types of authentication supported by OSPF.
✑ Null AuthenticationThis is also called Type 0 and it means no authentication information is included in the packet header. It is the default.
✑ Plain Text AuthenticationThis is also called Type 1 and it uses simple clear-text passwords.
✑ MD5 AuthenticationThis is also called Type 2 and it uses MD5 cryptographic passwords.
Authentication does not need to be set. However, if it is set, all peer routers on the same segment must have the same password and authentication method. The examples in this document demonstrate configurations for both plain text and MD5 authentication.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13697-25.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #9
Which two features do CoPP and CPPr use to protect the control plane? (Choose two.)
- AQoS
- Btraffic classification
- Caccess lists
- Dpolicy maps
- Eclass maps
- FCisco Express Forwarding
Correct Answer:
AB
AB
send
light_mode
delete
Question #10
Which two statements about stateless firewalls are true? (Choose two.)
- AThey compare the 5-tuple of each incoming packet against configurable rules.
- BThey cannot track connections.
- CThey are designed to work most efficiently with stateless protocols such as HTTP or HTTPS.
- DCisco IOS cannot implement them because the platform is stateful by nature.
- EThe Cisco ASA is implicitly stateless because it blocks all traffic by default.
Correct Answer:
AB
However, since iptables and Netfilter were introduced and connection tracking in particular, this option was gotten rid of. The reason for this is that connection tracking can not work properly without defragmenting packets, and hence defragmenting has been incorporated into conntrack and is carried out automatically. It can not be turned off, except by turning off connection tracking. Defragmentation is always carried out if connection tracking is turned on.
Reference:
http://www.iptables.info/en/connection-state.html
AB
However, since iptables and Netfilter were introduced and connection tracking in particular, this option was gotten rid of. The reason for this is that connection tracking can not work properly without defragmenting packets, and hence defragmenting has been incorporated into conntrack and is carried out automatically. It can not be turned off, except by turning off connection tracking. Defragmentation is always carried out if connection tracking is turned on.
Reference:
http://www.iptables.info/en/connection-state.html
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
