Cisco® 200-125 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (1926 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Given an IP address 172.16.28.252 with a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0, what is the correct network address?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
You are working in a data center environment and are assigned the address range 10.188.31.0/23.
You are asked to develop an IP addressing plan to allow the maximum number of subnets with as many as 30 hosts each.
Which IP address range meets these requirements?
You are asked to develop an IP addressing plan to allow the maximum number of subnets with as many as 30 hosts each.
Which IP address range meets these requirements?
- A10.188.31.0/27
- B10.188.31.0/26
- C10.188.31.0/29
- D10.188.31.0/28
- E10.188.31.0/25
Correct Answer:
A
A
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
The network administrator needs to address seven LANs. RIP version 1 is the only routing protocol in use on the network and subnet 0 is not being used. What is the maximum number of usable IP addresses that can be supported on each LAN if the organization is using one class C address block?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Refer to the exhibit. The networks connected to router R2 have been summarized as a 192.168.176.0/21 route and sent to R1. Which two packet destination addresses will R1 forward to R2? (Choose two.)
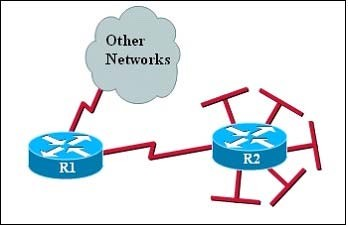

- A192.168.194.160
- B192.168.183.41
- C192.168.159.2
- D192.168.183.255
- E192.168.179.4
- F192.168.184.45
Correct Answer:
BE
BE
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
Which ip address would a network technician ping on the local host, to test the ip stack?
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
How many subnets can be gained by subnetting 172.17.32.0/23 into a /27 mask, and how many usable host addresses will there be per subnet?
- A8 subnets, 31 hosts
- B8 subnets, 32 hosts
- C16 subnets, 30 hosts
- D16 subnets, 32 hosts
- EA Class B address cant be subnetted into the fourth octet.
Correct Answer:
C
Subnetting from /23 to /27 gives us 27 23 = 4 bits -> 24 = 16 subnets.
/27 has 5 bit 0s so it gives 25 2 = 30 hosts-per-subnet.
C
Subnetting from /23 to /27 gives us 27 23 = 4 bits -> 24 = 16 subnets.
/27 has 5 bit 0s so it gives 25 2 = 30 hosts-per-subnet.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
The network administrator has asked you to check the status of the workstations IP stack by pinging the loopback address. Which address would you ping to perform this task?
- A10.1.1.1
- B127.0.0.1
- C192.168.0.1
- D239.1.1.1
Correct Answer:
B
The IP address of 127.0.0.1 is the well-known loopback IP address on a computer. When try pinging this address, you are testing if the TCP/IP stack is working or not.
B
The IP address of 127.0.0.1 is the well-known loopback IP address on a computer. When try pinging this address, you are testing if the TCP/IP stack is working or not.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
Refer to the exhibit. What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose three.)
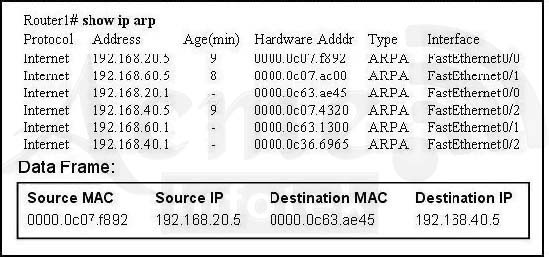

- ARouter1 will strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c36.6965.
- BRouter1 will strip off the source IP address and replace it with the IP address 192.168.40.1.
- CRouter1 will strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c07.4320.
- DRouter1 will strip off the destination IP address and replace it with the IP address of 192.168.40.1.
- ERouter1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/1.
- FRouter1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/2.
Correct Answer:
ACF
The router will decapsulate the frame, thus removing the source and destination MAC addresses. It will consult its routing table to work out on which interface to send the packet which is going to 192.168.40.5: interface FastEthernet0/2. The router will then encapsulate the packet into a new frame with its own MAC address as the source MAC address and the MAC address of 192.168.40.5 as the destination MAC address.
Looking at the ARP table, the MAC address for 192.168.40.5 is 0000.0c07.4320 (the one which has been dynamically learned and has age 9 minutes). So what is the routers MAC address on this link? The ARP table shows a static entry (no age) for 192.168.40.1 which is 0000.0c36.6965. As it is static, we can conclude that these are the routers IP and MAC address.
ACF
The router will decapsulate the frame, thus removing the source and destination MAC addresses. It will consult its routing table to work out on which interface to send the packet which is going to 192.168.40.5: interface FastEthernet0/2. The router will then encapsulate the packet into a new frame with its own MAC address as the source MAC address and the MAC address of 192.168.40.5 as the destination MAC address.
Looking at the ARP table, the MAC address for 192.168.40.5 is 0000.0c07.4320 (the one which has been dynamically learned and has age 9 minutes). So what is the routers MAC address on this link? The ARP table shows a static entry (no age) for 192.168.40.1 which is 0000.0c36.6965. As it is static, we can conclude that these are the routers IP and MAC address.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
Refer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the output MTU 1500 bytes?
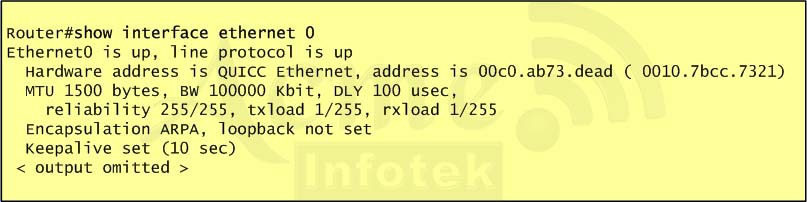

- AThe maximum number of bytes that can traverse this interface per second is 1500.
- BThe minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
- CThe maximum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
- DThe minimum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
- EThe maximum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
- FThe maximum frame size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
Correct Answer:
E
E
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
Which command would you use on a Cisco router to verify the Layer 3 path to a host?
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
