PMI PMI-SP Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (320 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
You are the project manager of the NHQ Project. You have created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
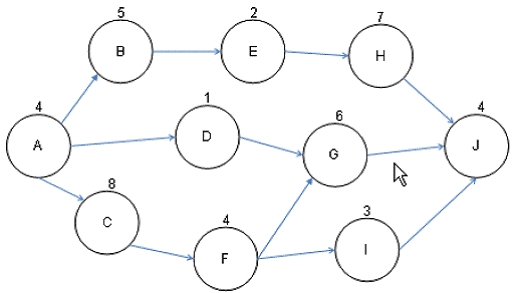
You are concerned about a risk on Activity G that if it happens will delay the project by four days. You would like to utilize float for Activity G. How much float is available for Activity G to help offset the risk event?

You are concerned about a risk on Activity G that if it happens will delay the project by four days. You would like to utilize float for Activity G. How much float is available for Activity G to help offset the risk event?
- AFive days
- BFour days
- CEleven days
- DZero
Correct Answer:
D
There is no float available for Activity G because it is on the critical path. Float or total float (TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C: There is no float available for Activity G because it is on the critical path.
D
There is no float available for Activity G because it is on the critical path. Float or total float (TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C: There is no float available for Activity G because it is on the critical path.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Beth is the project manager for her organization. Her current project has many deliverables that have been defined at a high level, but the details of the deliverables are still unknown. In her project, Beth is planning in detail only the activities that are most imminent in the project work. This approach to project management planning is known as what?
- AImminent activity management
- BRolling wave planning
- CPredecessor-only diagramming
- DDecomposition
Correct Answer:
B
Rolling wave planning is a technique to plan and do the most imminent project work before moving onto the details that are far off in the project schedule and project plan. Rolling wave planning is a technique for performing progressive elaboration planning where the work to be accomplished in the near future is planned in detail at a low level of the work breakdown structure. The work to be performed within another one or two reporting periods in the near future is planned in detail as work is being completed during the current period.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: These are not valid project management terms.
D: Decomposition is the process of breaking down work packages into the activity list.
B
Rolling wave planning is a technique to plan and do the most imminent project work before moving onto the details that are far off in the project schedule and project plan. Rolling wave planning is a technique for performing progressive elaboration planning where the work to be accomplished in the near future is planned in detail at a low level of the work breakdown structure. The work to be performed within another one or two reporting periods in the near future is planned in detail as work is being completed during the current period.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: These are not valid project management terms.
D: Decomposition is the process of breaking down work packages into the activity list.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Gina is the project manager for her organization and she is working with her project team to define the project activities. In this project, the stakeholders are sensitive to the project completion date, so Gina is stressing to her project team members that while they need to provide and account for all of the project activities, they should focus on one work package in the WBS at a time. In order to start the decomposition of the project work packages into activities, Gina will need all of the following except for which one?
- AScope baseline
- BOrganizational process assets
- CWBS
- DEnterprise environmental factors
Correct Answer:
C
According to the PMBOK, Gina will not need the WBS directly, but will rely on the scope baseline. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management is a tool that defines a project and groups the project's discrete work elements in a way that helps organize and define the total work scope of the project. A WBS element may be a product, data, a service, or any combination. WBS also provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control.
Incorrect Answers:
A: The scope baseline is an input to define the project activities.
B: Organizational process assets are an input to define the project activities.
D: Enterprise environmental factors are an input to define the project activities.
C
According to the PMBOK, Gina will not need the WBS directly, but will rely on the scope baseline. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management is a tool that defines a project and groups the project's discrete work elements in a way that helps organize and define the total work scope of the project. A WBS element may be a product, data, a service, or any combination. WBS also provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control.
Incorrect Answers:
A: The scope baseline is an input to define the project activities.
B: Organizational process assets are an input to define the project activities.
D: Enterprise environmental factors are an input to define the project activities.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
You have created the project network diagram for the ABC project. You are exploring total float and free float for that project. Martin, a project team member, wants to know the difference between total float and free float. What is the difference between total float and free float?
- ATotal float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
- BTotal float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors.
- CTotal float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project predecessors.
- DTotal float is the amount of time a non-critical activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the amount of time an
Correct Answer:
B
Total float is the time you can delay an activity without delaying the project end date, whereas free float is on each activity and does not affect the early start date of successor activities. Float, also called slack, is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting any subsequent activities. There are two types of floats available: Free Float: It is the amount of time a schedule activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediately following schedule activities. Total Float: It is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating schedule constraint. Float is calculated by using the critical path method technique.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D: These are not accurate definitions of free float and total float.
B
Total float is the time you can delay an activity without delaying the project end date, whereas free float is on each activity and does not affect the early start date of successor activities. Float, also called slack, is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting any subsequent activities. There are two types of floats available: Free Float: It is the amount of time a schedule activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediately following schedule activities. Total Float: It is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating schedule constraint. Float is calculated by using the critical path method technique.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D: These are not accurate definitions of free float and total float.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
John works as a project manager of the NHQ Project. He has created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
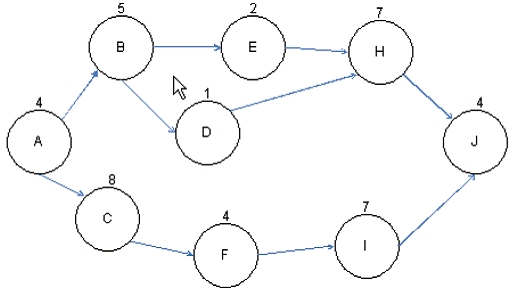
Based on the project network diagram, how much float is available for Activity H if Activity B is delayed by four days and Activity E is delayed by two days?

Based on the project network diagram, how much float is available for Activity H if Activity B is delayed by four days and Activity E is delayed by two days?
- AZero
- BOne
- CFour
- DFive
Correct Answer:
A
The path of ABEHJ will take 22 days to complete and cannot exceed 28 days or else the project will be late. If Activity B takes four additional days and Activity E takes two additional days, this adds (4+2= 6) six days to the path, bringing the path's duration to exactly (22+6 = 28) days. There is no available float left for
Activity D or H. Float or total float (TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C, D: There is no float available because the path's duration has increased to 28 days.
A
The path of ABEHJ will take 22 days to complete and cannot exceed 28 days or else the project will be late. If Activity B takes four additional days and Activity E takes two additional days, this adds (4+2= 6) six days to the path, bringing the path's duration to exactly (22+6 = 28) days. There is no available float left for
Activity D or H. Float or total float (TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C, D: There is no float available because the path's duration has increased to 28 days.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
Ben is the project manager for his organization. His project has 26 stakeholders this week and will have five additional stakeholders next week. How many more communication channels will Ben's project have next week?
- A140
- B10
- C325
- D5
Correct Answer:
A
Ben's project will have 140 more communication channels because of the five additional stakeholders. To solve the question, you will need to find the current stakeholder communication channels first, which is (26*25)/2= 325, and then find the difference of the number of channels for the five additional stakeholders. You can use the formula of N(N-1), where N is the number of stakeholders. In this example, the formula would read: Total number of communication channels that Ben will have next = ((31*30)/2)-((26*25)/2 =140
Incorrect Answers:
B: 10 is the number of communication channels among just five stakeholders.
C: 325 is the number of current communication channels.
D: Five is the number of additional stakeholders.
A
Ben's project will have 140 more communication channels because of the five additional stakeholders. To solve the question, you will need to find the current stakeholder communication channels first, which is (26*25)/2= 325, and then find the difference of the number of channels for the five additional stakeholders. You can use the formula of N(N-1), where N is the number of stakeholders. In this example, the formula would read: Total number of communication channels that Ben will have next = ((31*30)/2)-((26*25)/2 =140
Incorrect Answers:
B: 10 is the number of communication channels among just five stakeholders.
C: 325 is the number of current communication channels.
D: Five is the number of additional stakeholders.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
You are the project manager for your company. You are working with the activities defined in the figure below.
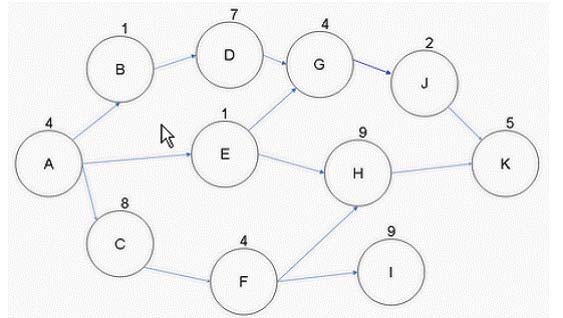
What will happen to your project if Activity F takes five additional days to complete than what was expected?

What will happen to your project if Activity F takes five additional days to complete than what was expected?
- AYour project's critical path will shift to ACFI.
- BYour project will be late by five days.
- CYour project can still complete on time as float is available on Activity I.
- DYour project will now have two critical paths.
Correct Answer:
B
Activity F is on the critical path of ACFHK of 30 days. By adding five additional days to Activity F, the project will now take 35 days to complete.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D: These are not the valid answers.
B
Activity F is on the critical path of ACFHK of 30 days. By adding five additional days to Activity F, the project will now take 35 days to complete.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D: These are not the valid answers.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
You are the project manager for your organization. You need the oak cabinets for your project delivered by December 1 in order to install the floors around the oak cabinets by December 15. Your company's procurement office generally takes 45 days to complete procurement orders. Based on this information, how should you schedule the lead time for the cabinet delivery?
- ACabinet procurement December 1, plus 45 days lead time
- BCabinet procurement November 15
- CCabinet procurement December 1, minus 45 days lead time
- DCabinet procurement December 15 minus 45 days lead time
Correct Answer:
C
The cabinet procurement and delivery must be completed by December 1. By scheduling the activity to finish on December 1 with minus 45 days lead time for procurement, the cabinets will arrive by the needed date.
Incorrect Answers:
A: Lead time is always negative time, lag time is positive time. This choice would cause the cabinets to not arrive until 45 days after December 1.
B: This choice is not the best answer because it does not necessarily account for holidays, weekends, or other factors in the project calendar. By scheduling the cabinet for December 1 and working backwards through lead time, the project's PMIS will account for these breaks in the project work.
D: This choice would cause the cabinets to arrive on December 15 when the floors are to be installed.
C
The cabinet procurement and delivery must be completed by December 1. By scheduling the activity to finish on December 1 with minus 45 days lead time for procurement, the cabinets will arrive by the needed date.
Incorrect Answers:
A: Lead time is always negative time, lag time is positive time. This choice would cause the cabinets to not arrive until 45 days after December 1.
B: This choice is not the best answer because it does not necessarily account for holidays, weekends, or other factors in the project calendar. By scheduling the cabinet for December 1 and working backwards through lead time, the project's PMIS will account for these breaks in the project work.
D: This choice would cause the cabinets to arrive on December 15 when the floors are to be installed.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
Your project has a BAC of $750,000 and is 75 percent complete. According to your plan, however, your project should actually be 80 percent complete. You have spent $575,000 of your project budget to reach this point and you are worried about the project not being able to complete based on your current project budget.
What is the to-complete performance index for this project?
What is the to-complete performance index for this project?
- A0.98
- B-$16,677
- C1.07
- D0.94
Correct Answer:
C
The to-complete performance index can be found by using the formula (BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) for a value of 1.07. The higher the value is from 1, the less likely the project will meet the BAC.
To-complete Performance Index (TCPI) is the measured projection of the anticipated performance required to achieve either the BAC or the EAC.
TCPI indicates the future required cost efficiency needed to achieve a target EAC (Estimate At Complete).Once approved, the EAC supersedes the BAC as the cost performance goal. Any significant difference between TCPI and the CPI needed to meet the EAC should be accounted for by management in their forecast of the final cost. The formula for TCPI is as follows:
TCPI = {(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC)}
Incorrect Answers:
A: 0.98 is the project's cost performance index.
B: -$16,667 is the project's variance at completion.
D: This is the project's schedule performance index.
C
The to-complete performance index can be found by using the formula (BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) for a value of 1.07. The higher the value is from 1, the less likely the project will meet the BAC.
To-complete Performance Index (TCPI) is the measured projection of the anticipated performance required to achieve either the BAC or the EAC.
TCPI indicates the future required cost efficiency needed to achieve a target EAC (Estimate At Complete).Once approved, the EAC supersedes the BAC as the cost performance goal. Any significant difference between TCPI and the CPI needed to meet the EAC should be accounted for by management in their forecast of the final cost. The formula for TCPI is as follows:
TCPI = {(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC)}
Incorrect Answers:
A: 0.98 is the project's cost performance index.
B: -$16,667 is the project's variance at completion.
D: This is the project's schedule performance index.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
You are the project manager of the NHT Project. This project has 12,345 office doors to install throughout a campus. Each of the doors costs the project $456 and requires special hardware to electronically lock and open the doors. You've gathered the project team before they begin the installation for a hands-on training. As a group you and the project team install 50 doors following a checklist of instructions so that every door will be installed exactly the same throughout the campus and with minimal waste. This is an example of what project execution technique?
- APreventive action
- BDefect repair validation
- CImplemented corrective action
- DQuality control
Correct Answer:
A
This is an example of a preventive action as you're working with the team before they install the doors to train them on the installation. The checklist is a quality control tool but the question was asking for a project execution activity. Preventive and corrective actions are part of project execution.
Incorrect Answers:
B: The defect repair validation comes after the project team has corrected an error - something that has not occurred in this instance.
C: Corrective action is a response to something that needs to be corrected in the project.
D: Quality control is a controlling and monitoring process, not an executing process.
A
This is an example of a preventive action as you're working with the team before they install the doors to train them on the installation. The checklist is a quality control tool but the question was asking for a project execution activity. Preventive and corrective actions are part of project execution.
Incorrect Answers:
B: The defect repair validation comes after the project team has corrected an error - something that has not occurred in this instance.
C: Corrective action is a response to something that needs to be corrected in the project.
D: Quality control is a controlling and monitoring process, not an executing process.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
