Oracle 1z0-820 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (130 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
You have been asked to troubleshoot the initial configuration of a virtual network connecting two local zones with the outside world.
View the exhibit.
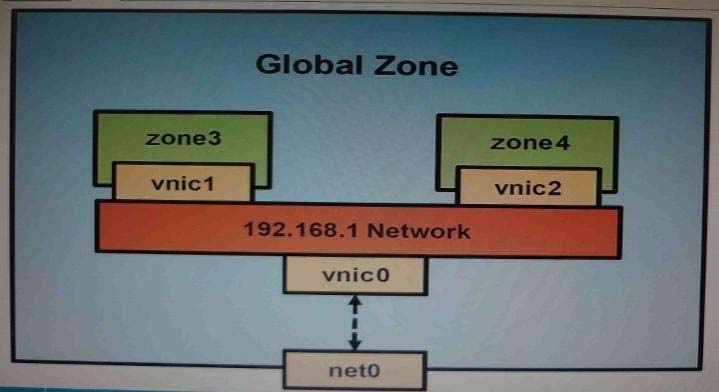
The command -
dladm create-vnic -1 vswitch192.168.1 vnic1
fails with the error
dladm: invalid link name vswitch192.168.1
What is the reason for this error?
View the exhibit.

The command -
dladm create-vnic -1 vswitch192.168.1 vnic1
fails with the error
dladm: invalid link name vswitch192.168.1
What is the reason for this error?
- AThe name vswitch192.168.1 is not legal.
- BThe zone must be specified with dladm create-vnic -z zone3 vnic1.
- CThe virtual interface must be specified with dladm create-vnic -z zone3 vnic1.
- DThe virtual interface must be created with ipadm create-vnic -1 switch192.168.1.
- EThe virtual switch must be created first with dladm create -etherstub vswitch192.168.1.
Correct Answer:
E
There is no data-link named vswitch192.168.
We need to create an etherstub first.
See Note and example below for details.
Note: Create a VNIC in the system's global zone.
# dladm create-vnic -l data-link vnic-name
data-link is the name of the interface where the VNIC is to be configured.
-l link, --link=link
link can be a physical link or an etherstub.
vnic-name is the name that you want to give the VNIC.
For example, to create a VNIC named vnic0 on interface e1000g0, you would type the following:
# dladm create-vnic -l e1000g0 vnic0
Example: Creating a Virtual Network Without a Physical NIC
First, create an etherstub with name stub1:
# dladm create-etherstub stub1
Create two VNICs with names hello0 and test1 on the etherstub. This operation implicitly creates a virtual switch connecting hello0 and test1.
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 hello0
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 test1
Reference: man dladm
E
There is no data-link named vswitch192.168.
We need to create an etherstub first.
See Note and example below for details.
Note: Create a VNIC in the system's global zone.
# dladm create-vnic -l data-link vnic-name
data-link is the name of the interface where the VNIC is to be configured.
-l link, --link=link
link can be a physical link or an etherstub.
vnic-name is the name that you want to give the VNIC.
For example, to create a VNIC named vnic0 on interface e1000g0, you would type the following:
# dladm create-vnic -l e1000g0 vnic0
Example: Creating a Virtual Network Without a Physical NIC
First, create an etherstub with name stub1:
# dladm create-etherstub stub1
Create two VNICs with names hello0 and test1 on the etherstub. This operation implicitly creates a virtual switch connecting hello0 and test1.
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 hello0
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 test1
Reference: man dladm
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
You want to deploy oracle Solaris 11 with the automated installer (AI). You need to make sure that your server and network meet the requirements for using AI.
Choose the three options that describe; the requirements for using AI.
Choose the three options that describe; the requirements for using AI.
- AYou can create only one manifest per install service. If you need more than one manifest, create multiple install services.
- BIf two client machines have different architectures and need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS, then create two AI manifests and a single Install service.Most Voted
- CYou need a separate install service for each different client architecture that you plan to install, and for each different version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS that you plan to install on client systems.
- DIf two client machines have different architectures and need to be installed with different versions of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS, then create two AI manifests and two install services.
- EThe install server needs to be able to access an Oracle Solaris Image Packaging System (IPS) software package repository; the clients do not.Most Voted
- FThe install server can be either an x86 machine or a SPARC machine.Most Voted
Correct Answer:
BEF
B:
Note: You can create custom AI manifests for particular clients.
Create a custom XML AI manifest file. This method is best suited to an environment where few systems require custom provisioning. Most systems to be installed have identical or similar hardware and will be provisioned identically.
Write a script that dynamically creates an AI manifest for each client at installation time. Use this method to create a custom installation for each client, based on client characteristics discovered at installation time.
E: AI Server Software Requirements include
Software package repository -
Ensure that the install server can access an IPS software package repository. AI requires the install/installadm package.
F: Install Server Requirements -
Any system that meets these requirements can be used as an AI install server, including laptops, desktops, virtual machines, and enterprise servers. The install server can be either an x86 machine or a SPARC machine. An x86 install server can install both SPARC and x86 clients, and a SPARC install server can install both SPARC and x86 clients.
Note: To install clients over the network, AI requires a separate system to be an install server. On the install server, create an AI install service to provide a net image and instructions for installing the Oracle Solaris 11 OS on different clients.
BEF
B:
Note: You can create custom AI manifests for particular clients.
Create a custom XML AI manifest file. This method is best suited to an environment where few systems require custom provisioning. Most systems to be installed have identical or similar hardware and will be provisioned identically.
Write a script that dynamically creates an AI manifest for each client at installation time. Use this method to create a custom installation for each client, based on client characteristics discovered at installation time.
E: AI Server Software Requirements include
Software package repository -
Ensure that the install server can access an IPS software package repository. AI requires the install/installadm package.
F: Install Server Requirements -
Any system that meets these requirements can be used as an AI install server, including laptops, desktops, virtual machines, and enterprise servers. The install server can be either an x86 machine or a SPARC machine. An x86 install server can install both SPARC and x86 clients, and a SPARC install server can install both SPARC and x86 clients.
Note: To install clients over the network, AI requires a separate system to be an install server. On the install server, create an AI install service to provide a net image and instructions for installing the Oracle Solaris 11 OS on different clients.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Which three options are valid methods of installing a Solaris 10 branded zone on a system running Oracle Solaris 11?
- AUse the V2V process to migrate an existing Solaris 8 or 9 non-global zone from a Solaris 10 system to a solaris10 branded zone.
- BUse the V2V process to migrate an existing Solaris 10 non global whole root zone from a Solaris 10 system to a solaris10 branded whole root zone.
- CInstall a solaris10 branded zone directly from the Oracle Solaris 10 media.
- DMigrate an existing 64-bit Solaris 10 system to a solaris10 branded non-global zone using the P2V process.
- EMigrate an existing 32 bit Solaris10 system to a solaris10 branded non-global zone using the P2V process.
- FUse the V2V process to migrate an existing Solaris 10 non-global sparse root zone from a Solaris 10 system to a solaris10 branded sparse root zone.
Correct Answer:
BDE
B: Due to change in package system (SRV4 to IPS) there is no direct upgrade from S10 to S11 one can use
* P2Vconverting s10 physical system to solaris10 branded zone in s11 (32-bit or 64-bit)
* V2V converting s10 native full root zone to solaris10 branded zone in s11 (B)
BDE
B: Due to change in package system (SRV4 to IPS) there is no direct upgrade from S10 to S11 one can use
* P2Vconverting s10 physical system to solaris10 branded zone in s11 (32-bit or 64-bit)
* V2V converting s10 native full root zone to solaris10 branded zone in s11 (B)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Which command should you choose to display the current parameters for the FSS scheduler?
- Adispadmin - c FSS
- Bprionctl -c FSS
- Cdispadmin -c FSS -g
- Dpriocntl -c FSS -g
Correct Answer:
C
The dispadmin command displays or changes process scheduler parameters while the system is running.
-c class
Specifies the class whose parameters are to be displayed or changed. Valid class values are: RT for the real-time class, TS for the time-sharing class, IA for the inter-active class, FSS for the fair-share class, and FX for the fixed-priority class. The time-sharing and inter-active classes share the same scheduler, so changes to the scheduling parameters of one will change those of the other.
-g
Gets the parameters for the specified class and writes them to the standard output.
Reference: man dispadmin
C
The dispadmin command displays or changes process scheduler parameters while the system is running.
-c class
Specifies the class whose parameters are to be displayed or changed. Valid class values are: RT for the real-time class, TS for the time-sharing class, IA for the inter-active class, FSS for the fair-share class, and FX for the fixed-priority class. The time-sharing and inter-active classes share the same scheduler, so changes to the scheduling parameters of one will change those of the other.
-g
Gets the parameters for the specified class and writes them to the standard output.
Reference: man dispadmin
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
This iron is displayed on the desktop of a laptop computer, which is running Oracle Solaris 11.

Which two statements describe the Information conveyed by this Icon?

Which two statements describe the Information conveyed by this Icon?
- ANWAM is disabled.
- BNWAM is automatically configuring the network.
- CThe wireless network card is manually configured and operational.
- DThe wireless network card is manually configured but not operational.
- EThe wireless network card is automatically configured and operational.
- FThe wireless network card is automatically configured but not operational.
Correct Answer:
BC
B: The Network Status notification icon is only displayed on the desktop if you are using NWAM to automatically configure your network.
C: All online (Wireless)
Indicates all manually enabled connections in the enabled network profile are online and that the required number of connections in the enabled profile group (if such a group exists) are online. The required number is the same as those described for the All online (Wired) status.
Note that at least one online connection is wireless.
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Network Interfaces and Network Virtualization , Checking the Status of Your Network Connection
BC
B: The Network Status notification icon is only displayed on the desktop if you are using NWAM to automatically configure your network.
C: All online (Wireless)
Indicates all manually enabled connections in the enabled network profile are online and that the required number of connections in the enabled profile group (if such a group exists) are online. The required number is the same as those described for the All online (Wired) status.
Note that at least one online connection is wireless.
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Network Interfaces and Network Virtualization , Checking the Status of Your Network Connection
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
