Oracle 1z0-595 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (75 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #6
Which GDAL/OGR command will load a geotiff file named satellite.tif into a georaster column named GEORASTER, in a table named IMAGES with an RDT table named IMAGES_RDT? Assume that the database name, username, and password are mvdemo.
- Agdal_create of georaster GDAL_IMPORT, GDAL_RDT gdal_import of georaster satellite.tif geor:mvdemo/mvdemo@mvdemo, IMAGES, IMAGES_RDT
- Bgdal_import –of georaster satellite.tif geor:mvdemo/mvdemo@mvdemo, GDAL_IMPORT, GDAL_RDT
- Cgdal_warp –of georaster satellite.tif geor:mvdemo/mvdemo@mvdemo, GDAL_IMPORT, GDAL_RDT
- Dgdal_translate –of georaster satellite.tif geor:mvdemo/mvdemo@mvdemo, images, georaster
Correct Answer:
D
The gdal_translate utility can be used to convert raster data between different formats, potentially performing some operations like subsettings, resampling, and rescaling pixels in the process.
Parameter -of format: Select the output format. The default is GeoTIFF (GTiff). Use the short format name.
Incorrect Answers:
A: There is no gdal command gdal_create.
B: There is no gdal command gdal_import.
C: The gdalwarp utility is an image mosaicing, reprojection and warping utility. The program can reproject to any supported projection, and can also apply GCPs stored with the image if the image is "raw" with control information. gdal_translate converts raster data between different formats.
References:
http://www.gdal.org/gdal_translate.html
D
The gdal_translate utility can be used to convert raster data between different formats, potentially performing some operations like subsettings, resampling, and rescaling pixels in the process.
Parameter -of format: Select the output format. The default is GeoTIFF (GTiff). Use the short format name.
Incorrect Answers:
A: There is no gdal command gdal_create.
B: There is no gdal command gdal_import.
C: The gdalwarp utility is an image mosaicing, reprojection and warping utility. The program can reproject to any supported projection, and can also apply GCPs stored with the image if the image is "raw" with control information. gdal_translate converts raster data between different formats.
References:
http://www.gdal.org/gdal_translate.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #7
Which command will combine two simple overlapping polygons (geom1 and geom2) into a single geometry that excludes the overlapped region?
- ASDO_GEOM.SDO_EXCLUDE(geom1, geom2, .05)
- BSDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION(geom1, geom2, .05)
- CSDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION(geom1, geom2, .05)
- DSDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR(geom1, geom2, .05)
- ESDO_GEOM.SDO_AGGR_UNION(geom1, geom2, .05)
- FSDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE(geom1, geom2, .05)
Correct Answer:
D
returns a geometry object that is the topological symmetric difference (XOR operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR -
In Figure below, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_XOR is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).
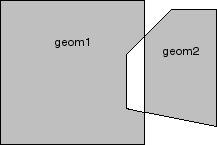
References:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/appdev.111/b28400/sdo_objgeom.htm
D
returns a geometry object that is the topological symmetric difference (XOR operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR -
In Figure below, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_XOR is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).

References:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/appdev.111/b28400/sdo_objgeom.htm
send
light_mode
delete
Question #8
Identify the partitioning type that is supported in Oracle Spatial.
- AHASH
- BRANGE
- CINTERVAL
- DLIST
- ECOMPOSITE
Correct Answer:
B
Oracles scalable database architecture includes partitioning, in which a single logical table and its indexes are broken up into one or more physical tables, each with its own index. There are many different ways to partition data, however this paper will focus on range partitioning with Oracle Spatial. Range partitioning is the currently the only partitioning scheme used with spatial indexes.
References:
http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/products/spatial/pdf/spatial_wp10_bestprac.pdf
(page 3)
B
Oracles scalable database architecture includes partitioning, in which a single logical table and its indexes are broken up into one or more physical tables, each with its own index. There are many different ways to partition data, however this paper will focus on range partitioning with Oracle Spatial. Range partitioning is the currently the only partitioning scheme used with spatial indexes.
References:
http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/products/spatial/pdf/spatial_wp10_bestprac.pdf
(page 3)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #9
How is the outer ring rotation defined?
- Acounterclockwise
- Bclockwise
- Cdoes not matter
- Ddepending on the type of polygons
Correct Answer:
A
Outer rings should be counterclockwise, inner rings clockwise.
References:
http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/products/spatial/pdf/spatial_wp09_bestprac.pdf
(page 6)
A
Outer rings should be counterclockwise, inner rings clockwise.
References:
http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/products/spatial/pdf/spatial_wp09_bestprac.pdf
(page 6)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #10
To convert an SDO_GEOMETRY object to a GML object, special consideration must be given to the SDO_GEOMETRY object that is to be converted. Which operation should be completed before SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY is used?
- AAll geometries should be converted to LRS geometries.
- BAll points should be labeled.
- CCircular arcs and circlers should be densified.
- DThe SRID in user_sdo_geom_metadata should be updated to 54004.
- EAll polygons with holes should be removed.
Correct Answer:
C
Any circular arcs or circles must be densified (using the SDO_GEOM.SDO_ARC_DENSIFY function) or represented as polygons (using the
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER function) before being passed to the TO_GMLGEOMETRY function.
Note: SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY converts a Spatial geometry object to a geography markup language (GML 2.0) fragment based on the geometry types defined in the Open GIS geometry.xsd schema document.
This function does not convert circles, geometries containing any circular arcs, LRS geometries, or geometries with an SDO_ETYPE value of 0 (type 0 elements); it returns an empty CLOB in these cases.
Incorrect Answers:
A: LRS geometries must be converted to standard geometries (using the SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_GEOM or SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_LAYER function) before being passed to the TO_GMLGEOMETRY function.
E: For a polygon with holes, the outer boundary must be stored first in the SDO_ORDINATES definition, followed by coordinates of the inner boundaries.
References:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/appdev.111/b28400/sdo_util.htm#SPATL1249
C
Any circular arcs or circles must be densified (using the SDO_GEOM.SDO_ARC_DENSIFY function) or represented as polygons (using the
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER function) before being passed to the TO_GMLGEOMETRY function.
Note: SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY converts a Spatial geometry object to a geography markup language (GML 2.0) fragment based on the geometry types defined in the Open GIS geometry.xsd schema document.
This function does not convert circles, geometries containing any circular arcs, LRS geometries, or geometries with an SDO_ETYPE value of 0 (type 0 elements); it returns an empty CLOB in these cases.
Incorrect Answers:
A: LRS geometries must be converted to standard geometries (using the SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_GEOM or SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_LAYER function) before being passed to the TO_GMLGEOMETRY function.
E: For a polygon with holes, the outer boundary must be stored first in the SDO_ORDINATES definition, followed by coordinates of the inner boundaries.
References:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/appdev.111/b28400/sdo_util.htm#SPATL1249
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
