Oracle 1z0-338 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (81 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which two statements are true about metrics in the DBMCLI utility? (Choose two.)
- AMetric values are computed and stored in memory, and then permanently stored on disk.
- BDBMCLI can be used to report on Exadata storage server metrics.
- CMetrics are reported as one of four types: cumulative, instantaneous, rate, or transition.
- DFields in AlertHistory cannot be modified.
- EDBMCLI reported metrics are informational only and cannot be used to trigger alerts or reported events.
Correct Answer:
AC
Reference:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E50790_01/doc/doc.121/e51951/app_dbmcli.htm#DBMMN22246
AC
Reference:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E50790_01/doc/doc.121/e51951/app_dbmcli.htm#DBMMN22246
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
What happens in an Exadata Database Machine when the DUPLICATE sub-clause of the INMEMORY attribute is specified?
- AThe DUPLICATE sub-clause enables parallel execution NUMA support.
- BEach In-Memory Compression Unit in the IM column store will have a mirrored copy placed on another node in the RAC cluster.
- CThe command allows the current instance to exceed DRAM limits and expand across memory, flash, and disk.
- DThe command creates an in-memory snapshot for write_only access.
- EThe In-Memory Compression Unit will have a mirrored copy placed on every other node in the RAC cluster.
Correct Answer:
B
Reference:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/in-memory/learnmore/twp-dbim-exadata-2556211.pdf
(page 3)
B
Reference:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/in-memory/learnmore/twp-dbim-exadata-2556211.pdf
(page 3)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Which statement explains the difference between Normal and High redundancy ASM failure groups?
- ANormal redundancy protects the DATA diskgroup, whereas High redundancy protects the RECO diskgroup.
- BNormal redundancy (best practice) provides protection against two simultaneous disk failures, whereas High redundancy provides protection against a single disk failure or an entire storage server failure.
- CHigh redundancy gives more usable storage, whereas Normal redundancy provides better I/O performance.
- DNormal redundancy protects from disk failure when a cell is offline or being updated, whereas High redundancy protects the system when all the cells are offline.
- ENormal redundancy tolerates a single cell failure, whereas High redundancy tolerates a two-cell failure.
Correct Answer:
E
Reference:
http://blog.umairmansoob.com/tag/using-high-vs-normal-redundancy-in-exadata/
E
Reference:
http://blog.umairmansoob.com/tag/using-high-vs-normal-redundancy-in-exadata/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
You are measuring the I/O savings provided by storage indexes for Table A. One of your scripts displays the I/O sayings as a result of the storage indexes.
Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
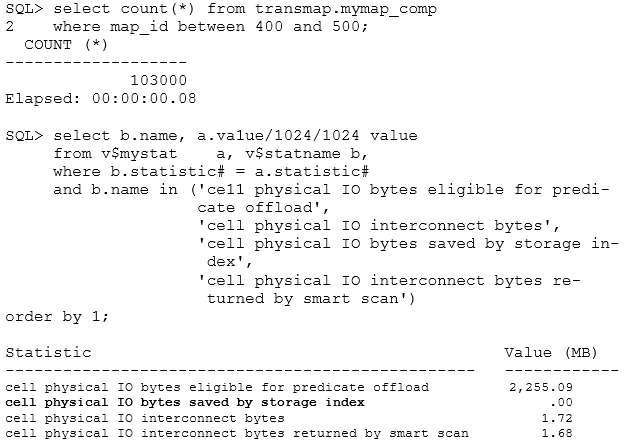
Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)

- AThe accumulated I/O saved by the storage index is 1.68 MB.
- BThe storage indexes reduced the amount of physical I/O bytes significantly for this query.
- CSince the database was started, no queries were run against this table with the same predicate.
- DThe storage index data is not on the Cell Server's region index memory structures yet because this predicate has not been used.
- EThe storage indexes were disabled by using the DISABLE_STORAGE_INDEX parameter.
Correct Answer:
BD
BD
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
When backing up a storage cell, what is actually being backed up?
- Athe first two disks in a storage cell that contain the Linux operating system
- Ball the disk headers and storage indexes in the storage cell
- Cthe contents of the CELLBOT USB flash drive
- Dthe Linux RPM that is used to deploy the storage cell software
Correct Answer:
B
B
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
