Oracle 1z0-070 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (90 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #16
Which two are true concerning Columnar Flash Caching?
- AIt can be enabled or disabled for individual databases by using I/O Resource Manager database plans.
- BIt automatically transforms ROW STORE COMPRESS compressed data into a pure columnar format during Exadata Smart Flash Cache population.
- CData is either cached in Hybrid Columnar Compressed format or in pure compressed format, but never in both formats at the same time.
- DIt is enabled by default.
- EIt automatically transforms Hybrid Columnar Compressed (HCC) data into a pure columnar format during Exadata Smart Flash Cache population.
- FIt improves single-row lookup performance.
Correct Answer:
DE
D: In-Memory Columnar Caching on cells is enabled by default when the INMEMORY_SIZE is configured. You do not need to do anything to get this enhancement.
E: Columnar Flash Caching implements a dual format architecture in Exadata flash by automatically transforming frequently scanned Hybrid Columnar
Compressed data into a pure columnar format as it is loaded into the flash cache.
Incorrect Answers:
F: Columnar Flash Caching accelerates reporting and analytic queries while maintaining excellent performance for OLTP style single row lookups.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server-monitoring.htm#SAGUG20883 http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/exadata/exadata-x5-8-ds-2745934.pdf
DE
D: In-Memory Columnar Caching on cells is enabled by default when the INMEMORY_SIZE is configured. You do not need to do anything to get this enhancement.
E: Columnar Flash Caching implements a dual format architecture in Exadata flash by automatically transforming frequently scanned Hybrid Columnar
Compressed data into a pure columnar format as it is loaded into the flash cache.
Incorrect Answers:
F: Columnar Flash Caching accelerates reporting and analytic queries while maintaining excellent performance for OLTP style single row lookups.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server-monitoring.htm#SAGUG20883 http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/exadata/exadata-x5-8-ds-2745934.pdf
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
You are evaluating the performance of a SQL statement that accesses a very large table.
You run this query:
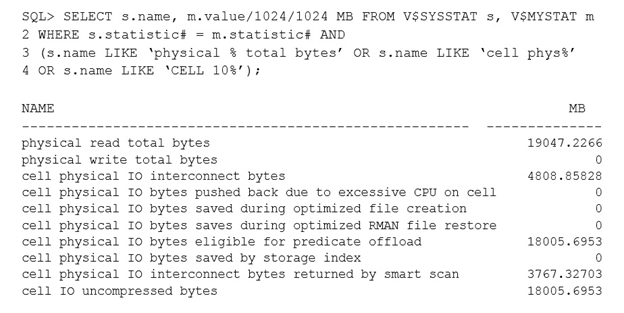
Identify two reasons why the "cell physical IO interconnect bytes" statistic is greater than the "cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan" statistic.
You run this query:

Identify two reasons why the "cell physical IO interconnect bytes" statistic is greater than the "cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan" statistic.
- AThere is a transaction, which committed after the query began, that has modified some of the table blocks, causing some "cell single block physical reads" to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- BThere are chained rows in the table, causing some "single block physical reads" to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- CThe table is a hash clustered table, causing "cell multiblock physical reads" to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- DThe table is list partitioned, causing "cell list of blocks physical reads" to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- EThere is a local index on a list partitioned table on the column used in the WHERE clause, causing "cell list of blocks physical reads" to be requested by the
Correct Answer:
CD
C: Scan on a clustered table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
D: Scan on an index-organized table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
Note: The Cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan metric shows how many bytes of I/O were returned by a smart scan to the database server.
References:
https://uhesse.com/2011/01/19/exadata-part-i-smart-scan/
CD
C: Scan on a clustered table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
D: Scan on an index-organized table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
Note: The Cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan metric shows how many bytes of I/O were returned by a smart scan to the database server.
References:
https://uhesse.com/2011/01/19/exadata-part-i-smart-scan/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
You wish to determine if the I/O resource management plan that you created has helped improve the performance of OLTP category I/Os on your X6 Exadata
Database Machine.
You decide to examine the relevant metrics on all the cells, to see whether the I/O rate has improved for this category compared to last week, and whether waits and wait time have been reduced.
You issue this command on the first cell:

You examine the output from the first cell which contains:
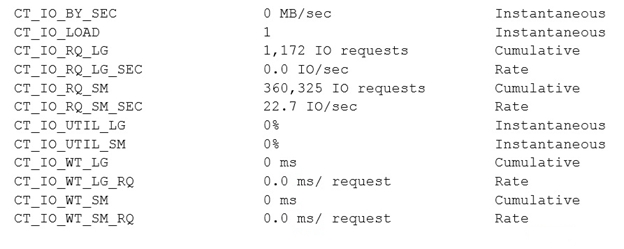
Which two sets of metrics would you use to determine whether the I/O performance has improved for the OLTP category for the duration of the one-hour measurement period?
Database Machine.
You decide to examine the relevant metrics on all the cells, to see whether the I/O rate has improved for this category compared to last week, and whether waits and wait time have been reduced.
You issue this command on the first cell:

You examine the output from the first cell which contains:

Which two sets of metrics would you use to determine whether the I/O performance has improved for the OLTP category for the duration of the one-hour measurement period?
- ACT_IO_RQ_SM, CT_IO_RQ_LG, CT_IO_RQ_SM_SEC, and CT_IO_RQ_LG_SEC
- BCT_IO_UTIL_SM and CT_IO_UTIL_LG
- CCT_IO_RQ_SM_SEC and CT_IO_RQ_LG_SEC
- DCT_IO_WT_SM, CT_IO_WT_LG, CT_IO_WT_SM_RQ, and CT_IO_WT_LG_RQ
Correct Answer:
D
✑ CT_IO_RQ_SM
The cumulative number of small I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category.
✑ CT_IO_RQ_LG
The cumulative number of large I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category.
✑ CT_IO_WT_SM_RQ
The average IORM wait time per request for small I/O requests issued to hard disks by an IORM category.
✑ CT_IO_WT_LG_RQ
The average IORM wait time per request for large I/O requests issued to hard disks by an IORM category.
Incorrect Answers:
A: CT_IO_RQ_SM_SEC -
This metric is derived from CT_IO_RQ_SM. It specifies the rate of small I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. Its units are number of I/O requests per second. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category in the past minute.
B: CT_IO_UTIL_SM -
The percentage of disk resources utilized by small requests from this category.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server-monitoring.htm
D
✑ CT_IO_RQ_SM
The cumulative number of small I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category.
✑ CT_IO_RQ_LG
The cumulative number of large I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category.
✑ CT_IO_WT_SM_RQ
The average IORM wait time per request for small I/O requests issued to hard disks by an IORM category.
✑ CT_IO_WT_LG_RQ
The average IORM wait time per request for large I/O requests issued to hard disks by an IORM category.
Incorrect Answers:
A: CT_IO_RQ_SM_SEC -
This metric is derived from CT_IO_RQ_SM. It specifies the rate of small I/O requests issued by the category for hard disks. Its units are number of I/O requests per second. A large value indicates a heavy I/O workload from this category in the past minute.
B: CT_IO_UTIL_SM -
The percentage of disk resources utilized by small requests from this category.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server-monitoring.htm
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
Which three are true about Exadata Smart Flash Log?
- ADatabases on the Database Machine use Exadata Smart Flash Log by default.
- BI/O Resource Manager database plans can be used to enable or disable Exadata Smart Flash Log for individual databases.
- CLGWR will not wait for writes to Exadata Smart Flash Log if the write to a disk-based logfile completes first.
- DI/O Resource Manager category plans can be used to enable or disable Exadata Smart Flash Log for different I/O categories.
- EThe use of Exadata Smart Flash Logs is mandatory for support of production databases.
Correct Answer:
ABC
A: Exadata I/O Resource Manager (IORM) has been enhanced to enable or disable Smart Flash Logging for the different databases running on the Database
Machine, reserving flash for the most performance critical databases.
B: The Exadata I/O Resource Manager (IORM) has been enhanced to enable or disable Smart Flash Logging for the different databases running on the Database
Machine.
C: Smart Flash Logging works as follows. When receiving a redo log write request, Exadata will do parallel writes to the on-disk redo logs as well as a small amount of space reserved in the flash hardware. When either of these writes has successfully completed the database will be immediately notified of completion. If the disk drives hosting the logs experience slow response times, then the Exadata Smart Flash Cache will provide a faster log write response time.
Conversely, if the Exadata Smart Flash Cache is temporarily experiencing slow response times (e.g., due to wear leveling algorithms), then the disk drive will provide a faster response time.
This algorithm will significantly smooth out redo write response times and provide overall better database performance.
Incorrect Answers:
D: Category plans are configured and enabled using the CellCLI utility on the cell. Only one category plan can be enabled at a time.
References:
http://structureddata.org/2011/10/12/exadata-smart-flash-logging-explained/
ABC
A: Exadata I/O Resource Manager (IORM) has been enhanced to enable or disable Smart Flash Logging for the different databases running on the Database
Machine, reserving flash for the most performance critical databases.
B: The Exadata I/O Resource Manager (IORM) has been enhanced to enable or disable Smart Flash Logging for the different databases running on the Database
Machine.
C: Smart Flash Logging works as follows. When receiving a redo log write request, Exadata will do parallel writes to the on-disk redo logs as well as a small amount of space reserved in the flash hardware. When either of these writes has successfully completed the database will be immediately notified of completion. If the disk drives hosting the logs experience slow response times, then the Exadata Smart Flash Cache will provide a faster log write response time.
Conversely, if the Exadata Smart Flash Cache is temporarily experiencing slow response times (e.g., due to wear leveling algorithms), then the disk drive will provide a faster response time.
This algorithm will significantly smooth out redo write response times and provide overall better database performance.
Incorrect Answers:
D: Category plans are configured and enabled using the CellCLI utility on the cell. Only one category plan can be enabled at a time.
References:
http://structureddata.org/2011/10/12/exadata-smart-flash-logging-explained/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
Which components of an Exadata storage server image, if updated, may require that a patch also be applied to the database servers in an Exadata X6 Database
Machine?
Machine?
- ALinux operating system on the storage server
- BInfiniBand HCA firmware on the storage server
- CStorage server hard disk device drivers
- DStorage server flash device drivers
Correct Answer:
D
Exadata patches are intended for and include fixes for both the storage servers and Compute servers, and optionally InfiniBand switches.
Patching order -
You should patch the Exadata Database Machines in the following sequence
✑ Oracle GI/RDBMS Homes
✑ Exadata Storage Cells
✑ Compute nodes
✑ Infiniband Switches
References: https://www.toadworld.com/platforms/oracle/w/wiki/11640.oracle-exadata-patching
D
Exadata patches are intended for and include fixes for both the storage servers and Compute servers, and optionally InfiniBand switches.
Patching order -
You should patch the Exadata Database Machines in the following sequence
✑ Oracle GI/RDBMS Homes
✑ Exadata Storage Cells
✑ Compute nodes
✑ Infiniband Switches
References: https://www.toadworld.com/platforms/oracle/w/wiki/11640.oracle-exadata-patching
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
