Oracle 1z0-061 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (339 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Examine the structure of the transactions table:

You want to display the date, time, and transaction amount of transactions that where done before 12 noon. The value zero should be displayed for transactions where the transaction amount has not been entered.
Which query gives the required result?


You want to display the date, time, and transaction amount of transactions that where done before 12 noon. The value zero should be displayed for transactions where the transaction amount has not been entered.
Which query gives the required result?

send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Examine the data in the ename and hiredate columns of the employees table:
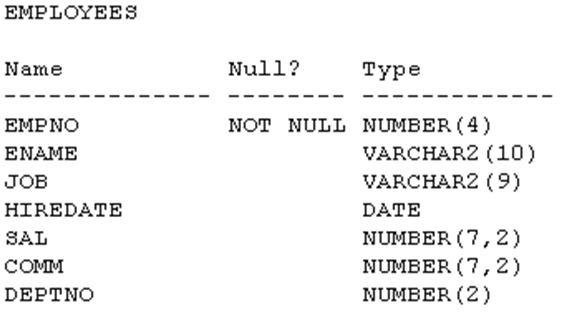

You want to generate a list of user IDs as follows:
You issue the following query:
What is the outcome?


You want to generate a list of user IDs as follows:

You issue the following query:
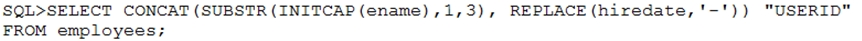
What is the outcome?
- AIt executes successfully and gives the correct output.
- BIt executes successfully but does not give the correct output.
- CIt generates an error because the REPLACE function is not valid.
- DIt generates an error because the SUBSTR function cannot be nested in the CONCAT function.
Correct Answer:
A
REPLACE (text, search_string, replacement_string)
Searches a text expression for a character string and, if found, replaces it with a specified replacement string
The REPLACE Function -
The REPLACE function replaces all occurrences of a search item in a source string with a replacement term and returns the modified source string. If the length of the replacement term is different from that of the search item, then the lengths of the returned and source strings will be different. If the search string is not found, the source string is returned unchanged. Numeric and date literals and expressions are evaluated before being implicitly cast as characters when they occur as parameters to the REPLACE function.
The REPLACE function takes three parameters, with the first two being mandatory. Its syntax is REPLACE (source string, search item, [replacement term]).
If the replacement term parameter is omitted, each occurrence of the search item is removed from the source string. In other words, the search item is replaced by an empty string. .
The following queries illustrate the REPLACE function with numeric and date expressions:
Query 1: select replace(10000-3, '9', '85') from dual
Query 2: select replace(sysdate, 'DEC', 'NOV') from dual
A
REPLACE (text, search_string, replacement_string)
Searches a text expression for a character string and, if found, replaces it with a specified replacement string
The REPLACE Function -
The REPLACE function replaces all occurrences of a search item in a source string with a replacement term and returns the modified source string. If the length of the replacement term is different from that of the search item, then the lengths of the returned and source strings will be different. If the search string is not found, the source string is returned unchanged. Numeric and date literals and expressions are evaluated before being implicitly cast as characters when they occur as parameters to the REPLACE function.
The REPLACE function takes three parameters, with the first two being mandatory. Its syntax is REPLACE (source string, search item, [replacement term]).
If the replacement term parameter is omitted, each occurrence of the search item is removed from the source string. In other words, the search item is replaced by an empty string. .
The following queries illustrate the REPLACE function with numeric and date expressions:
Query 1: select replace(10000-3, '9', '85') from dual
Query 2: select replace(sysdate, 'DEC', 'NOV') from dual
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Evaluate the following SQL commands:
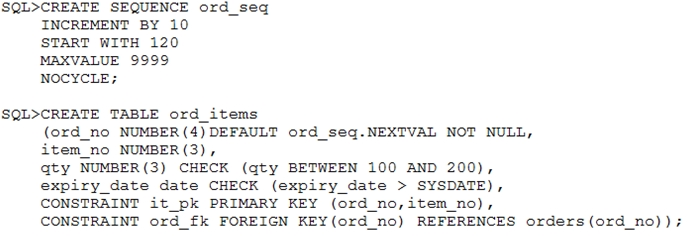
The command to create a table fails. Identify the two reasons for the SQL statement failure?

The command to create a table fails. Identify the two reasons for the SQL statement failure?
- AYou cannot use SYSDATE in the condition of a check constraint.
- BYou cannot use the BETWEEN clause in the condition of a check constraint.
- CYou cannot use the NEXTVAL sequence value as a default value for a column.
- DYou cannot use ORD_NO and ITEM_NO columns as a composite primary key because ORD_NO is also the foreign key.
Correct Answer:
AC
CHECK Constraint -
The CHECK constraint defines a condition that each row must satisfy. The condition can use the same constructs as the query conditions, with the following exceptions:
References to the CURRVAL, NEXTVAL, LEVEL, and ROWNUM pseudocolumns
Calls to SYSDATE, UID, USER, and USERENV functions
Queries that refer to other values in other rows
A single column can have multiple CHECK constraints that refer to the column in its definition.
There is no limit to the number of CHECK constraints that you can define on a column.
CHECK constraints can be defined at the column level or table level.
CREATE TABLE employees -
(...
Salary NUMBER(8, 2) CONSTRAINT emp_salary_min
CHECK (salary > 0),
AC
CHECK Constraint -
The CHECK constraint defines a condition that each row must satisfy. The condition can use the same constructs as the query conditions, with the following exceptions:
References to the CURRVAL, NEXTVAL, LEVEL, and ROWNUM pseudocolumns
Calls to SYSDATE, UID, USER, and USERENV functions
Queries that refer to other values in other rows
A single column can have multiple CHECK constraints that refer to the column in its definition.
There is no limit to the number of CHECK constraints that you can define on a column.
CHECK constraints can be defined at the column level or table level.
CREATE TABLE employees -
(...
Salary NUMBER(8, 2) CONSTRAINT emp_salary_min
CHECK (salary > 0),
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the SALES table.
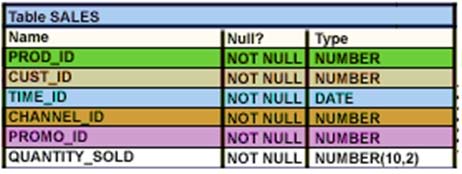
The following query is written to retrieve all those product IDs from the SALES table that have more than 55000 sold and have been ordered more than 10 times.
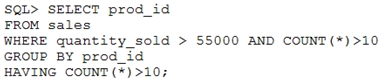
Which statement is true regarding this SQL statement?

The following query is written to retrieve all those product IDs from the SALES table that have more than 55000 sold and have been ordered more than 10 times.

Which statement is true regarding this SQL statement?
- AIt executes successfully and generates the required result.
- BIt produces an error because count(*) should be specified in the SELECT clause also.
- CIt produces an error because count{*) should be only in the HAVING clause and not in the WHERE clause.
- DIt executes successfully but produces no result because COUNT (prod_id) should be used instead of COUNT (*).
Correct Answer:
C
Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
You use the HAVING clause to specify the groups that are to be displayed, thus further restricting the groups on the basis of aggregate information.
In the syntax, group_condition restricts the groups of rows returned to those groups for which the specified condition is true.
The Oracle server performs the following steps when you use the HAVING clause:
1. Rows are grouped.
2. The group function is applied to the group.
3. The groups that match the criteria in the HAVING clause are displayed.
The HAVING clause can precede the GROUP BY clause, but it is recommended that you place the GROUP BY clause first because it is more logical. Groups are formed and group functions are calculated before the HAVING clause is applied to the groups in the SELECT list.
Note: The WHERE clause restricts rows, whereas the HAVING clause restricts groups.
C
Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
You use the HAVING clause to specify the groups that are to be displayed, thus further restricting the groups on the basis of aggregate information.
In the syntax, group_condition restricts the groups of rows returned to those groups for which the specified condition is true.
The Oracle server performs the following steps when you use the HAVING clause:
1. Rows are grouped.
2. The group function is applied to the group.
3. The groups that match the criteria in the HAVING clause are displayed.
The HAVING clause can precede the GROUP BY clause, but it is recommended that you place the GROUP BY clause first because it is more logical. Groups are formed and group functions are calculated before the HAVING clause is applied to the groups in the SELECT list.
Note: The WHERE clause restricts rows, whereas the HAVING clause restricts groups.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the customers table.
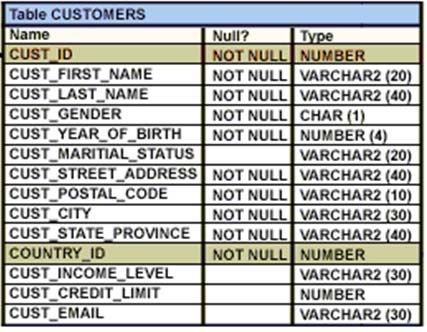
Using the customers table, you need to generate a report that shows an increase in the credit limit by 15% for all customers. Customers whose credit limit has not been entered should have the message "Not Available" displayed.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?


Using the customers table, you need to generate a report that shows an increase in the credit limit by 15% for all customers. Customers whose credit limit has not been entered should have the message "Not Available" displayed.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?

- AOption A
- BOption B
- COption C
- DOption D
Correct Answer:
D
NVL Function -
Converts a null value to an actual value:
Data types that can be used are date, character, and number.
Data types must match:
NVL(commission_pct, 0)
NVL(hire_date, '01-JAN-97')
NVL(job_id, 'No Job Yet')
D
NVL Function -
Converts a null value to an actual value:
Data types that can be used are date, character, and number.
Data types must match:
NVL(commission_pct, 0)
NVL(hire_date, '01-JAN-97')
NVL(job_id, 'No Job Yet')
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the promotions table.
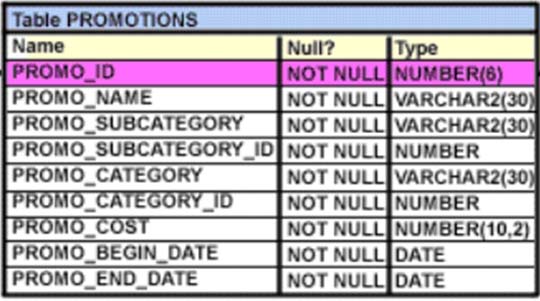
Evaluate the following SQL statement:

Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?

Evaluate the following SQL statement:

Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?
- AIt shows COST_REMARK for all the promos in the table.
- BIt produces an error because the SUBQUERY gives an error.
- CIt shows COST_REMARK for all the promos in the promo category 'TV'
- DIt produces an error because SUBQUERIES cannot be used with the case expression.
Correct Answer:
A
A
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
Examine the structure and data of the CUST_TRANS table:
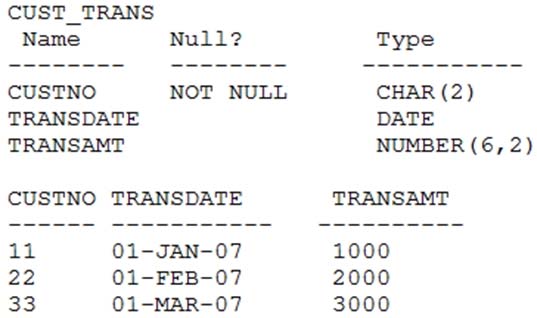
Dates are stored in the default date format dd-mon-rr in the CUST_TRANS table. Which three SQL statements would execute successfully?

Dates are stored in the default date format dd-mon-rr in the CUST_TRANS table. Which three SQL statements would execute successfully?
- ASELECT transdate + '10' FROM cust_trans;
- BSELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate = '01-01-07';
- CSELECT transamt FROM cust_trans WHERE custno > '11';
- DSELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate='01-JANUARY-07';
- ESELECT custno + 'A' FROM cust_trans WHERE transamt > 2000;
Correct Answer:
ACD
ACD
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the customers table.
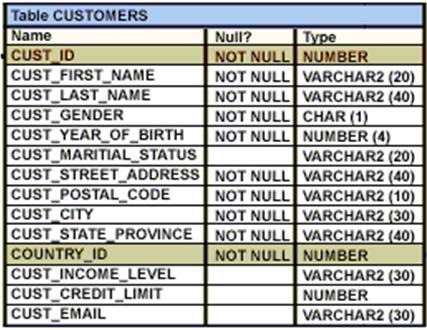
NEW_CUSTOMERS is a new table with the columns CUST_ID, CUST_NAME and CUST_CITY that have the same data types and size as the corresponding columns in the customers table.
Evaluate the following insert statement:

The insert statement fails when executed.
What could be the reason?

NEW_CUSTOMERS is a new table with the columns CUST_ID, CUST_NAME and CUST_CITY that have the same data types and size as the corresponding columns in the customers table.
Evaluate the following insert statement:

The insert statement fails when executed.
What could be the reason?
- AThe values clause cannot be used in an INSERT with a subquery.
- BColumn names in the NEW_CUSTOMERS and CUSTOMERS tables do not match.
- CThe where clause cannot be used in a subquery embedded in an INSERT statement.
- DThe total number of columns in the NEW_CUSTOMERS table does not match the total number of columns in the CUSTOMERS table.
Correct Answer:
A
Copying Rows from Another Table -
Write your INSERT statement with a subquery:
Do not use the VALUES clause.
Match the number of columns in the INSERT clause to those in the subquery.
Inserts all the rows returned by the subquery in the table, sales_reps.
A
Copying Rows from Another Table -
Write your INSERT statement with a subquery:
Do not use the VALUES clause.
Match the number of columns in the INSERT clause to those in the subquery.
Inserts all the rows returned by the subquery in the table, sales_reps.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
YOU need to display the date ll-oct-2007 in words as Eleventh of October, Two Thousand Seven'.
Which SQL statement would give the required result?

Which SQL statement would give the required result?

- AOption A
- BOption B
- COption C
- DOption D
Correct Answer:
C
The '11-oct-2007' is a string not a date. We need to user the TO_DATE function and convert it to a date.
C
The '11-oct-2007' is a string not a date. We need to user the TO_DATE function and convert it to a date.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
Examine the data in the ORD_ITEMS table:
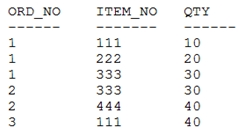
Evaluate the following query:

Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?

Evaluate the following query:

Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?
- AIt gives an error because the having clause should be specified after the group by clause.
- BIt gives an error because all the aggregate functions used in the having clause must be specified in the select list.
- CIt displays the item nos with their average quantity where the average quantity is more than double the minimum quantity of that item in the table.
- DIt displays the item nos with their average quantity where the average quantity is more than double the overall minimum quantity of all the items in the table.
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
