Oracle 1z0-051 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (290 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which two statements are true about sequences created in a single instance database? (Choose two.)
- ACURRVAL is used to refer to the last sequence number that has been generated
- BDELETE <sequencename> would remove a sequence from the database
- CThe numbers generated by a sequence can be used only for one table
- DWhen the MAXVALUE limit for a sequence is reached, you can increase the MAXVALUE limit by using the ALTER SEQUENCE statement
- EWhen a database instance shuts down abnormally, the sequence numbers that have been cached but not used would be available once again when the database instance is restarted
Correct Answer:
AD
Gaps in the Sequence -
Although sequence generators issue sequential numbers without gaps, this action occurs independent of a commit or rollback. Therefore, if you roll back a statement containing a sequence, the number is lost.
Another event that can cause gaps in the sequence is a system crash. If the sequence caches values in memory, those values are lost if the system crashes.
Because sequences are not tied directly to tables, the same sequence can be used for multiple tables.
However, if you do so, each table can contain gaps in the sequential numbers.
Modifying a Sequence -
If you reach the MAXVALUE limit for your sequence, no additional values from the sequence are allocated and you will receive an error indicating that the sequence exceeds the MAXVALUE. To continue to use the sequence, you can modify it by using the ALTER SEQUENCE statement
To remove a sequence, use the DROP statement:
DROP SEQUENCE dept_deptid_seq;
AD
Gaps in the Sequence -
Although sequence generators issue sequential numbers without gaps, this action occurs independent of a commit or rollback. Therefore, if you roll back a statement containing a sequence, the number is lost.
Another event that can cause gaps in the sequence is a system crash. If the sequence caches values in memory, those values are lost if the system crashes.
Because sequences are not tied directly to tables, the same sequence can be used for multiple tables.
However, if you do so, each table can contain gaps in the sequential numbers.
Modifying a Sequence -
If you reach the MAXVALUE limit for your sequence, no additional values from the sequence are allocated and you will receive an error indicating that the sequence exceeds the MAXVALUE. To continue to use the sequence, you can modify it by using the ALTER SEQUENCE statement
To remove a sequence, use the DROP statement:
DROP SEQUENCE dept_deptid_seq;
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
The ORDERS TABLE belongs to the user OE. OE has granted the SELECT privilege on the ORDERS table to the user HR.
Which statement would create a synonym ORD so that HR can execute the following query successfully?
SELECT * FROM ord;
Which statement would create a synonym ORD so that HR can execute the following query successfully?
SELECT * FROM ord;
- ACREATE SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
- BCREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
- CCREATE SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database administrator.
- DCREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database administrator.
Correct Answer:
D
Creating a Synonym for an Object
To refer to a table that is owned by another user, you need to prefix the table name with the name of the user who created it, followed by a period. Creating a synonym eliminates the need to qualify the object name with the schema and provides you with an alternative name for a table, view, sequence, procedure, or other objects.
This method can be especially useful with lengthy object names, such as views.
In the syntax:
PUBLIC Creates a synonym that is accessible to all users synonym Is the name of the synonym to be created object Identifies the object for which the synonym is created
Guidelines -
The object cannot be contained in a package.
A private synonym name must be distinct from all other objects that are owned by the same user.
If you try to execute the following command (alternative B, issued by OE):
D
Creating a Synonym for an Object
To refer to a table that is owned by another user, you need to prefix the table name with the name of the user who created it, followed by a period. Creating a synonym eliminates the need to qualify the object name with the schema and provides you with an alternative name for a table, view, sequence, procedure, or other objects.
This method can be especially useful with lengthy object names, such as views.
In the syntax:
PUBLIC Creates a synonym that is accessible to all users synonym Is the name of the synonym to be created object Identifies the object for which the synonym is created
Guidelines -
The object cannot be contained in a package.
A private synonym name must be distinct from all other objects that are owned by the same user.
If you try to execute the following command (alternative B, issued by OE):
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Evaluate this SQL statement:
SELECT e.emp_name, d.dept_name -
FROM employees e -
JOIN departments d -
USING (department_id)
WHERE d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)
ORDER BY dept_name;
The statement fails when executed. Which change fixes the error?
SELECT e.emp_name, d.dept_name -
FROM employees e -
JOIN departments d -
USING (department_id)
WHERE d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)
ORDER BY dept_name;
The statement fails when executed. Which change fixes the error?
- Aremove the ORDER BY clause
- Bremove the table alias prefix from the WHERE clause
- Cremove the table alias from the SELECT clause
- Dprefix the column in the USING clause with the table alias
- Eprefix the column in the ORDER BY clause with the table alias
- Freplace the condition"d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)"in the WHERE clause with"d.department_id <> 10 AND d.department_id <> 40"
Correct Answer:
B
B
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Examine the statement:
Create synonym emp for hr.employees;
What happens when you issue the statement?
Create synonym emp for hr.employees;
What happens when you issue the statement?
- AAn error is generated.
- BYou will have two identical tables in the HR schema with different names.
- CYou create a table called employees in the HR schema based on you EMP table.
- DYou create an alternative name for the employees table in the HR schema in your own schema. D
Correct Answer:
Explanation
Explanation
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
Evaluate the following SQL query;
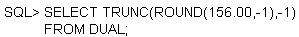
What would be the outcome?
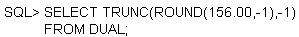
What would be the outcome?
- A200
- B16
- C160
- D150
- E100
Correct Answer:
C
Function Purpose -
ROUND(column|expression, n) Rounds the column, expression, or value to n decimal places or, if n is omitted, no decimal places (If n is negative, numbers to the left of decimal point are rounded.)
TRUNC(column|expression, n) Truncates the column, expression, or value to n decimal places or, if n is omitted, n defaults to zero
C
Function Purpose -
ROUND(column|expression, n) Rounds the column, expression, or value to n decimal places or, if n is omitted, no decimal places (If n is negative, numbers to the left of decimal point are rounded.)
TRUNC(column|expression, n) Truncates the column, expression, or value to n decimal places or, if n is omitted, n defaults to zero
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
