MuleSoft MCIA - Level 1 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (101 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #16
What operation can be performed through a JMX agent enabled in a Mule application?
- AView object store entries
- BReplay an unsuccessful message
- CDeploy a Mule application
- DSet a particular log4j2 log level to TRACEMost Voted
Correct Answer:
D
D
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
A retailer is designing a data exchange interface to be used by its suppliers. The interface must support secure communication over the public internet. The interface must also work with a wide variety of programming languages and IT systems used by suppliers.
What are suitable interface technologies for this data exchange that are secure, cross-platform, and internet friendly, assuming that Anypoint Connectors exist for these interface technologies?
What are suitable interface technologies for this data exchange that are secure, cross-platform, and internet friendly, assuming that Anypoint Connectors exist for these interface technologies?
- ACSV over FTP YAML over TLS JSON over HTTPS
- BSOAP over HTTPS IIOP over TLS gRPC over HTTPS
- CEDIFACT XML over SFTP JSON/REST over HTTPSMost Voted
- DXML over ActiveMQ XML over SFTP XML/REST over HTTPS
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
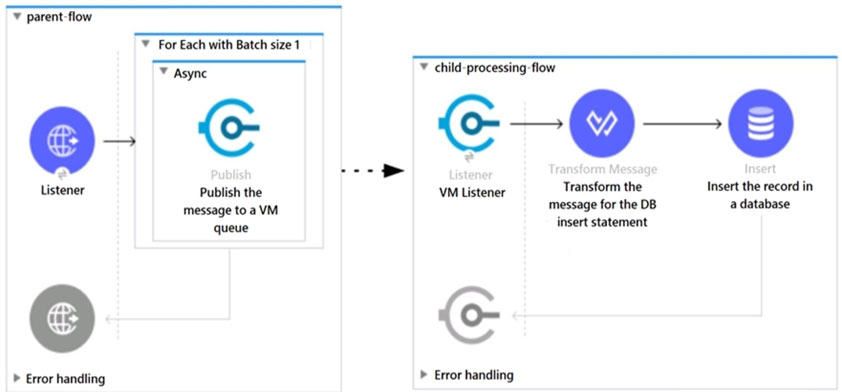
Refer to the exhibit. A Mule 4 application has a parent flow that breaks up a JSON array payload into 200 separate items, then sends each item one at a time inside an Async scope to a VM queue.
A second flow to process orders has a VM Listener on the same VM queue. The rest of this flow processes each received item by writing the item to a database.
This Mule application is deployed to four CloudHub workers with persistent queues enabled.
What message processing guarantees are provided by the VM queue and the CloudHub workers, and how are VM messages routed among the CloudHub workers for each invocation of the parent flow under normal operating conditions where all the CloudHub workers remain online?
A second flow to process orders has a VM Listener on the same VM queue. The rest of this flow processes each received item by writing the item to a database.
This Mule application is deployed to four CloudHub workers with persistent queues enabled.
What message processing guarantees are provided by the VM queue and the CloudHub workers, and how are VM messages routed among the CloudHub workers for each invocation of the parent flow under normal operating conditions where all the CloudHub workers remain online?

- AEACH item VM message is processed AT LEAST ONCE by ONE ARBITRARY CloudHub worker Each of the four CloudHub workers can be expected to process some item VM messagesMost Voted
- BALL item VM messages are processed AT MOST ONCE by ONE ARBITRARY CloudHub worker This one CloudHub worker processes ALL 200 item VM messages
- CALL item VM messages are processed AT LEAST ONCE by the SAME CloudHub worker where the parent flow was invoked This one CloudHub worker processes ALL 200 item VM messages
- DEACH item VM message is processed AT MOST ONCE by ONE CloudHub worker, with workers chosen in a deterministic round-robin fashion Each of the four CloudHub workers can be expected to process 1/4 of the item VM messages (about 50 items)
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
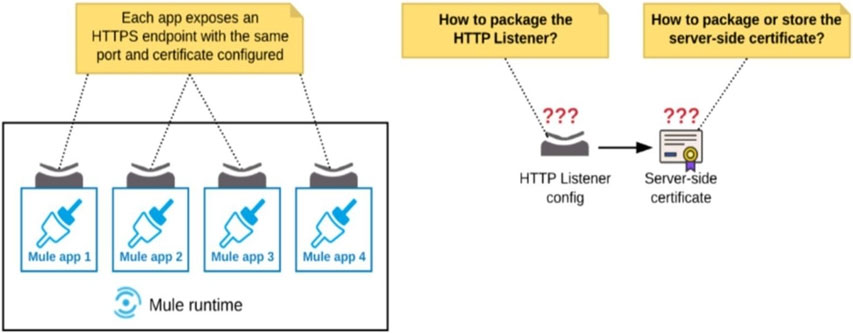
Refer to the exhibit. An organization deploys multiple Mule applications to the same customer-hosted Mule runtime. Many of these Mule applications must expose an HTTPS endpoint on the same port using a server-side certificate that rotates often.
What is the most effective way to package the HTTP Listener and package or store the server-side certificate when deploying these Mule applications, so the disruption caused by certificate rotation is minimized?
What is the most effective way to package the HTTP Listener and package or store the server-side certificate when deploying these Mule applications, so the disruption caused by certificate rotation is minimized?

- APackage the HTTPS Listener configuration in a Mule DOMAIN project, referencing it from all Mule applications that need to expose an HTTPS endpoint Store the server-side certificate in a shared filesystem location in the Mule runtime's classpath, OUTSIDE the Mule DOMAIN or any Mule APPLICATIONMost Voted
- BPackage the HTTPS Listener configuration in a Mule DOMAIN project, referencing it from all Mule applications that need to expose an HTTPS endpoint Package the server-side certificate in ALL Mule APPLICATIONS that need to expose an HTTPS endpoint
- CPackage the HTTPS Listener configuration in a Mule DOMAIN project, referencing it from all Mule applications that need to expose an HTTPS endpoint Package the server-side certificate in the SAME Mule DOMAIN project
- DPackage an HTTPS Listener configuration in all Mule APPLICATIONS that need to expose an HTTPS endpoint Package the server-side certificate in a NEW Mule DOMAIN project
Correct Answer:
A
A
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
What metrics about API invocations are available for visualization in custom charts using Anypoint Analytics?
- ARequest size, request HTTP verbs, response time
- BRequest size, number of requests, JDBC Select operation result set size
- CRequest size, number of requests, JDBC Select operation response time
- DRequest size, number of requests, response size, response timeMost Voted
Correct Answer:
D
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/monitoring/api-analytics-dashboard
D
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/monitoring/api-analytics-dashboard
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
