Microsoft DP-420 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (194 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
HOTSPOT -
You are creating a database in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account. The database will be used by an application that will provide users with the ability to share online posts. Users will also be able to submit comments on other users' posts.
You need to store the data shown in the following table.

The application has the following characteristics:
✑ Users can submit an unlimited number of posts.
✑ The average number of posts submitted by a user will be more than 1,000.
✑ Posts can have an unlimited number of comments from different users.
✑ The average number of comments per post will be 100, but many posts will exceed 1,000 comments.
✑ Users will be limited to having a maximum of 20 interests.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

You are creating a database in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account. The database will be used by an application that will provide users with the ability to share online posts. Users will also be able to submit comments on other users' posts.
You need to store the data shown in the following table.

The application has the following characteristics:
✑ Users can submit an unlimited number of posts.
✑ The average number of posts submitted by a user will be more than 1,000.
✑ Posts can have an unlimited number of comments from different users.
✑ The average number of comments per post will be 100, but many posts will exceed 1,000 comments.
✑ Users will be limited to having a maximum of 20 interests.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Box 1: Yes -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.
Box 2: Yes -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.
Box 3: No -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.

Box 1: Yes -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.
Box 2: Yes -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.
Box 3: No -
Non-relational data increases write costs, but can decrease read costs.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
DRAG DROP -
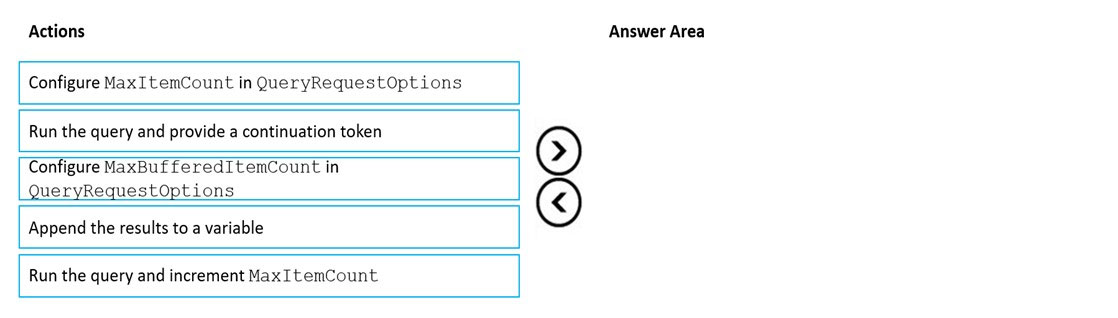
You have an app that stores data in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account The app performs queries that return large result sets.
You need to return a complete result set to the app by using pagination. Each page of results must return 80 items.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
You have an app that stores data in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account The app performs queries that return large result sets.
You need to return a complete result set to the app by using pagination. Each page of results must return 80 items.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
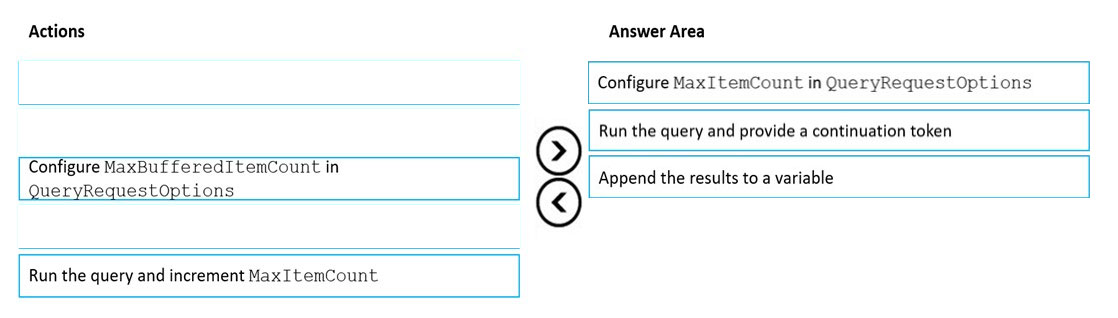
Step 1: Configure the MaxItemCount in QueryRequestOptions
You can specify the maximum number of items returned by a query by setting the MaxItemCount. The MaxItemCount is specified per request and tells the query engine to return that number of items or fewer.
Box 2: Run the query and provide a continuation token
In the .NET SDK and Java SDK you can optionally use continuation tokens as a bookmark for your query's progress. Azure Cosmos DB query executions are stateless at the server side and can be resumed at any time using the continuation token.
If the query returns a continuation token, then there are additional query results.
Step 3: Append the results to a variable
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/sql-query-pagination

Step 1: Configure the MaxItemCount in QueryRequestOptions
You can specify the maximum number of items returned by a query by setting the MaxItemCount. The MaxItemCount is specified per request and tells the query engine to return that number of items or fewer.
Box 2: Run the query and provide a continuation token
In the .NET SDK and Java SDK you can optionally use continuation tokens as a bookmark for your query's progress. Azure Cosmos DB query executions are stateless at the server side and can be resumed at any time using the continuation token.
If the query returns a continuation token, then there are additional query results.
Step 3: Append the results to a variable
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/sql-query-pagination
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYesMost Voted
- BNo
Correct Answer:
A
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Note: Alerts are used to set up recurring tests to monitor the availability and responsiveness of your Azure Cosmos DB resources. Alerts can send you a notification in the form of an email, or execute an Azure Function when one of your metrics reaches the threshold or if a specific event is logged in the activity log.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
A
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Note: Alerts are used to set up recurring tests to monitor the availability and responsiveness of your Azure Cosmos DB resources. Alerts can send you a notification in the form of an email, or execute an Azure Function when one of your metrics reaches the threshold or if a specific event is logged in the activity log.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure the function to have an Azure CosmosDB trigger.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure the function to have an Azure CosmosDB trigger.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNoMost Voted
Correct Answer:
B
Instead configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
B
Instead configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure an application to use the change feed processor to read the change feed and you configure the application to trigger the function.
Does this meet the goal?
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account 1 that uses autoscale throughput.
You need to run an Azure function when the normalized request units per second for a container in account1 exceeds a specific value.
Solution: You configure an application to use the change feed processor to read the change feed and you configure the application to trigger the function.
Does this meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNoMost Voted
Correct Answer:
B
Instead configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
B
Instead configure an Azure Monitor alert to trigger the function.
You can set up alerts from the Azure Cosmos DB pane or the Azure Monitor service in the Azure portal.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/create-alerts
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
