Microsoft AZ-202 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (61 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
DRAG DROP -
You are implementing an order processing system. A point of sale application publishes orders to topics in an Azure Service Bus queue. The label property for the topic includes the following data:
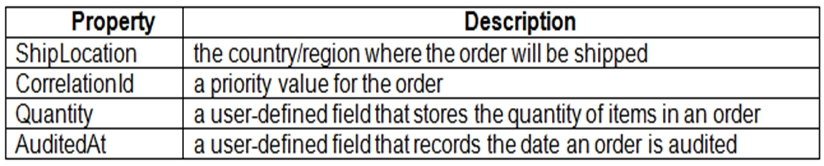
The system has the following requirements for subscriptions:
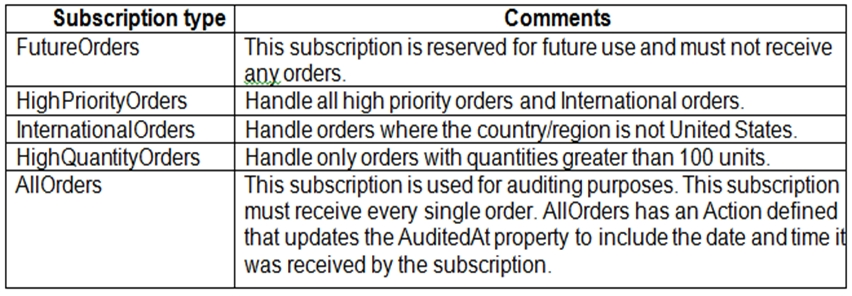
You need to implement filtering and maximize throughput while evaluating filters.
Which filter types should you implement? To answer, drag the appropriate filter types to the correct subscriptions. Each filter type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

You are implementing an order processing system. A point of sale application publishes orders to topics in an Azure Service Bus queue. The label property for the topic includes the following data:

The system has the following requirements for subscriptions:

You need to implement filtering and maximize throughput while evaluating filters.
Which filter types should you implement? To answer, drag the appropriate filter types to the correct subscriptions. Each filter type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
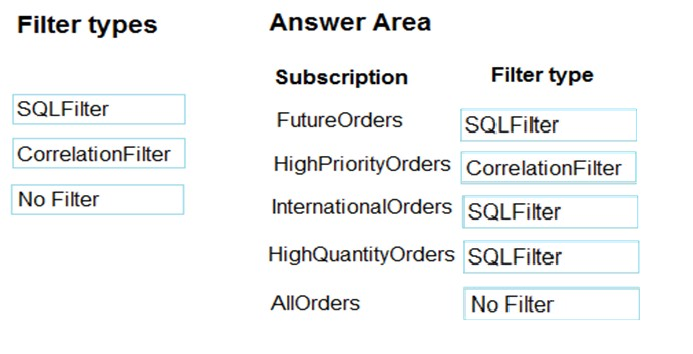
FutureOrders: SQLFilter -
HighPriortyOrders: CorrelationFilter
CorrelationID only -
InternationalOrders: SQLFilter -
Country NOT USA requires an SQL Filter
HighQuantityOrders: SQLFilter -
Need to use relational operators so an SQL Filter is needed.
AllOrders: No Filter -
SQL Filter: SQL Filters - A SqlFilter holds a SQL-like conditional expression that is evaluated in the broker against the arriving messages' user-defined properties and system properties. All system properties must be prefixed with sys. in the conditional expression. The SQL-language subset for filter conditions tests for the existence of properties (EXISTS), as well as for null-values (IS NULL), logical NOT/AND/OR, relational operators, simple numeric arithmetic, and simple text pattern matching with LIKE.
Correlation Filters - A CorrelationFilter holds a set of conditions that are matched against one or more of an arriving message's user and system properties. A common use is to match against the CorrelationId property, but the application can also choose to match against ContentType, Label, MessageId, ReplyTo,
ReplyToSessionId, SessionId, To, and any user-defined properties. A match exists when an arriving message's value for a property is equal to the value specified in the correlation filter. For string expressions, the comparison is case-sensitive. When specifying multiple match properties, the filter combines them as a logical
AND condition, meaning for the filter to match, all conditions must match.
Boolean filters - The TrueFilter and FalseFilter either cause all arriving messages (true) or none of the arriving messages (false) to be selected for the subscription.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-bus-messaging/topic-filters

FutureOrders: SQLFilter -
HighPriortyOrders: CorrelationFilter
CorrelationID only -
InternationalOrders: SQLFilter -
Country NOT USA requires an SQL Filter
HighQuantityOrders: SQLFilter -
Need to use relational operators so an SQL Filter is needed.
AllOrders: No Filter -
SQL Filter: SQL Filters - A SqlFilter holds a SQL-like conditional expression that is evaluated in the broker against the arriving messages' user-defined properties and system properties. All system properties must be prefixed with sys. in the conditional expression. The SQL-language subset for filter conditions tests for the existence of properties (EXISTS), as well as for null-values (IS NULL), logical NOT/AND/OR, relational operators, simple numeric arithmetic, and simple text pattern matching with LIKE.
Correlation Filters - A CorrelationFilter holds a set of conditions that are matched against one or more of an arriving message's user and system properties. A common use is to match against the CorrelationId property, but the application can also choose to match against ContentType, Label, MessageId, ReplyTo,
ReplyToSessionId, SessionId, To, and any user-defined properties. A match exists when an arriving message's value for a property is equal to the value specified in the correlation filter. For string expressions, the comparison is case-sensitive. When specifying multiple match properties, the filter combines them as a logical
AND condition, meaning for the filter to match, all conditions must match.
Boolean filters - The TrueFilter and FalseFilter either cause all arriving messages (true) or none of the arriving messages (false) to be selected for the subscription.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-bus-messaging/topic-filters
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
You are developing an Azure Batch solution to perform CPU intensive calculations. The calculations occur at a specific time each week and last for approximately one hour.
Before any changes are made, a timer must be created to measure the initial duration. The timer must start before the first calculation is queued to run on the computer node.
You need to implement the timer.
Before which line should the timer be created?
Before any changes are made, a timer must be created to measure the initial duration. The timer must start before the first calculation is queued to run on the computer node.
You need to implement the timer.
Before which line should the timer be created?
- ACloudJob = batchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob();
- BbatchClient.JobOperations.AddTask(JobId, tasks);
- CbatchClient.Utilities.CreateTaskStateMonitor().WaitAll(addedTasks, TaskState.Completed, timeout);
- Dusing (BatchClient batchClient = BatchClient.Open(cred))
Correct Answer:
B
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet
B
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution. Determine whether the solution meets the stated goals.
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Create a Service Fabric Cluster with a stateless Reliable Service for Routing Service. Create stateful Reliable Services for all other components.
Does the solution meet the goal?
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Create a Service Fabric Cluster with a stateless Reliable Service for Routing Service. Create stateful Reliable Services for all other components.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
A
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
Note:
For stateful services, the Reliable Services programming model allows you to consistently and reliably store your state right inside your service by using Reliable
Collections.
A stateless service is one where there is no state maintained within the service across calls. Any state that is present is entirely disposable and doesn't require synchronization, replication, persistence, or high availability.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
A
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
Note:
For stateful services, the Reliable Services programming model allows you to consistently and reliably store your state right inside your service by using Reliable
Collections.
A stateless service is one where there is no state maintained within the service across calls. Any state that is present is entirely disposable and doesn't require synchronization, replication, persistence, or high availability.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution. Determine whether the solution meets the stated goals.
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Create a Service Fabric Cluster with a stateful Reliable Service for Routing Service. Deploy a Guest Executable to Service Fabric for each component.
Does the solution meet the goal?
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Create a Service Fabric Cluster with a stateful Reliable Service for Routing Service. Deploy a Guest Executable to Service Fabric for each component.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
B
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution. Determine whether the solution meets the stated goals.
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Deploy a Windows container to Azure Service Fabric for each component.
Does the solution meet the goal?
You develop an entertainment application where users can buy and trade virtual real estate. The application must scale to support thousands of users.
The current architecture includes five Azure Virtual Machines (VM) that connect to an Azure SQL Database for account information and Azure Table Storage for backend services. A user interacts with these components in the cloud at any given time
- Routing Service "" Routes a request to the appropriate service and must not persist data across sessions
- Account Service "" Stores and manages all account information and authentication and requires data to persist across sessions.
- User Service "" Stores and manages all user information and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Housing Network Service "" Stores and manages the current real-estate economy and requires data to persist across sessions.
- Trade Service "" Stores and manages virtual trade between accounts and requires data to persist across sessions.
Due to volatile user traffic, a microservices solution is selected for scale agility.
You need to migrate to a distributed microservices solution on Azure Service Fabric.
Solution: Deploy a Windows container to Azure Service Fabric for each component.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- AYes
- BNo
Correct Answer:
B
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
B
We should use stateful services when we want data to persist, and stateless service when data must not persist.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-fabric/service-fabric-reliable-services-introduction
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
