Microsoft 70-410 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (550 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #31
DRAG DROP -
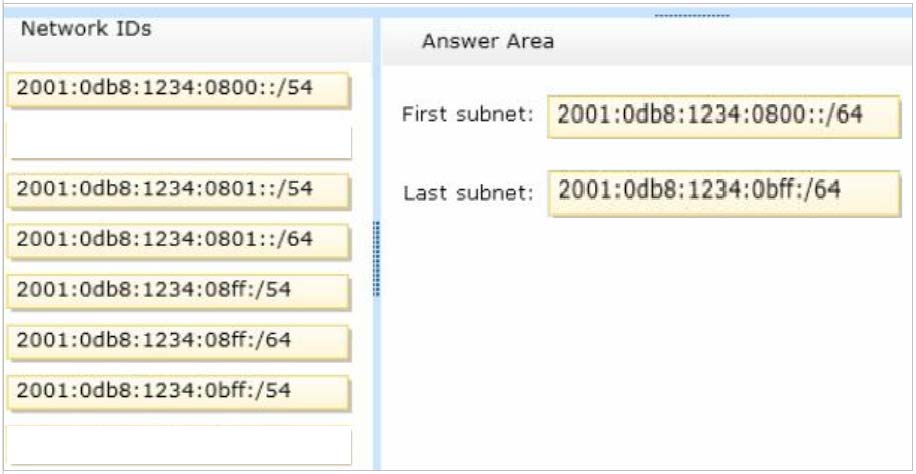
You are configuring a multi-subnet IPv6 network for a regional office.
The corporate network administrator allocates the 2001:0db8:1234:0800::/54 address space for your use.
You need to identify network IDs of the first and last subnets that you will be able to create at the office.
Which network IDs should you identify?
To answer, drag the appropriate network IDs to the correct subnets. Each network ID may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
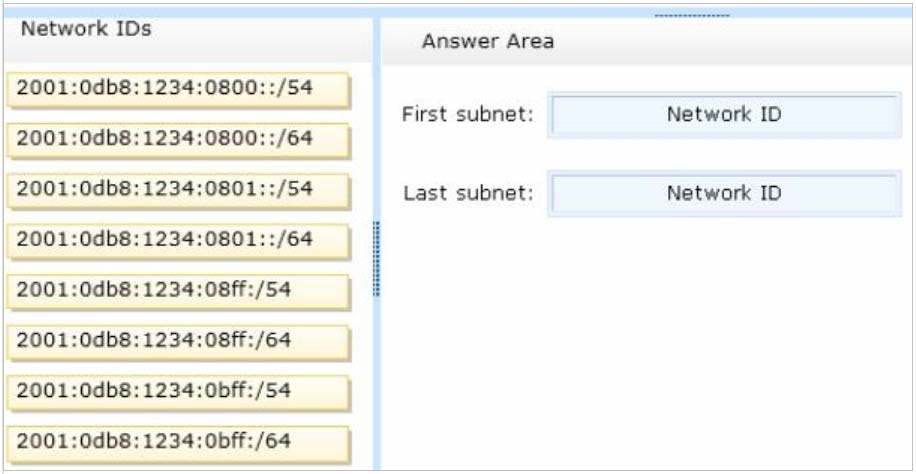
You are configuring a multi-subnet IPv6 network for a regional office.
The corporate network administrator allocates the 2001:0db8:1234:0800::/54 address space for your use.
You need to identify network IDs of the first and last subnets that you will be able to create at the office.
Which network IDs should you identify?
To answer, drag the appropriate network IDs to the correct subnets. Each network ID may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:

send
light_mode
delete
Question #32
DRAG DROP -
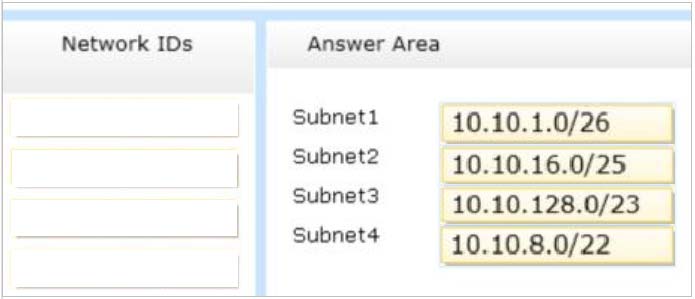
You plan to deploy a DHCP server that will support four subnets. The subnets will be configured as shown in the following table.
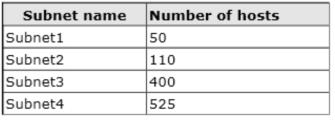
You need to identify which network ID you should use for each subnet.
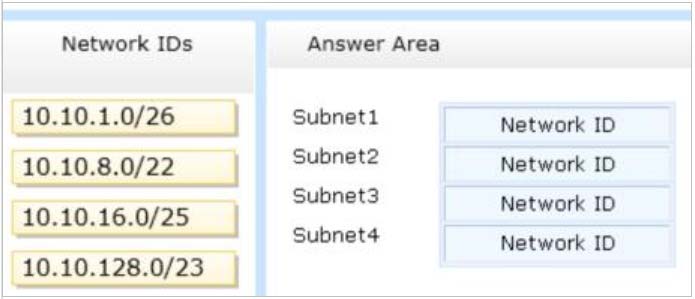
What should you identify?
To answer, drag the appropriate network ID to the each subnet in the answer area.
Select and Place:
You plan to deploy a DHCP server that will support four subnets. The subnets will be configured as shown in the following table.

You need to identify which network ID you should use for each subnet.
What should you identify?
To answer, drag the appropriate network ID to the each subnet in the answer area.
Select and Place:

send
light_mode
delete
Question #33
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a DHCP server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
You create a DHCP scope named Scope1. The scope has a start address of 192.168.1.10, an end address of 192.168.1.50, and a subnet mask of
255.255.255.192.
You need to ensure that Scope1 has a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
What should you do first?
You create a DHCP scope named Scope1. The scope has a start address of 192.168.1.10, an end address of 192.168.1.50, and a subnet mask of
255.255.255.192.
You need to ensure that Scope1 has a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
What should you do first?
- AFrom the DHCP console, reconcile Scope1.
- BFrom the DHCP console, delete Scope1.
- CFrom the DHCP console, modify the Scope Options of Scope1.
- DFrom Windows PowerShell, run the Set-DhcpServerv4Scope cmdlet.
Correct Answer:
B
You cannot change the subnet mask of a DHCP scope without deleting the scope and recreating it with the new subnet mask.
Set-DhcpServerv4Scope does not include a parameter for the subnet mask.
B
You cannot change the subnet mask of a DHCP scope without deleting the scope and recreating it with the new subnet mask.
Set-DhcpServerv4Scope does not include a parameter for the subnet mask.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #34
DRAG DROP -
You have a server named Server1.Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
Server1 has two network adapters. Each network adapter must be configured as shown in the following table.
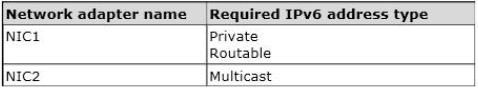
You need to configure the correct IPv6 address prefix for each network adapter.
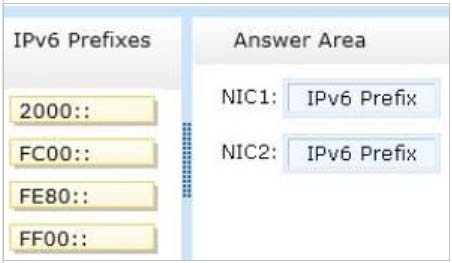
Which prefix should you select for each network adapter?
To answer, drag the appropriate IPv6 prefix to the correct network adapter in the answer area.
Each prefix may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
You have a server named Server1.Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
Server1 has two network adapters. Each network adapter must be configured as shown in the following table.

You need to configure the correct IPv6 address prefix for each network adapter.
Which prefix should you select for each network adapter?
To answer, drag the appropriate IPv6 prefix to the correct network adapter in the answer area.
Each prefix may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
An IPv6 multicast address always begins with 11111111 or FF and includes additional structure that identifies the scope of the address and the multicast group to which the interface belongs.IPv6 multicast addresses, therefore, are always of the form FF00::/8.
Reference: http://www.ianA.org/assignments/ipv6-address-space/ipv6-address-spacE.xml

An IPv6 multicast address always begins with 11111111 or FF and includes additional structure that identifies the scope of the address and the multicast group to which the interface belongs.IPv6 multicast addresses, therefore, are always of the form FF00::/8.
Reference: http://www.ianA.org/assignments/ipv6-address-space/ipv6-address-spacE.xml
send
light_mode
delete
Question #35
Your company has a main office and two branch offices. The offices connect to each other by using a WAN link.
In the main office, you have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
Server1 is configured to use an IPv4 address only.
You need to assign an IPv6 address to Server1. The IP address must be private and routable.
Which IPv6 address should you assign to Server1?
In the main office, you have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
Server1 is configured to use an IPv4 address only.
You need to assign an IPv6 address to Server1. The IP address must be private and routable.
Which IPv6 address should you assign to Server1?
- Afe80:ab32:145c::32cc:401b
- Bff00:3fff:65df:145c:dca8::82a4
- C2001:ab32:145c::32cc:401b
- Dfd00:ab32:14:ad88:ac:58:abc2:4
Correct Answer:
D
Unique local addresses are IPv6 addresses that are private to an organization in the same way that private addressessuch as 10.x.x.x, 192.168.x.x, or
172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255 can be used on an IPv4 network.
Unique local addresses, therefore, are not routable on the IPv6 Internet in the same way that an address like 10.20.100.55 is not routable on the IPv4 Internet. A unique local address is always structured as follows:
The first 8 bits are always 11111101 in binary format. This means that a unique local address always begins with FD and has a prefix identifier of FD00::/8.
D
Unique local addresses are IPv6 addresses that are private to an organization in the same way that private addressessuch as 10.x.x.x, 192.168.x.x, or
172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255 can be used on an IPv4 network.
Unique local addresses, therefore, are not routable on the IPv6 Internet in the same way that an address like 10.20.100.55 is not routable on the IPv4 Internet. A unique local address is always structured as follows:
The first 8 bits are always 11111101 in binary format. This means that a unique local address always begins with FD and has a prefix identifier of FD00::/8.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #36
In an isolated test environment, you deploy a server named Server1 that runs a Server Core Installation of Windows Server 2012 R2. The test environment does not have Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) installed.
You install the Active Directory Domain Services server role on Server1.
You need to configure Server1 as a domain controller.
Which cmdlet should you run?
You install the Active Directory Domain Services server role on Server1.
You need to configure Server1 as a domain controller.
Which cmdlet should you run?
- AInstall-ADDSDomainController
- BInstall-ADDSDomain
- CInstall-ADDSForest
- DInstall-WindowsFeature
Correct Answer:
C
Install-ADDSDomainController Installs a domain controller in Active Directory.
Install-ADDSDomain Installs a new Active Directory domain configuration.
Install-ADDSForest Installs a new Active Directory forest configuration.
Install-WindowsFeature Installs one or more Windows Server roles, role services, or features on either the local or a specified remote server that is running
Windows Server 2012 R2. This cmdlet is equivalent to and replaces Add-WindowsFeature, the cmdlet that was used to install roles, role services, and features.
C:\PS>Install-ADDSForest -DomainName corp.contoso.com -CreateDNSDelegation DomainMode Win2008 - ForestMode Win 2008 R2 -DatabasePath "d:\NTDS"
-SysvolPath "d:\SYSVOL" –LogPath "e:\Logs"Installs a new forest named corp.contoso.com, creates a DNS delegation in the contoso.com domain, sets domain functional level to Windows Server 2008 R2 and sets forest functional level to Windows Server 2008,installs the Active Directory database and SYSVOL on the D:\ drive, installs the log files on the E:\ drive and has the server automatically restart after AD DS installation is complete and prompts the user to provide and confirm the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password.
C
Install-ADDSDomainController Installs a domain controller in Active Directory.
Install-ADDSDomain Installs a new Active Directory domain configuration.
Install-ADDSForest Installs a new Active Directory forest configuration.
Install-WindowsFeature Installs one or more Windows Server roles, role services, or features on either the local or a specified remote server that is running
Windows Server 2012 R2. This cmdlet is equivalent to and replaces Add-WindowsFeature, the cmdlet that was used to install roles, role services, and features.
C:\PS>Install-ADDSForest -DomainName corp.contoso.com -CreateDNSDelegation DomainMode Win2008 - ForestMode Win 2008 R2 -DatabasePath "d:\NTDS"
-SysvolPath "d:\SYSVOL" –LogPath "e:\Logs"Installs a new forest named corp.contoso.com, creates a DNS delegation in the contoso.com domain, sets domain functional level to Windows Server 2008 R2 and sets forest functional level to Windows Server 2008,installs the Active Directory database and SYSVOL on the D:\ drive, installs the log files on the E:\ drive and has the server automatically restart after AD DS installation is complete and prompts the user to provide and confirm the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #37
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
You promote Server1 to a domain controller.
You need to view the service location (SRV) records that Server1 registers in DNS.
What should you do on Server1?
You promote Server1 to a domain controller.
You need to view the service location (SRV) records that Server1 registers in DNS.
What should you do on Server1?
- AOpen the Srv.sys file.
- BOpen the Netlogon.dns file.
- CRun ipconfig /displaydns.
- DRun Get-DnsServerDiagnostics.
Correct Answer:
B
Netlogon service creates a log file that contains all the locator resource records stored in netlogon.
Incorrect Answers:
A: The Srv.sys file is the Timestamp server driver
C: ipconfig /displaydns is used to display current DNS resolver cache content
D: The Get-DnsServerDiagnostics cmdlet displays DNS event logging details
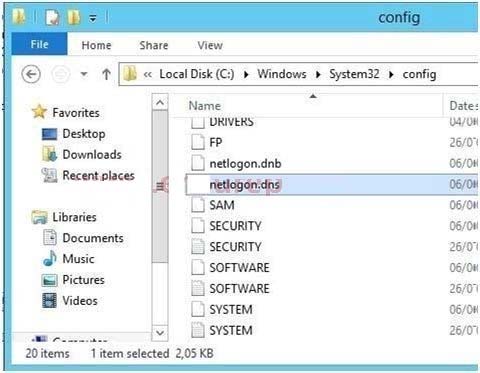
B
Netlogon service creates a log file that contains all the locator resource records stored in netlogon.
Incorrect Answers:
A: The Srv.sys file is the Timestamp server driver
C: ipconfig /displaydns is used to display current DNS resolver cache content
D: The Get-DnsServerDiagnostics cmdlet displays DNS event logging details

send
light_mode
delete
Question #38
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains several thousand member servers that run Windows Server 2012
R2. All of the computer accounts for the member servers are in an organizational unit (OU) named ServersAccounts.
Servers are restarted only occasionally.
You need to identify which servers were restarted during the last two days.
What should you do?
R2. All of the computer accounts for the member servers are in an organizational unit (OU) named ServersAccounts.
Servers are restarted only occasionally.
You need to identify which servers were restarted during the last two days.
What should you do?
- ARun dsquery computer and specify the –staiepwd parameter.
- BRun Get-ADComputer and specify the SearchScope parameter.
- CRun Get-ADComputer and specify the IastLogon property.
- DRun dsquery server and specify the –o parameter
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #39
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain named contoso.com. The domain contains four domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table.
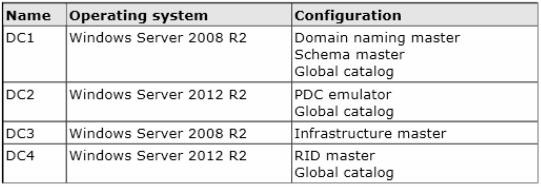
All domain controllers are DNS servers.
You plan to deploy a new domain controller named DC5 in the contoso.com domain.
You need to identify which domain controller must be online to ensure that DC5 can be promoted successfully to a domain controller.
Which domain controller should you identify?

All domain controllers are DNS servers.
You plan to deploy a new domain controller named DC5 in the contoso.com domain.
You need to identify which domain controller must be online to ensure that DC5 can be promoted successfully to a domain controller.
Which domain controller should you identify?
- ADC1
- BDC2
- CDC3
- DDC4
Correct Answer:
D
Relative ID (RID) Master:
Allocates active and standby RID pools to replica domain controllers in the same domain. (corp.contoso.com).
Must be online for newly promoted domain controllers to obtain a local RID pool that is required to advertise or when existing domain controllers have to update their current or standby RID pool allocation.
The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DCs allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domains RID master.
The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domains unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.
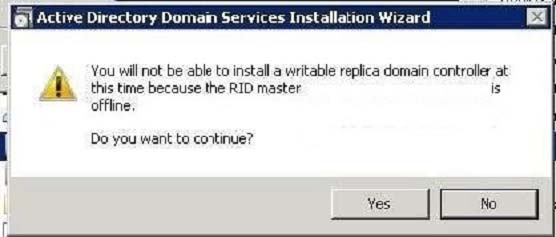
The Infrastructure Master The purpose of this role is to ensure that cross-domain object references are correctly handled. For example, if you add a user from one domain to a security group from a different domain, the Infrastructure Master makes sure this is done properly. As you can guess however, if your Active
Directory deployment has only a single domain, then the Infrastructure Master role does no work at all, and even in a multi-domain environment it is rarely used except when complex user administration tasks are performed, so the machine holding this role doesnt need to have much horsepower at all.
D
Relative ID (RID) Master:
Allocates active and standby RID pools to replica domain controllers in the same domain. (corp.contoso.com).
Must be online for newly promoted domain controllers to obtain a local RID pool that is required to advertise or when existing domain controllers have to update their current or standby RID pool allocation.
The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DCs allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domains RID master.
The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domains unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.

The Infrastructure Master The purpose of this role is to ensure that cross-domain object references are correctly handled. For example, if you add a user from one domain to a security group from a different domain, the Infrastructure Master makes sure this is done properly. As you can guess however, if your Active
Directory deployment has only a single domain, then the Infrastructure Master role does no work at all, and even in a multi-domain environment it is rarely used except when complex user administration tasks are performed, so the machine holding this role doesnt need to have much horsepower at all.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #40
Your network contains an Active Directory forest that contains three domains.
A group named Group1 is configured as a domain local distribution group in the forest root domain.
You plan to grant Group1 read-only access to a shared folder named Share1.Share1 is located in a child domain.
You need to ensure that the members of Group1 can access Share1.
What should you do first?
A group named Group1 is configured as a domain local distribution group in the forest root domain.
You plan to grant Group1 read-only access to a shared folder named Share1.Share1 is located in a child domain.
You need to ensure that the members of Group1 can access Share1.
What should you do first?
- AConvert Group1 to a universal security group.
- BConvert Group1 to a global distribution group.
- CConvert Group1 to a universal distribution group.
- DConvert Group1 to a domain local security group.
Correct Answer:
A
Universal can be used for any domain or forest. Furthermore a Universal group can span multiple domains, even the entire forest.
References:
Active Directory groups and Organization units, p. 289-291, 293 http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781446(v=ws.10).aspx http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755692(v=ws.10).aspx
A
Universal can be used for any domain or forest. Furthermore a Universal group can span multiple domains, even the entire forest.
References:
Active Directory groups and Organization units, p. 289-291, 293 http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781446(v=ws.10).aspx http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755692(v=ws.10).aspx
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages