CompTIA N10-006 Exam Practice Questions (P. 3)
- Full Access (741 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which of the following refers to a network that spans several buildings that are within walking distance of each other?
- ACAN
- BWAN
- CPAN
- DMAN
Correct Answer:
A
CAN stands for Campus Area Network or Corporate Area Network. Universities or colleges often implement CANs to link the buildings in a network. The range of
CAN is 1KM to 5KM. If multiple buildings have the same domain and they are connected with a network, then it will be considered as a CAN.
A
CAN stands for Campus Area Network or Corporate Area Network. Universities or colleges often implement CANs to link the buildings in a network. The range of
CAN is 1KM to 5KM. If multiple buildings have the same domain and they are connected with a network, then it will be considered as a CAN.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Which of the following network infrastructure implementations would be used to support files being transferred between Bluetooth-enabled smartphones?
- APAN
- BLAN
- CWLAN
- DMAN
Correct Answer:
A
PAN stands for Personal Area Network. It is a network of devices in the area of a person typically within a range of 10 meters and commonly using a wireless technology such as Bluetooth or IR (Infra-Red).
A
PAN stands for Personal Area Network. It is a network of devices in the area of a person typically within a range of 10 meters and commonly using a wireless technology such as Bluetooth or IR (Infra-Red).
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
Which of the following describes an IPv6 address of ::1?
- ABroadcast
- BLoopback
- CClassless
- DMulticast
Correct Answer:
B
The loopback address is a special IP address that is designated for the software loopback interface of a computer. The loopback interface has no hardware associated with it, and it is not physically connected to a network. The loopback address causes any messages sent to it to be returned to the sending system. The loopback address allows client software to communicate with server software on the same computer. Users specify the loopback address which will point back to the computer's TCP/IP network configuration.
In IPv4, the loopback address is 127.0.0.1.
In IPv6, the loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, which can be shortened to ::1
B
The loopback address is a special IP address that is designated for the software loopback interface of a computer. The loopback interface has no hardware associated with it, and it is not physically connected to a network. The loopback address causes any messages sent to it to be returned to the sending system. The loopback address allows client software to communicate with server software on the same computer. Users specify the loopback address which will point back to the computer's TCP/IP network configuration.
In IPv4, the loopback address is 127.0.0.1.
In IPv6, the loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, which can be shortened to ::1
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Which of the following is an example of an IPv4 address?
- A192:168:1:55
- B192.168.1.254
- C00:AB:FA:B1:07:34
- D::1
Correct Answer:
B
AnIPv4 address is notated as four decimal numbers each between 0 and 255 separated by dots (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx). Each number is known as an octet as it represents eight binary bits. All four octets make up a 32-bit binary IPv4 address.
In this question, 192.168.1.254 is a valid IPv4 address.
B
AnIPv4 address is notated as four decimal numbers each between 0 and 255 separated by dots (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx). Each number is known as an octet as it represents eight binary bits. All four octets make up a 32-bit binary IPv4 address.
In this question, 192.168.1.254 is a valid IPv4 address.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
A technician, Joe, needs to troubleshoot a recently installed NIC. He decides to ping the local loopback address.
Which of the following is a valid IPv4 loopback address?
Which of the following is a valid IPv4 loopback address?
- A10.0.0.1
- B127.0.0.1
- C172.16.1.1
- D192.168.1.1
Correct Answer:
B
The loopback address is a special IP address that is designated for the software loopback interface of a computer. The loopback interface has no hardware associated with it, and it is not physically connected to a network. The loopback address causes any messages sent to it to be returned to the sending system. The loopback address allows client software to communicate with server software on the same computer. Users specify the loopback address which will point back to the computer's TCP/IP network configuration.
In IPv4, the loopback address is 127.0.0.1.
In IPv6, the loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, more commonly notated as follows. ::1
B
The loopback address is a special IP address that is designated for the software loopback interface of a computer. The loopback interface has no hardware associated with it, and it is not physically connected to a network. The loopback address causes any messages sent to it to be returned to the sending system. The loopback address allows client software to communicate with server software on the same computer. Users specify the loopback address which will point back to the computer's TCP/IP network configuration.
In IPv4, the loopback address is 127.0.0.1.
In IPv6, the loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, more commonly notated as follows. ::1
send
light_mode
delete
Question #26
A technician, Joe, has been tasked with assigning two IP addresses to WAN interfaces on connected routers.
In order to conserve address space, which of the following subnet masks should Joe use for this subnet?
In order to conserve address space, which of the following subnet masks should Joe use for this subnet?
- A/24
- B/32
- C/28
- D/29
- E/30
Correct Answer:
E
An IPv4 address consists of 32 bits. The first x number of bits in the address is the network address and the remaining bits are used for the host addresses. The subnet mask defines how many bits form the network address and from that, we can calculate how many bits are used for the host addresses.
In this question, the /30 subnet mask dictates that the first 30 bits of the IP address are used for network addressing and the remaining 2 bits are used for host addressing. The formula to calculate the number of hosts in a subnet is 2n - 2. The "n" in the host's formula represents the number of bits used for host addressing. If we apply the formula (22 2), a /30 subnet mask will provide 2 IP addresses.
E
An IPv4 address consists of 32 bits. The first x number of bits in the address is the network address and the remaining bits are used for the host addresses. The subnet mask defines how many bits form the network address and from that, we can calculate how many bits are used for the host addresses.
In this question, the /30 subnet mask dictates that the first 30 bits of the IP address are used for network addressing and the remaining 2 bits are used for host addressing. The formula to calculate the number of hosts in a subnet is 2n - 2. The "n" in the host's formula represents the number of bits used for host addressing. If we apply the formula (22 2), a /30 subnet mask will provide 2 IP addresses.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #27
HOTSPOT -
Corporate headquarters provided your office a portion of their class B subnet to use at a new office location. Allocate the minimum number of addresses (using
CIDR notation) needed to accommodate each department.

After accommodating each department, identify the unused portion of the subnet by responding to the question on the graphic. All drop downs must be filled.
Instructions: When the simulation is complete, please select the Done button to submit.
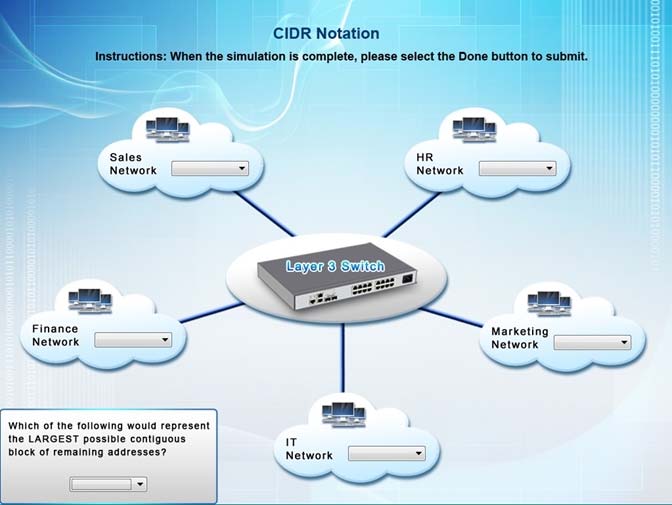
All Networks have the range from /0 to/32
Hot Area:
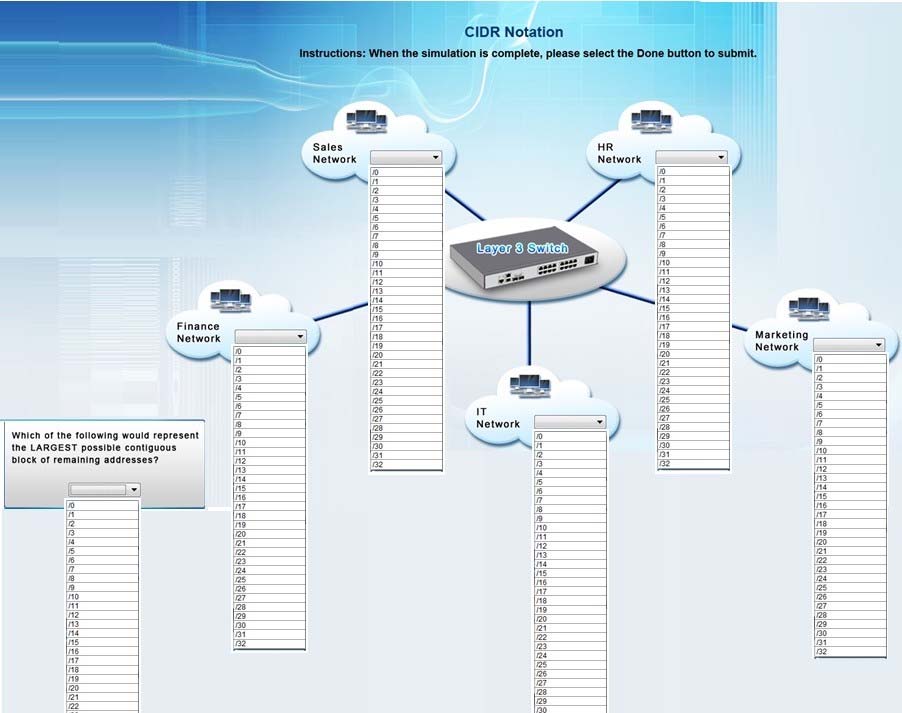
Corporate headquarters provided your office a portion of their class B subnet to use at a new office location. Allocate the minimum number of addresses (using
CIDR notation) needed to accommodate each department.

After accommodating each department, identify the unused portion of the subnet by responding to the question on the graphic. All drop downs must be filled.
Instructions: When the simulation is complete, please select the Done button to submit.

All Networks have the range from /0 to/32
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
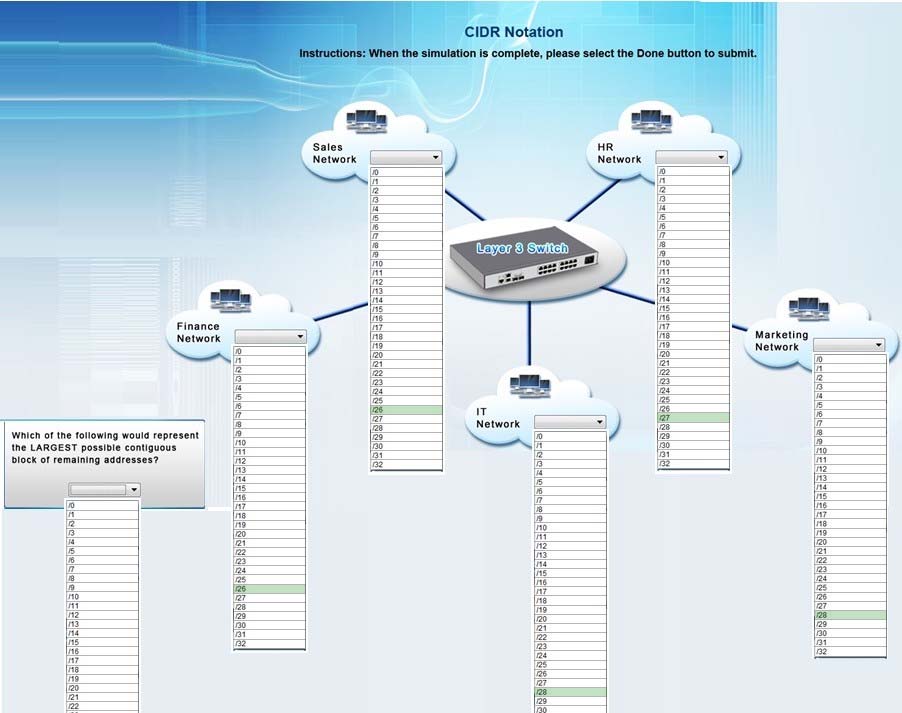
An IPv4 address consists of 32 bits. The first x number of bits in the address is the network address and the remaining bits are used for the host addresses. The subnet mask defines how many bits form the network address and from that, we can calculate how many bits are used for the host addresses.
The formula to calculate the number of hosts in a subnet is 2n - 2. The "n" in the host's formula represents the number of bits used for host addressing. If we apply the formula (22 2), we can determine that the following subnets should be configured:
Sales network /26 This will provide up to 62 usable IP addresses (64-2 for subnet and broadcast IP)
HR network - /27 This will provide for up to 30usable IPs (32-2)
IT - /28 This will provide for up to 14 usable IPs (16-2)
Finance - /26 Note that a /27 is 32 IP addresses but 2 of those are reserved for the network and broadcast IPs and cant be used for hosts.
Marketing - /28 -
If we add up how many IP blocks are used that is 64+32+16+64+16=192.
A /24 contains 256 IP addresses, so 256-192=64.
So the last unused box should be a /26, which equates to 64 addresses

An IPv4 address consists of 32 bits. The first x number of bits in the address is the network address and the remaining bits are used for the host addresses. The subnet mask defines how many bits form the network address and from that, we can calculate how many bits are used for the host addresses.
The formula to calculate the number of hosts in a subnet is 2n - 2. The "n" in the host's formula represents the number of bits used for host addressing. If we apply the formula (22 2), we can determine that the following subnets should be configured:
Sales network /26 This will provide up to 62 usable IP addresses (64-2 for subnet and broadcast IP)
HR network - /27 This will provide for up to 30usable IPs (32-2)
IT - /28 This will provide for up to 14 usable IPs (16-2)
Finance - /26 Note that a /27 is 32 IP addresses but 2 of those are reserved for the network and broadcast IPs and cant be used for hosts.
Marketing - /28 -
If we add up how many IP blocks are used that is 64+32+16+64+16=192.
A /24 contains 256 IP addresses, so 256-192=64.
So the last unused box should be a /26, which equates to 64 addresses
send
light_mode
delete
Question #28
A host has been assigned the address 169.254.0.1.
This is an example of which of the following address types?
This is an example of which of the following address types?
- AAPIPA
- BMAC
- CStatic
- DPublic
Correct Answer:
A
APIPA stands for Automatic Private IP Addressing and is a feature of Windows operating systems. When a client computer is configured to use automatic addressing (DHCP), APIPA assigns a class B IP address from 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 to the client when a DHCP server is unavailable.
When a client computer configured to use DHCP boots up, it first looks for a DHCP server to provide the client with IP address and subnet mask. If the client is unable to contact a DHCP server, it uses APIPA to automatically configure itself with an IP address from a range that has been reserved especially for Microsoft.
The client also configures itself with a default class Bsubnet mask of 255.255.0.0. The client will use the self-configured IP address until a DHCP server becomes available.
A
APIPA stands for Automatic Private IP Addressing and is a feature of Windows operating systems. When a client computer is configured to use automatic addressing (DHCP), APIPA assigns a class B IP address from 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 to the client when a DHCP server is unavailable.
When a client computer configured to use DHCP boots up, it first looks for a DHCP server to provide the client with IP address and subnet mask. If the client is unable to contact a DHCP server, it uses APIPA to automatically configure itself with an IP address from a range that has been reserved especially for Microsoft.
The client also configures itself with a default class Bsubnet mask of 255.255.0.0. The client will use the self-configured IP address until a DHCP server becomes available.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #29
A company wants to create highly available datacenters.
Which of the following will allow the company to continue to maintain an Internet presence at all sites in the event that a WAN circuit at one site goes down?
Which of the following will allow the company to continue to maintain an Internet presence at all sites in the event that a WAN circuit at one site goes down?
- ALoad balancer
- BVRRP
- COSPF
- DBGP
Correct Answer:
D
A collection of networks that fall within the same administrative domain is called an autonomous system (AS). In this question, each datacenter will be an autonomous system.
The routers within an AS use an interior gateway protocol, such as the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, to exchange routing information among themselves. At the edges of an AS are routers that communicate with the other ASs on the Internet, using an exterior gateway protocol such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
If a WAN link goes down, BGP will route data through another WAN link if redundant WAN links are available.
D
A collection of networks that fall within the same administrative domain is called an autonomous system (AS). In this question, each datacenter will be an autonomous system.
The routers within an AS use an interior gateway protocol, such as the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, to exchange routing information among themselves. At the edges of an AS are routers that communicate with the other ASs on the Internet, using an exterior gateway protocol such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
If a WAN link goes down, BGP will route data through another WAN link if redundant WAN links are available.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #30
An organization requires a second technician to verify changes before applying them to network devices. When checking the configuration of a network device, a technician determines that a coworker has improperly configured the AS number on the device.
This would result in which of the following?
This would result in which of the following?
- AThe OSPF not-so-stubby area is misconfigured
- BReduced wireless network coverage
- CSpanning tree ports in flooding mode
- DBGP routing issues
Correct Answer:
D
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is used to route data between autonomous systems (ASs)
A collection of networks that fall within the same administrative domain is called an autonomous system (AS).
The routers within an AS use an interior gateway protocol, such as the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, to exchange routing information among themselves. At the edges of an AS are routers that communicate with the other ASs on the Internet, using an exterior gateway protocol such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
D
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is used to route data between autonomous systems (ASs)
A collection of networks that fall within the same administrative domain is called an autonomous system (AS).
The routers within an AS use an interior gateway protocol, such as the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, to exchange routing information among themselves. At the edges of an AS are routers that communicate with the other ASs on the Internet, using an exterior gateway protocol such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
