Cisco® 642-887 Exam Practice Questions (P. 5)
- Full Access (183 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #21
Which statement is correct regarding the default MPLS TTL behavior?
- AWhen an ingress edge LSR receives an IP packet, it will decrement the IP TTL field by 1; then it will set the MPLS Label TTL field to 255.
- BWhen an ingress edge LSR receives an IP packet, it will decrement the IP TTL field by 1; then it will copy the decremented IP TTL field into the MPLS Label TTL field.
- CWhen an ingress edge LSR receives an IP packet, it will just copy the IP TTL field into the MPLS Label TTL field.
- DWhen an ingress edge LSR receives an IP packet, it will copy the IP TTL field into the MPLS Label TTL field first; then it will only decrement the MPLS Label TTL field by 1.
- EWhen an ingress edge LSR receives an IP packet, it will copy the IP TTL field into the MPLS Label TTL field first; then it will only decrement the IP TTL field by
Correct Answer:
B
B
send
light_mode
delete
Question #22
Which three statements are correct regarding ping mpls command operations? (Choose three.)
- AMPLS OAM has to be enabled on the router using the mpls oam command.
- BThey use a 127/8 address as the destination address in the MPLS echo request packet.
- CThey use ICMP echo request and ICMP echo reply packets.
- DThey are used to test for a broken LSP.
- EIf there is a broken LSP, instead of using label switching, the packet can still be forwarded based on the destination IP address in the mpls ping echo request
Correct Answer:
ABD
How MPLS Ping works?
MPLS Ping doesnt rely on ICMP echo messages. Instead it uses UDP protocol with both source and destination port as 3503 and relies on MPLS Echo request and MPLS Echo reply.
When MPLS ping is triggered from any MPLS router, it will generate UDP segment with source/destination port as 3503. The source address will be selected as usual while the destination address will be 127.0.0.1. The IP TTL will be set to 1.
Below is a sample IP format when MPLS Ping is originated from R5 to 150.1.6.6/32,
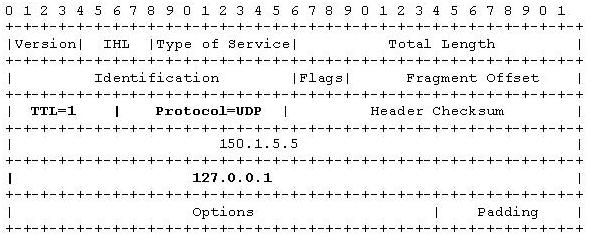
Now the originating LSR will look into the LFIB and populate the label header with respective labels to reach the FEC, in our case 150.1.6.6/32.
R4 on receiving the MPLS packet will be able to send to the actual destination only if the LSP is end to end. If the LSP is broken between R4 and R6, R4 will look into the destination IP address which will be 127.0.0.1 and wont be able to perform IP forwarding. As per RFC 1812, a router should not forward any packet that has destination address of 127.0.0.0/8
ABD
How MPLS Ping works?
MPLS Ping doesnt rely on ICMP echo messages. Instead it uses UDP protocol with both source and destination port as 3503 and relies on MPLS Echo request and MPLS Echo reply.
When MPLS ping is triggered from any MPLS router, it will generate UDP segment with source/destination port as 3503. The source address will be selected as usual while the destination address will be 127.0.0.1. The IP TTL will be set to 1.
Below is a sample IP format when MPLS Ping is originated from R5 to 150.1.6.6/32,

Now the originating LSR will look into the LFIB and populate the label header with respective labels to reach the FEC, in our case 150.1.6.6/32.
R4 on receiving the MPLS packet will be able to send to the actual destination only if the LSP is end to end. If the LSP is broken between R4 and R6, R4 will look into the destination IP address which will be 127.0.0.1 and wont be able to perform IP forwarding. As per RFC 1812, a router should not forward any packet that has destination address of 127.0.0.0/8
send
light_mode
delete
Question #23
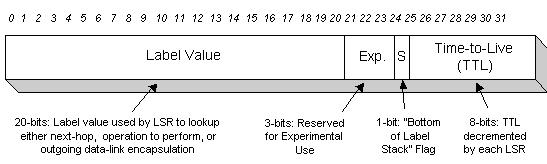
What are the four fields inside the MPLS shim header? (Choose four.)
send
light_mode
delete
Question #24
Which two of the following statements are correct regarding LSPs? (Choose two.)
- AAn LSP is created for every routing protocol entry.
- BEach LSP is bidirectional, that is, packets traveling in the opposite direction use the same LSP.
- CAn IGP is used to populate routing tables in all routers in an MPLS domain.
- DLDP is used to propagate labels and build LSPs.
- EThe FIB is used to forward MPLS-labeled packets down an LSP.
Correct Answer:
CD
CD
send
light_mode
delete
Question #25
Which four pieces of information are stored for each prefix in the LFIB? (Choose four.)
- Alocal label
- Boutgoing label
- Cnext-hop IP address
- Doutgoing interface
- Eincoming interface
- FLayer 2 header rewrite information
Correct Answer:
ABCD
Forwarding Labeled Packets -
LSR forwards the packet based on:
Top Label value of the received packet
Corresponding entry in LFIB (LABEL <=> INTERFACE)
#show mpls forwarding-table - will show:
local label
outgoing label
prefix (network)
outgoing interface
next-hop
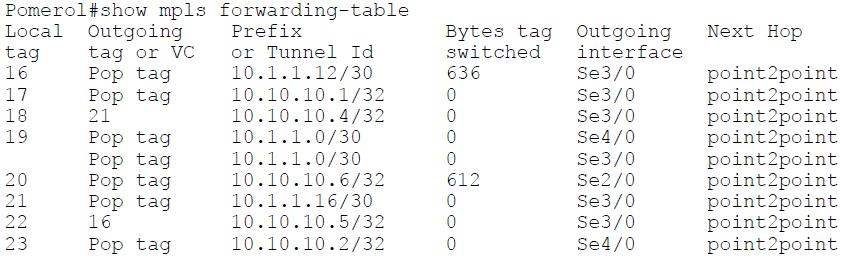
LSR expects packet to come with "top" label being "Local" (from show mpls forwarding-table).
If Outgoing label is "Aggregate", then that means that this is a summary route and more specific lookup is performed.
If LSR cannot find label/interface mapping in LFIB, then it drops the packet.
There are several "RESERVED" labels numbered from 0 to 15:
0 - explicit NULL - is used to preserver QoS info through EXP bits. It copies 'ip prec' or DiffServ.
1 - Router alert label - forces LSR to software switch the packet.
3 - Implicit NULL - this label is used for "connected" or "summary" routes. This way LSR signals its neighbors to execute "POP label" operation on "connected" routes. It is called PHP, Penultimate Hop Popping, and is used to make sure that LSR does not perform 2 lookups (label + ip).
14 - OEM alert label - is used for monitoring purpose.
In Cisco IOS, the default range is 16 through 100,000, but can be expanded by using "mpls label range" command.
ABCD
Forwarding Labeled Packets -
LSR forwards the packet based on:
Top Label value of the received packet
Corresponding entry in LFIB (LABEL <=> INTERFACE)
#show mpls forwarding-table - will show:
local label
outgoing label
prefix (network)
outgoing interface
next-hop

LSR expects packet to come with "top" label being "Local" (from show mpls forwarding-table).
If Outgoing label is "Aggregate", then that means that this is a summary route and more specific lookup is performed.
If LSR cannot find label/interface mapping in LFIB, then it drops the packet.
There are several "RESERVED" labels numbered from 0 to 15:
0 - explicit NULL - is used to preserver QoS info through EXP bits. It copies 'ip prec' or DiffServ.
1 - Router alert label - forces LSR to software switch the packet.
3 - Implicit NULL - this label is used for "connected" or "summary" routes. This way LSR signals its neighbors to execute "POP label" operation on "connected" routes. It is called PHP, Penultimate Hop Popping, and is used to make sure that LSR does not perform 2 lookups (label + ip).
14 - OEM alert label - is used for monitoring purpose.
In Cisco IOS, the default range is 16 through 100,000, but can be expanded by using "mpls label range" command.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages