Cisco® 400-051 Exam Practice Questions (P. 2)
- Full Access (939 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #11
Which two statements about the Peer Firmware Sharing option for IP phone firmware distribution are true? (Choose two.)
- AThis option uses a parent-child hierarchy in which a firmware image is downloaded by a parent phone to up to three directly associated child phones.
- BThis option must be enabled on Cisco Unified Communications Manager service parameters for Cisco TFTP.
- CThis option mandates that the parent phone and child phones be identical, selected phone models.
- DThis option allows firmware transfers between phones in different subnets, as long as the round-trip delay is less than 5 milliseconds.
- EThis option uses a parent-child hierarchy that must be manually defined by the Cisco Unified Communications Manager administrator.
- FThis option allows falling back to the TFTP server in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster.
Correct Answer:
CF
Peer Firmware Sharing works by setting up a parent-child hierarchy of the phones in which a firmware image is downloaded by the parent phone to a child phone.
The advantage of using Peer Firmware Sharing is that instead of all phones individually retrieving a software image, they pass the image along from one phone to another phone on the same subnet.
Advantage of PFS:
✑ Hierarchy is automatic
✑ One download per phone model on a subnet
✑ Uses TCP
✑ Fails back to TFTP
✑ Speeds up LAN upgrades
✑ Reduces TFTP CPU load during upgrade
CF
Peer Firmware Sharing works by setting up a parent-child hierarchy of the phones in which a firmware image is downloaded by the parent phone to a child phone.
The advantage of using Peer Firmware Sharing is that instead of all phones individually retrieving a software image, they pass the image along from one phone to another phone on the same subnet.
Advantage of PFS:
✑ Hierarchy is automatic
✑ One download per phone model on a subnet
✑ Uses TCP
✑ Fails back to TFTP
✑ Speeds up LAN upgrades
✑ Reduces TFTP CPU load during upgrade
send
light_mode
delete
Question #12
Which two statements about the Cisco UC on UCS specs-based virtualization support model are true? (Choose two.)
- AIt has a configuration-based approach.
- BIt has a rule-based approach.
- CIt has less hardware flexibility compared to the third-party server specs-based support model.
- DIt has less hardware flexibility compared to the UC on UCS TRC support model.
- EVMware vCenter is optional with this support model.
Correct Answer:
BC
References: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/UC_Virtualization_Supported_Hardware#UC_on_UCS_Tested_Reference_Configurations
BC
References: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/UC_Virtualization_Supported_Hardware#UC_on_UCS_Tested_Reference_Configurations
send
light_mode
delete
Question #13
Which definition is included in a Cisco UC on UCS TRC?
- Arequired RAID configuration, when the TRC uses direct-attached storage
- Bconfiguration of virtual-to-physical network interface mapping
- Cstep-by-step procedures for hardware BIOS, firmware, drivers, and RAID setup
- Dconfiguration settings and patch recommendations for VMware software
- Eserver model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) by name only; part numbers are not included because they change over time
Correct Answer:
A
Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
A
Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #14
Which capability is support by LLDP-MED but not by Cisco Discovery Protocol?
- ALAN speed discovery
- Bnetwork policy discovery
- Clocation identification discovery
- Dpower discovery
- Etrust extension
Correct Answer:
A
LLDP-MED supports both LAN speed and duplex discovery. Cisco Discovery Protocol supports duplex discovery only, but this limited support is not seen as a problem because if there is a speed mismatch, LLDP-MED and Cisco Discovery Protocol cannot be exchanged and thus cannot be used to detect the mismatch.
A
LLDP-MED supports both LAN speed and duplex discovery. Cisco Discovery Protocol supports duplex discovery only, but this limited support is not seen as a problem because if there is a speed mismatch, LLDP-MED and Cisco Discovery Protocol cannot be exchanged and thus cannot be used to detect the mismatch.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #15
In a Cisco EnergyWise domain, which two terms describe a Cisco IP phone? (Choose two.)
- Aendpoint
- Bdomain member
- Cchild domain member
- DEnergyWise agent
- ECisco power distribution unit
Correct Answer:
AC
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/energywise/phase2_5/ios/configuration/guide/one_ent.html
AC
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/energywise/phase2_5/ios/configuration/guide/one_ent.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #16
Which statement about Cisco EnergyWise domain member neighbor formation is true?
- ACisco EnergyWise supports static neighbors, but the neighbor relationship is only possible if a noncontiguous domain member and a contiguous domain member have a static neighbor entry pointing to each other.
- BCisco EnergyWise static neighbors can be formed even if domain members are not physically contiguous.
- CStatic neighbors can be manually defined on Cisco EnergyWise domain members, but TCP protocols must be used.
- DStatic neighbors can be manually defined on Cisco EnergyWise domain members, but they have a lower priority compared to the autodiscovered members.
- EStatic neighbors can be manually defined on Cisco EnergyWise domain members and the TCP or UDP protocol can be used.
Correct Answer:
B
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Energy_Management/energywisedg.html? referring_site=smartnavRD#wp554384
B
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Energy_Management/energywisedg.html? referring_site=smartnavRD#wp554384
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
Refer to the exhibit.
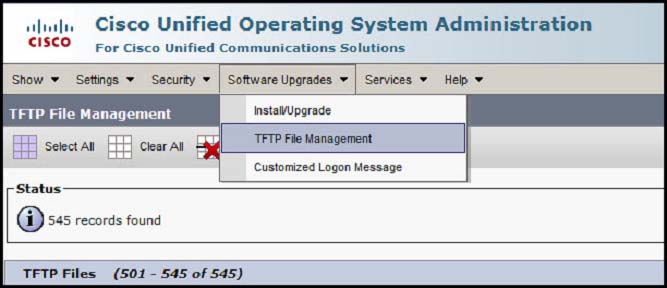
Assuming that the administrator has never performed any manual custom uploads, which two file types can be found when you choose Software Upgrades, followed by TFTP File Management on the Cisco Unified Operating System Administration web page for Cisco Unified Communications Manager? (Choose two.)

Assuming that the administrator has never performed any manual custom uploads, which two file types can be found when you choose Software Upgrades, followed by TFTP File Management on the Cisco Unified Operating System Administration web page for Cisco Unified Communications Manager? (Choose two.)
- AIP phone configuration files
- Bannouncement audio files
- Cringer files
- DIP phone license files
- Esample music-on-hold audio files
- Fsoftkey template files
Correct Answer:
BC
The two file types that we get are Announcement Audio Files and Ringer Files.
BC
The two file types that we get are Announcement Audio Files and Ringer Files.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
Which four attributes are needed to determine the time to complete a TFTP file transfer process? (Choose four.)
- Afile size
- Bfile type
- Cnetwork interface type
- Dround-trip time
- Epacket loss percentage
- Fresponse timeout
- Gnetwork throughput
Correct Answer:
ADEF
Four attributes that are needed to determine the time to complete TFTP file transfer process is:
1. File Size
2. Round-trip time
3. Packet loss percentage
4. Response timeout
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/voicesw/ps6882/ps6884/white_paper_c11-583891_ps10451_Products_White_Paper.html
ADEF
Four attributes that are needed to determine the time to complete TFTP file transfer process is:
1. File Size
2. Round-trip time
3. Packet loss percentage
4. Response timeout
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/voicesw/ps6882/ps6884/white_paper_c11-583891_ps10451_Products_White_Paper.html
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
What is the maximum number of call-processing subscribers in a standard deployment of a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition cluster?
- A3
- B4
- C5
- D8
- E16
Correct Answer:
D
There is no deployment difference between CUCM & CUCM session management Edition cluster. The only difference is that CUCM SME is designed to support a large number of trunk to trunk connections. Thus, 8 subscribers.
D
There is no deployment difference between CUCM & CUCM session management Edition cluster. The only difference is that CUCM SME is designed to support a large number of trunk to trunk connections. Thus, 8 subscribers.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
Which two SCCP call signaling messages are initiated by Cisco Unified Communications Manager to an IP phone? (Choose two.)
- ASoftKeyEvent
- BCloseReceiveChannelAck
- CCallState
- DKeypadButton
- EOpenReceiveChannel
- FOffhook
Correct Answer:
CE
Upon receiving an OpenReceiveChannelmessage, the IP phone selects the UDP port number it wants to use to receive RTP packets and reports this information to call manager.
With the SCCP protocol architecture, the majority of the H.323 processing power resides in an H.323 proxy the Cisco CallManager. The end stations (IP phones) run the Skinny client, which consumes less processing overhead. The client communicates with CallManager using connection-oriented (TCP/IP-based) communication to establish a call with another H.323-compliant end station. Once Cisco CallManager has established the call, the two H.323 end stations use connectionless (UDP/IP-based) communication for audio transmissions.
CE
Upon receiving an OpenReceiveChannelmessage, the IP phone selects the UDP port number it wants to use to receive RTP packets and reports this information to call manager.
With the SCCP protocol architecture, the majority of the H.323 processing power resides in an H.323 proxy the Cisco CallManager. The end stations (IP phones) run the Skinny client, which consumes less processing overhead. The client communicates with CallManager using connection-oriented (TCP/IP-based) communication to establish a call with another H.323-compliant end station. Once Cisco CallManager has established the call, the two H.323 end stations use connectionless (UDP/IP-based) communication for audio transmissions.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
