Cisco® 400-051 Exam Practice Questions (P. 1)
- Full Access (939 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #1
Company ABC is planning to migrate from MCS-hosted Cisco Unified Communications Manager applications to Cisco UC on UCS B-Series servers. Which statement about installation media support is true for this migration?
- AThe install log can be written to a USB flash drive that is attached to the UCS server.
- BThe answer file that is generated by the Answer File Generator (platformConfig.xml) can be read from a USB flash drive to perform an unattended installation on the UCS server.
- CThe Cisco Music on Hold USB audio sound card can be mapped to a virtual USB port on a VMware virtual machine on the UCS server.
- DThe answer file that is generated by the Answer File Generator (platformConfig.xml) can be read from an FLP image that is mounted in a virtual floppy drive.
- EThe Cisco Music on Hold USB audio sound card can be mapped to a virtual serial port on a VMware virtual machine on the UCS server.
Correct Answer:
D
Using the AFG will allow you to get this license mac before even touching the server. It is provided after filling in the main form of the AFG but it can also be found by looking at the last few lines of your platformconfig.xml file.
Once you have the xml files, you will need to map those to the floppy drive of the VM (no usb support on the VM OVA). There are many ways to do this. I simply use a freeware virtual floppy app that I drop the platformconfig.xml file on and then copy the*.flp image out to the datastore. Ill end up with a directory on my datastore called AFG that has the host named *.flp images that I will use during install. It also serves as archival of these files in the event the server needs to be re-imaged. This is important because the license mac will change if every parameter is not entered exactly as it was prior. If the license mac changes, you will have to go through the process of requesting new license files to be generated.
References: http://angryciscoguy.com/jello/cisco-answer-file-generator-to-the-rescue/
D
Using the AFG will allow you to get this license mac before even touching the server. It is provided after filling in the main form of the AFG but it can also be found by looking at the last few lines of your platformconfig.xml file.
Once you have the xml files, you will need to map those to the floppy drive of the VM (no usb support on the VM OVA). There are many ways to do this. I simply use a freeware virtual floppy app that I drop the platformconfig.xml file on and then copy the*.flp image out to the datastore. Ill end up with a directory on my datastore called AFG that has the host named *.flp images that I will use during install. It also serves as archival of these files in the event the server needs to be re-imaged. This is important because the license mac will change if every parameter is not entered exactly as it was prior. If the license mac changes, you will have to go through the process of requesting new license files to be generated.
References: http://angryciscoguy.com/jello/cisco-answer-file-generator-to-the-rescue/
send
light_mode
delete
Question #2
Which statement about the Cisco UC on UCS TRC and the third-party server specs-based virtualization support model is true?
- ABoth the UC on UCS TRC and the third-party servers spec-based support models have rule-based approaches.
- BThe UC on UCS TRC support model has a rule-based approach and the third-party servers spec-based support model has a configuration-based approach.
- CThe UC on UCS TRC support model requires a high level of virtualization experience while the third-party server spec-based support model requires a low to medium level virtualization experience.
- DVMware vCenter is mandatory for the UC on UCS TRC support model but it is optional for the third-party server spec-based support model.
- EVMware vCenter is optional for the UC on UCS TRC support model but it is mandatory for the third-party server spec-based support model.
Correct Answer:
E
is
VMware vCenter -
when deploying on
UC on UCS Tested Reference Configuration hardware
✑ optional
when deploying on
UC on UCS Specs-based and Third-party Server Specs-based hardware
.
✑ mandatory
✑ vCenter Statistics Level 4 logging is mandatory so that Cisco TAC is able to provide effective support.
Click here -
✑ for how to configure VMware vCenter to capture these logs. If not configured by default, Cisco TAC may request enabling these settings in order to provide effective support.
✑ Also note that enablement of specific VMware vSphere management features may require vCenter and/or a higher feature Edition of vSphere ESXi.
✑ Cisco Collaboration does not require its own dedicated vCenter.
✑ Note that when VMware vCenter is not required and is not used, then VMware vSphere ESXi's default management interface is its free/included VMware vSphere Client (formerly branded VI Client).
Reference: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/Unified_Communications_VMware_Requirements
E
is
VMware vCenter -
when deploying on
UC on UCS Tested Reference Configuration hardware
✑ optional
when deploying on
UC on UCS Specs-based and Third-party Server Specs-based hardware
.
✑ mandatory
✑ vCenter Statistics Level 4 logging is mandatory so that Cisco TAC is able to provide effective support.
Click here -
✑ for how to configure VMware vCenter to capture these logs. If not configured by default, Cisco TAC may request enabling these settings in order to provide effective support.
✑ Also note that enablement of specific VMware vSphere management features may require vCenter and/or a higher feature Edition of vSphere ESXi.
✑ Cisco Collaboration does not require its own dedicated vCenter.
✑ Note that when VMware vCenter is not required and is not used, then VMware vSphere ESXi's default management interface is its free/included VMware vSphere Client (formerly branded VI Client).
Reference: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/Unified_Communications_VMware_Requirements
send
light_mode
delete
Question #3
Which definition is included in a Cisco UC on UCS TRC?
- Astorage arrays such as those from EMC or NetApp, if applicable
- Bconfiguration of virtual-to-physical network interface mapping
- Cstep-by-step procedures for hardware BIOS, firmware, drivers, and RAID setup
- Dserver model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the part number level
- Econfiguration settings and patch recommendations for VMware software
Correct Answer:
D
What does a TRC definition include?
✑ Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup (e.g. click here).
-
Click here for detailed Cisco UCS server documentation
regarding hardware configuration procedures.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration settings or step by step procedures for hardware BIOS, firmware, drivers, RAID setup are not included.
Click here for detailed Cisco UCS
server documentation
.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
Reference: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/UC_Virtualization_Supported_Hardware#UC_on_UCS_Tested_Reference_Configurations
D
What does a TRC definition include?
✑ Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup (e.g. click here).
-
Click here for detailed Cisco UCS server documentation
regarding hardware configuration procedures.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration settings or step by step procedures for hardware BIOS, firmware, drivers, RAID setup are not included.
Click here for detailed Cisco UCS
server documentation
.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
Reference: http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/UC_Virtualization_Supported_Hardware#UC_on_UCS_Tested_Reference_Configurations
send
light_mode
delete
Question #4
Which definition is included in a Cisco UC on UCS TRC?
- Arequired RAID configuration, when the TRC uses direct-attached storage
- Bconfiguration of virtual-to-physical network interface mapping
- Cstep-by-step procedures for hardware BIOS, firmware, drivers, and RAID setup
- Dconfiguration settings and patch recommendations for VMware software
- Eserver model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) by name only; part numbers are not included because they change over time
Correct Answer:
A
Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
References:
A
Definition of server model and local components (CPU, RAM, adapters, local storage) at the orderable part number level.
✑ Required RAID configuration (e.g. RAID5, RAID10, etc.) - including battery backup cache or SuperCap - when the TRC uses DAS storage
✑ Guidance on hardware installation and basic setup.
- Configuration of Virtual-to-physical network interface mapping is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
- Configuration of adapters (such as Cisco VIC, 3rd-party CNA / NIC / HBA) is design-dependent and not included in TRC definition.
✑ Design, installation and configuration of external hardware is not included in TRC definition, such as:
- Network routing and switching (e.g. routers, gateways, MCUs, ethernet/FC/FCoE switches, Cisco Catalyst/Nexus/MDS, etc.)
- QoS configuration of route/switch network devices
- Cisco UCS B-Series chassis and switching components (e.g. Cisco UCS 6100/6200, Cisco UCS 2100/2200, Cisco UCS 5100)
- Storage arrays (such as those from EMC, NetApp or other vendors)
✑ Configuration settings, patch recommendations or step by step procedures for VMware software are not included in TRC definition.
✑ Infrastructure solutions such as Vblock from Virtual Computing Environment may also be leveraged for configuration details not included in the TRC definition.
References:
send
light_mode
delete
Question #5
Which capability is supported by Cisco Discovery Protocol but not by LLDP-MED?
- ALAN speed and duplex discovery
- BNetwork policy discovery
- CLocation identification discovery
- DPower discovery
- ETrust extension
Correct Answer:
E
Cisco Discovery Protocol provides an additional capability not found in LLDP-MED that allows the switch to extend trust to the phone. In this case, the phone is now trusted to mark the packets received on the PC port accordingly. This feature can be used to off-load the switch because now it does not need to police the information being received from the phone.
E
Cisco Discovery Protocol provides an additional capability not found in LLDP-MED that allows the switch to extend trust to the phone. In this case, the phone is now trusted to mark the packets received on the PC port accordingly. This feature can be used to off-load the switch because now it does not need to police the information being received from the phone.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #6
Which two mechanisms does Cisco EnergyWise use for neighbor discovery? (Choose two.)
- Amulticast
- BLLDP-MED
- CUDP broadcast
- DCisco Discovery Protocol
- ETCP
Correct Answer:
CD
Cisco EnergyWise Neighbor Discovery Process
The Cisco EnergyWise neighbor discovery process is the mechanism by which domain members discover each other and populate their Cisco EnergyWise neighbor tables. Cisco EnergyWise queries can subsequently be distributed to all domain members using the neighbor relationships to monitor and control the power usage of devices within a domain. Cisco EnergyWise domain members automatically discover their neighbors through one of two mechanisms:
UDP broadcast packets are automatically sent out switch ports which support Cisco EnergyWise, regardless of whether the interfaces are configured with the no energywise interface-level command. CDP packets are sent when CDP is configured for the switch ports.
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Energy_Management/energywisedg.html? referring_site=smartnavRD#wp555927
CD
Cisco EnergyWise Neighbor Discovery Process
The Cisco EnergyWise neighbor discovery process is the mechanism by which domain members discover each other and populate their Cisco EnergyWise neighbor tables. Cisco EnergyWise queries can subsequently be distributed to all domain members using the neighbor relationships to monitor and control the power usage of devices within a domain. Cisco EnergyWise domain members automatically discover their neighbors through one of two mechanisms:
UDP broadcast packets are automatically sent out switch ports which support Cisco EnergyWise, regardless of whether the interfaces are configured with the no energywise interface-level command. CDP packets are sent when CDP is configured for the switch ports.
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Borderless_Networks/Energy_Management/energywisedg.html? referring_site=smartnavRD#wp555927
send
light_mode
delete
Question #7
Which protocol does the Cisco Prime LAN Management Solution application use to communicate with Cisco EnergyWise domain members?
- AUDP broadcast
- BCisco Discovery Protocol
- CUDP unicast
- DTCP
- Emulticast
Correct Answer:
D
Cisco Prime LMS 4.1 uses TCP port 43440.
D
Cisco Prime LMS 4.1 uses TCP port 43440.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #8
Refer to the exhibit.
Assuming that the administrator has never performed any manual custom uploads, which two file types can be found when you choose Software Upgrades, followed by TFTP File Management on the Cisco Unified Operating System Administration web page? (Choose two.)

Assuming that the administrator has never performed any manual custom uploads, which two file types can be found when you choose Software Upgrades, followed by TFTP File Management on the Cisco Unified Operating System Administration web page? (Choose two.)
- AIP phone configuration files
- Bsample music-on-hold audio files
- CIdentity Trust List files
- DIP phone license files
- EMobile Voice Access audio files
- Fsoftkey template files
Correct Answer:
CE
We get option for Identity Trust list Files and Mobile Voice Access audio files.
CE
We get option for Identity Trust list Files and Mobile Voice Access audio files.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #9
Which statement describes a disadvantage of using the Cisco TFTP service to serve IP phone load files?
- AThe Cisco TFTP services can run on only one Cisco Unified Communications Manager server in a cluster.
- BBecause TFTP operates on top of UDP, there is a high risk of corrupted load file delivery at the completion of the TFTP process due to undetected data loss in the network.
- CIf a response is not received in the timeout period, the TFTP server will not resend the data packet.
- DPacket loss can significantly increase the TFTP session completion time.
- EBecause TFTP operates with an adaptive timeout period, the time to complete the file transfer is unpredictable.
Correct Answer:
D
Voice traffic cannot recapture lost packets. Rather than retransmitting a lost network connection, the phone resets and attempts to reconnect its network connection.
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/6921_6941_6961/7_1_2/english/admin/guide/6921trb.html#wp1031181
D
Voice traffic cannot recapture lost packets. Rather than retransmitting a lost network connection, the phone resets and attempts to reconnect its network connection.
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/6921_6941_6961/7_1_2/english/admin/guide/6921trb.html#wp1031181
send
light_mode
delete
Question #10
Which two statements about using the Load Server option for IP phone firmware distribution are true? (Choose two.)
- AThis option must be enabled on at least two servers in a Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster.
- BThis option must be enabled on Cisco Unified Communications Manager service parameters for Cisco TFTP.
- CPhone firmware must be manually copied to any applicable load servers.
- DThe load server will not function if its IP address is not in the same subnet as the IP phones.
- EThis option is only available for newer IP phone models.
- FThis option does not accommodate falling back to Cisco TFTP on error.
Correct Answer:
CF
Choosing the Right Distribution Method
Which of the three different image-distribution methods discussed so far is the best for a customer deployment? Each method has advantages and disadvantages, and they are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of Distribution Models
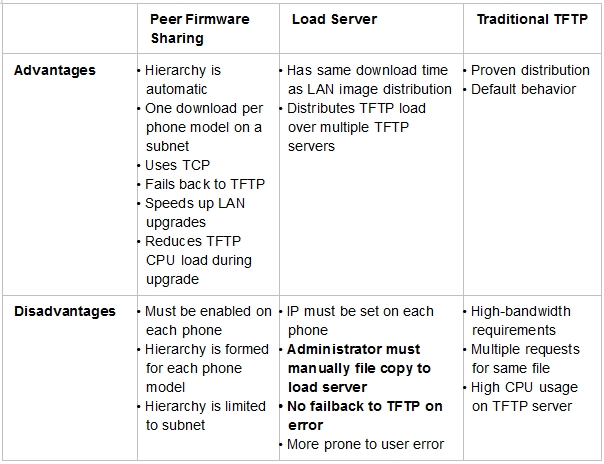
References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/voicesw/ps6882/ps6884/white_paper_c11-583891.pdf
CF
Choosing the Right Distribution Method
Which of the three different image-distribution methods discussed so far is the best for a customer deployment? Each method has advantages and disadvantages, and they are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of Distribution Models

References: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/voicesw/ps6882/ps6884/white_paper_c11-583891.pdf
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
