Cisco® 352-001 Exam Practice Questions (P. 4)
- Full Access (253 questions)
- Six months of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #16
Refer to the exhibit. In this network, all routers are configured to run EIGRP on all interfaces. All interface bandwidths are set to 1000, and the delays are configured as shown. In the topology table at Router C, you see only one path towards 10.1.1.0/24. What is the reason that Router C only has one path in its topology table?
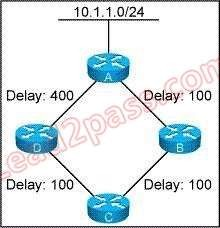

- ARouter D is not advertising 10.1.1.0/24 to Router C because Router C is its feasible successor.
- BRouter B is not advertising 10.1.1.0/24 to Router C because Router C is its feasible successor.
- CRouter D is not advertising 10.1.1.0/24 to Router C due to split horizon.
- DRouter B is not advertising 10.1.1.0/24 to Router C due to split horizon.
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #17
Refer to the exhibit. All routers in this network are configured to place all interfaces in OSPF area 5. R3 is the designated router on the 10.1.5.0/24 network. If you examine the OSPF database on R4, what would the network (type 2) LSA, generated by R3, contain?
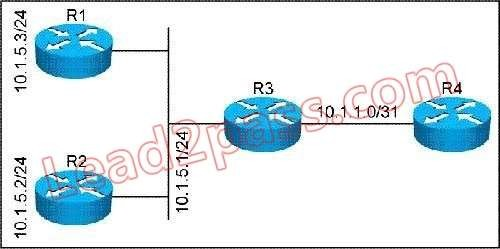

- Aa connection to 10.1.5.0/24 and links to R3, R2, and R1
- Ba connection to 10.1.5.0/24 and links to R2 and R1
- Cconnections to 10.1.5.0/24 and 10.1.1.0/31
- Dno connections, R3 does not generate a network (type 2) LSA in this network
Correct Answer:
A
A
send
light_mode
delete
Question #18
Refer to the exhibit. Which routes in this network will be installed in the routing table at router E?
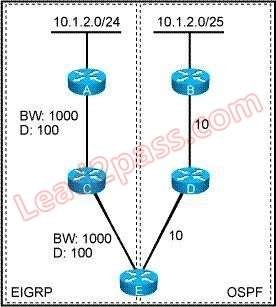

- Athe OSPF route
- Bthe EIGRP route
- Cthe OSPF and EIGRP routes
- Dneither the OSPF nor the EIGRP route
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #19
An enterprise network manager has decided to dual-home two service providers for Internet connectivity. In order to provide optimal outbound routing, the full
Internet routing table will be accepted from each provider. The enterprise has obtained address space and an AS to use in connecting to the Internet.
What is the simplest mechanism the network manager can use to prevent it from becoming a transit between the two service providers?
Internet routing table will be accepted from each provider. The enterprise has obtained address space and an AS to use in connecting to the Internet.
What is the simplest mechanism the network manager can use to prevent it from becoming a transit between the two service providers?
- ABuild a route filter that only allows the specific networks the enterprise owns to be advertised to each of the service providers.
- BBuild a traffic filter that only allows traffic originating from the specific networks the enterprise owns to be forwarded towards the service providers.
- CBuild a route filter that only allows networks with an empty AS path to be advertised to each of the service providers.
- DBuild a route filter that only allows networks which are tagged with the LOCAL community to be advertised to each of the service providers.
Correct Answer:
C
C
send
light_mode
delete
Question #20
Which statement correctly describes how MTU mismatches are addressed in the IS-IS neighbor-formation process?
- AIS-IS checks the locally configured MTU against the MTU advertised in neighbor hello packets.
- BIS-IS checks the locally configured MTU against the MTU advertised in neighbor LSPs.
- CIS-IS does not check for MTU mismatches when forming a neighbor relationship.
- DIS-IS pads hellos, so neighbor relationships will not be formed on links with mismatched MTUs.
Correct Answer:
D
D
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
