Netapp NS0-155 Exam Practice Questions (P. 1)
- Full Access (189 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #1
How can you "throttle" SnapValue updates and baseline transfers so that the primary or secondary is not transmitting data as it can?
- AUse the -k option in the snapvault start or snapshot modify commands.
- BSnapVault does not support throttling of network throughout.
- CUse the snapvault throttle command.
- DUse the -k option in the snapvault initialize command.
Correct Answer:
A
?️
http://backdrift.org/man/netapp/man1/na_snapvault.1.html
The snapvault subcommands are:
start [ -r ] [ -k n ] [ -t n ] [ -w ] [-p {inet | inet6 unspec}] [ -o options ]
[ -S [primary_filer:]primary_path ] secondary_qtree
modify [ -k n ] [ -t n ] [-p {inet | inet6 | unspec}] [ -o options ] [ -S primary_filer:primary_path ] sec_ondary_qtree
The -k option sets the maximum speed at which data is transferred in kilobytes per second. It is used to throttle disk, CPU, and network usage. If this option is not set, the filer transmits data as fast as it can. The setting applies to the initial transfer as well as subsequent update transfers from the primary.
http://backdrift.org/man/netapp/man1/na_snapvault.1.html
The snapvault subcommands are:
start [ -r ] [ -k n ] [ -t n ] [ -w ] [-p {inet | inet6 unspec}] [ -o options ]
[ -S [primary_filer:]primary_path ] secondary_qtree
modify [ -k n ] [ -t n ] [-p {inet | inet6 | unspec}] [ -o options ] [ -S primary_filer:primary_path ] sec_ondary_qtree
The -k option sets the maximum speed at which data is transferred in kilobytes per second. It is used to throttle disk, CPU, and network usage. If this option is not set, the filer transmits data as fast as it can. The setting applies to the initial transfer as well as subsequent update transfers from the primary.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #2
Node 1 in a clustered pair detects that it has lost connectivity to one of its disk shelves. Node 1 is still up, but it cannot see one of its disk shelves. However, the partner node, Node 2, can see all of the Node 1s disk shelves. Which feature will cause Node 2 to monitor this error condition for a period of three minutes by default, and then forcibly take over Node 1 if the error condition persists?
- AAuto enable of giveback
- BNegotiated Fail Over
- CTakeover on panic
- DCf.quickloop.enable
Correct Answer:
B
?️
http://www.wafl.co.uk/cf/
http://wafl.co.uk/options/
Negotiated failover is a general facility which supports negotiated failover on the basis of decisions made by various modules. cf.takeover.on_disk_shelf_miscompare
This option allows negotiated takeover to be enabled when the cluster nodes detect a mismatch in disk shelf count. By default, this option is set to off.
This option is available only when cluster is licensed and changing the value on one filer automatically changes the value on the partner filer.
http://www.wafl.co.uk/cf/
http://wafl.co.uk/options/
Negotiated failover is a general facility which supports negotiated failover on the basis of decisions made by various modules. cf.takeover.on_disk_shelf_miscompare
This option allows negotiated takeover to be enabled when the cluster nodes detect a mismatch in disk shelf count. By default, this option is set to off.
This option is available only when cluster is licensed and changing the value on one filer automatically changes the value on the partner filer.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #3
In Data ONTAP, the root user is exempt from those two quotas: ______________. (Choose two)
- AUser quotas
- BTree quotas
- CRoot quotas
- DGroup quotas
- EFile quotas
Correct Answer:
AD
?️
http://backdrift.org/man/netapp/man1/na_quota.1.html
User and group quotas do not apply to the root user or to the Windows Administrator account; tree quotas, however, do apply even to root and the Windows
Administrator account.
http://backdrift.org/man/netapp/man1/na_quota.1.html
User and group quotas do not apply to the root user or to the Windows Administrator account; tree quotas, however, do apply even to root and the Windows
Administrator account.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #4
Which two Volume SnapMirror (VSM) relationship are supported? (Choose two)
- AData ONTAP 8.0.2 64-bit -->Data ONTAP 8.1 64-bit
- BData ONTAP 8.0.2 32-bit --> Data ONTAP 8.0.2 64-bit
- CData ONTAP 7.3.2 32-bit --> Data ONTAP 8.1 64-bit
- DData ONTAP 7.3.2 32-bit --> Data ONTAP 8.0.2 64-bit
Correct Answer:
AC
?️
Volume SnapMirror Interoperability Matrix.
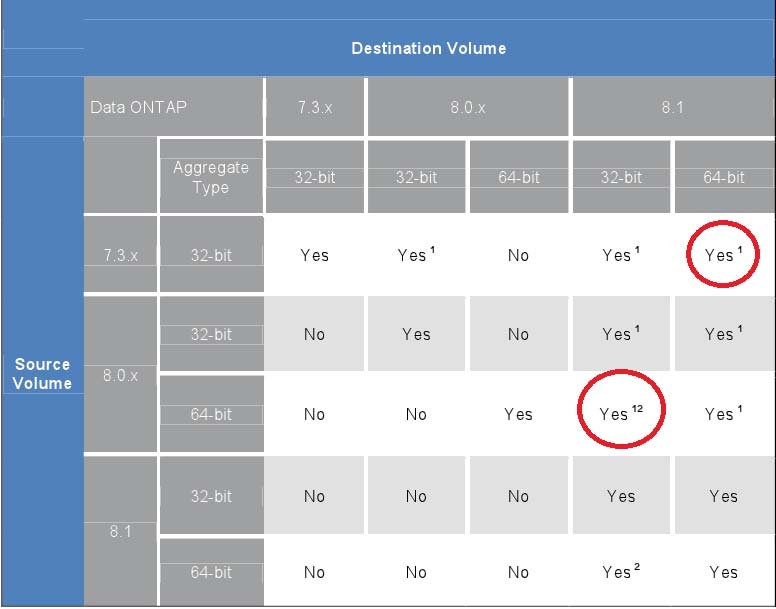
Reference: SnappMirror Async Overview and Best Practices guide.
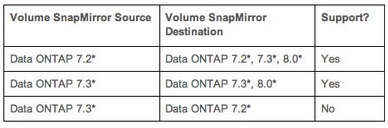
Volume SnapMirror Interoperability Matrix.

Reference: SnappMirror Async Overview and Best Practices guide.

send
light_mode
delete
Question #5
An aggregate is composed of twelve 36-Gigabyte disks. A drive fails and only 72-Gigabyte spare disks are available. Data ONTAP will then perform what action.
- AChooses a 72-Gigabyte disk and use it as is.
- BChooses a 72-Gigabyte disk and right-size it.
- CHalts after 24 hour of running in degraded mode.
- DAlerts you that there are no 36-Gigabyte disks and wait for one to be inserted.
Correct Answer:
B
?️
https://library.netapp.com/ecmdocs/ECMP1196986/html/GUID-8A91F6A2-61B8-42C3-AEAB7D5AA9BBE9CF.html
If a disk fails and no hot spare disk that exactly matches the failed disk is available, Data ONTAP uses the best available spare. Understanding how Data ONTAP chooses an appropriate spare when there is no matching spare enables you to optimize your spare allocation for your environment.
Data ONTAP picks a non-matching hot spare based on the following criteria (and more; in the link above):
If the available hot spares are not the correct size, Data ONTAP uses one that is the next size up, if there is one.
The replacement disk is downsized (aka right sized) to match the size of the disk it is replacing; the extra capacity is not available.
https://library.netapp.com/ecmdocs/ECMP1196986/html/GUID-8A91F6A2-61B8-42C3-AEAB7D5AA9BBE9CF.html
If a disk fails and no hot spare disk that exactly matches the failed disk is available, Data ONTAP uses the best available spare. Understanding how Data ONTAP chooses an appropriate spare when there is no matching spare enables you to optimize your spare allocation for your environment.
Data ONTAP picks a non-matching hot spare based on the following criteria (and more; in the link above):
If the available hot spares are not the correct size, Data ONTAP uses one that is the next size up, if there is one.
The replacement disk is downsized (aka right sized) to match the size of the disk it is replacing; the extra capacity is not available.
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
