GIAC GCED Exam Practice Questions (P. 1)
- Full Access (88 questions)
- One Year of Premium Access
- Access to one million comments
- Seamless ChatGPT Integration
- Ability to download PDF files
- Anki Flashcard files for revision
- No Captcha & No AdSense
- Advanced Exam Configuration
Question #1
Which type of media should the IR team be handling as they seek to understand the root cause of an incident?
- ARestored media from full backup of the infected host
- BMedia from the infected host, copied to the dedicated IR host
- COriginal media from the infected host
- DBit-for-bit image from the infected host
Correct Answer:
A
By imaging the media with tools such as dd or Ghost and analyzing the copy, you preserve the original media for later analysis so that the results can be recreated by another competent examiner if necessary.
A
By imaging the media with tools such as dd or Ghost and analyzing the copy, you preserve the original media for later analysis so that the results can be recreated by another competent examiner if necessary.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #2
An incident response team is handling a worm infection among their user workstations. They created an IPS signature to detect and block worm activity on the border IPS, then removed the worms artifacts or workstations triggering the rule. Despite this action, worm activity continued for days after. Where did the incident response team fail?
- AThe team did not adequately apply lessons learned from the incident
- BThe custom rule did not detect all infected workstations
- CThey did not receive timely notification of the security event
- DThe team did not understand the worm’s propagation method
Correct Answer:
B
Identifying and scoping an incident during triage is important to successfully handling a security incident. The detection methods used by the team didnt detect all the infected workstations.
B
Identifying and scoping an incident during triage is important to successfully handling a security incident. The detection methods used by the team didnt detect all the infected workstations.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #3
A legacy server on the network was breached through an OS vulnerability with no patch available. The server is used only rarely by employees across several business units. The theft of information from the server goes unnoticed until the company is notified by a third party that sensitive information has been posted on the Internet. Which control was the first to fail?
- ASecurity awareness
- BAccess control
- CData classification
- DIncident response
Correct Answer:
C
The legacy system was not properly classified or assigned an owner. It is critical that an organization identifies and classifies information so proper controls and measures should be put in place. The ultimate goal of data classification is to make sure that all information is properly protected at the correct level.
This was not a failure of incident response, access control or security awareness training.
C
The legacy system was not properly classified or assigned an owner. It is critical that an organization identifies and classifies information so proper controls and measures should be put in place. The ultimate goal of data classification is to make sure that all information is properly protected at the correct level.
This was not a failure of incident response, access control or security awareness training.
send
light_mode
delete
Question #4
Analyze the screenshot below. Which of the following attacks can be mitigated by these configuration settings?
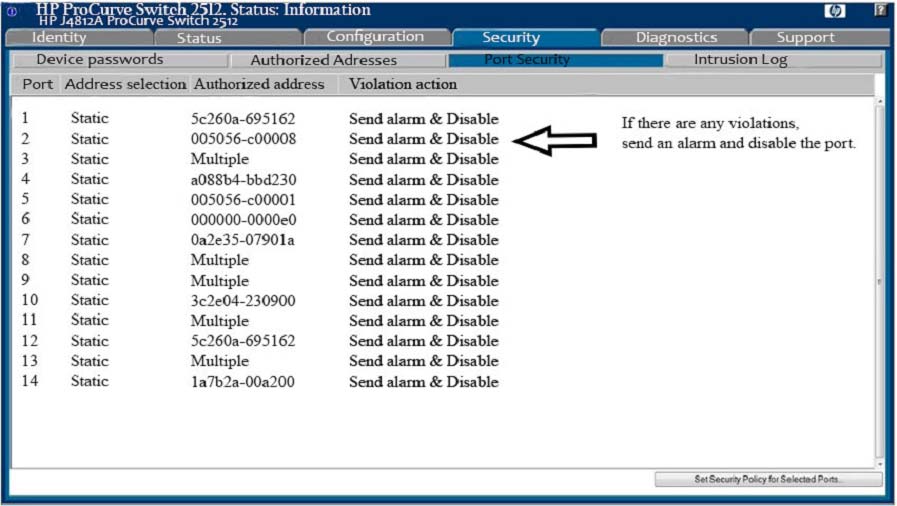

- AA Denial-of-Service attack using network broadcasts
- BA Replay attack
- CAn IP masquerading attack
- DA MAC Flood attack
Correct Answer:
D
Both BPDU Guard and Root Guard are used to prevent a new switch from becoming the Root Bridge. They are very similar but use different mechanisms.
Rootguard allows devices to use STP, but if they send superior BDPUs (i.e. they attempt to become the Root Bridge), Root Guard disables the port until the offending BPDUs cease. Recovery is automatic.
If Portfast is enabled on a port, BPDU Guard will disable the port if a BPDU is received. The port stays disabled until it is manually re-enabled. Devices behind such ports cannot use STP, as the port would be disabled as soon as they send BPDUs (which is the default behavior of switches).
D
Both BPDU Guard and Root Guard are used to prevent a new switch from becoming the Root Bridge. They are very similar but use different mechanisms.
Rootguard allows devices to use STP, but if they send superior BDPUs (i.e. they attempt to become the Root Bridge), Root Guard disables the port until the offending BPDUs cease. Recovery is automatic.
If Portfast is enabled on a port, BPDU Guard will disable the port if a BPDU is received. The port stays disabled until it is manually re-enabled. Devices behind such ports cannot use STP, as the port would be disabled as soon as they send BPDUs (which is the default behavior of switches).
send
light_mode
delete
Question #5
Of the following pieces of digital evidence, which would be collected FIRST from a live system involved in an incident?
- AEvent logs from a central repository
- BDirectory listing of system files
- CMedia in the CDrom drive
- DSwap space and page files
Correct Answer:
D
Best practices suggest that live response should follow the order of volatility, which means that you want to collect data which is changing the most rapidly. The order of volatility is:
Memory -
Swap or page file -
Network status and current / recent network connections
Running processes -
Open files
D
Best practices suggest that live response should follow the order of volatility, which means that you want to collect data which is changing the most rapidly. The order of volatility is:
Memory -
Swap or page file -
Network status and current / recent network connections
Running processes -
Open files
send
light_mode
delete
All Pages
